
The primary injection test is a critical commissioning and maintenance test which is used to verify the operation of current based protection schemes used in substation. In the primary injection test, a high current is injected into the primary circuit of equipment such as current transformer, circuit breaker, and busbar. The primary injection test is use to test the entire current path, CT polarity, ratio, wiring integrity, relay setting and tripping logic under near operating conditions.
The primary injection test is very important for substation as it checks and confirms that the protective relays or devices will operate correctly during actual electrical faults in the substation or in the transmission lines. The primary injection test helps detect incorrect CT connection, wrong ratio, wiring issues or loose connection which cannot be otherwise identified by the secondary injection test. The primary injection test requires a heavy current source and thus safety precaution must be adhered to during the test.
Table of Contents
Working principle of Primary Injection Test
The primary injection test works on the principle of applying a controlled high current directly into the primary circuit of the equipment under test in order to simulate the actual working of the equipment under load and fault conditions. The primary injection test kit applies a low voltage usually 2-10 volts and high current output 100 to few thousand amperes to the primary terminal of the equipment to be tested such as circuit breaker, busbar, current transformer.
As the injected current flows through the system, it is sensed by the associated protection system and measuring elements connected in the circuit. The operation of the relays and circuit breakers is then observed to verify correct pickup values, operating time and tripping sequence.
As the test current flows in the same path as in normal operating condition, the primary injecting test thus confirms the integrity of the primary conductors, wiring relay logic, breaker operation, CT polarity, ratio based on the secondary current output, response time like pickup, timing, indication of the associated relays connected to the secondary of the CT. This ensures that the entire protection system functions correctly during actual fault situations.
Test Equipment
High current primary injection test kit
The high current primary injection test kit is the main source of current for conducting the primary injection tests. It essentially consists of a step down transformer converting the normal supply voltage to deliver very low voltage, high current ranging from 100 amperes to few thousand amperes, which is required to simulate load or fault current conditions. The output current is adjustable and can be precisely controlled to match the test requirement. The kit typically includes timers, and auxiliary contact inputs for relay or trip coil feedback.
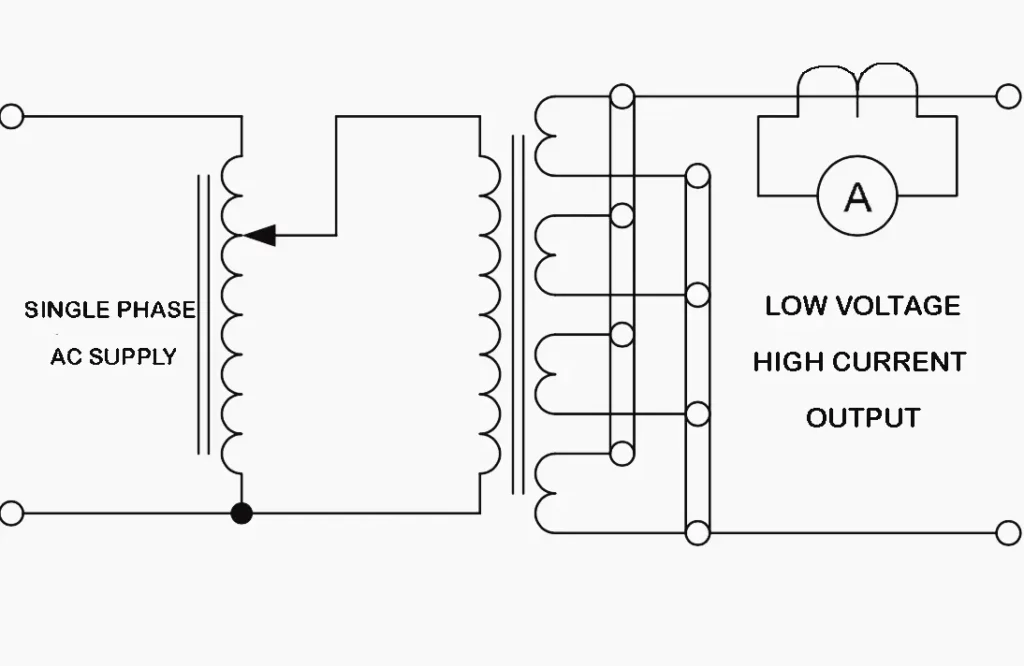
Heavy Duty current leads
Heavy duty current leads are used to carry high current injection test current from the test set to the primary circuit of the equipment to be tested. These conductors are designed with large cross-sectional areas to minimize resistance; voltage drop and heating during testing. Also, these are made flexible for ease of handling and ability to withstand mechanical stress caused by high current flow. Secure connection is essential to avoid overheating and inaccurate results.
Current measuring device
An ammeter or current measuring device is used to accurately measure the injected primary current during the test, which ensures that the required test current is applied and maintained through out the test procedure. Depending on the current level, the measurement can also be done with a high current ammeter, clamp on meter, or a current shunt with a display. Accurate current measurement is essential for verifying relay pickup current, operating time and overall protection performance. Any error in the measurement of the current can lead to incorrect interpretation of test results.
Test connection
The circuit breakers must be kept closed during the test and it should be isolated from the live system by the use of disconnectors or isolators on both sides. The test is basically performed on a dead isolated circuit. The connection is made by using the leads connecting the injection kit (supplying current) to one primary phase terminal of the circuit breaker. The return lead is connected between the same phase primary terminal of CT (P2 polarity side) to take the CT in the loop. The CT secondary circuit remains connected to the protection relays.
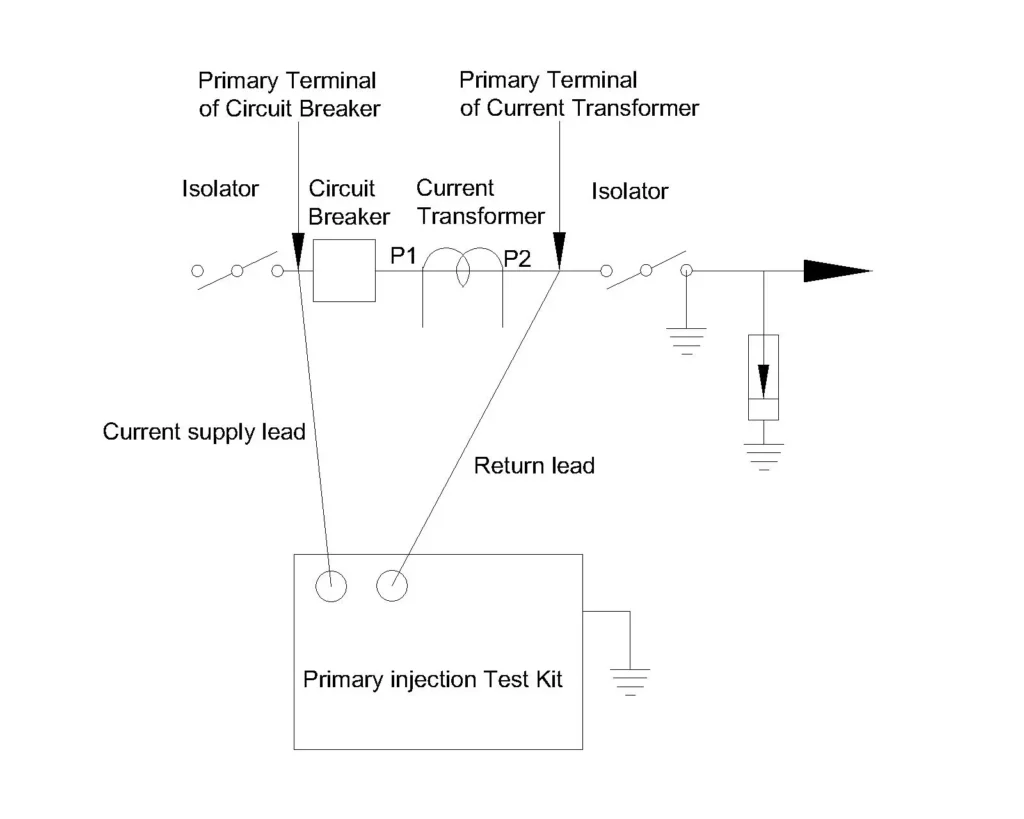
The primary current is measured by primary injection test kit’s internal sensor or by external clamp on ammeter and the secondary current is measured at the relay or test block.
Test procedure
Step 1: Ensure that the equipment to be tested is isolated from the live system and work permit is obtained.
Step 2: Make secure connections with the help of the connecting lead between the primary injection test kit and the equipment under test.
Step 3: Keep the protection relay, meters and circuit breaker closed in normal service condition.
Step 4: Set the protection relay pickup and time settings as per approved protection scheme.
Step 5: Gradually increase the injected current from zero and also monitor the current using the ammeter.
Step 6: Observe the relay pickup, indications, operating time and tripping of the circuit breaker.
Step 7: Record the injected current, relay response and breaker operation.
Step 8: Repeat the test for remaining phases or protection elements.
Step 9: After completion of each test, reduce the current to zero and disconnect the test set.
Parameters verified during the test
CT ratio and polarity
The primary injection test functionally verifies the current transformation and bidirectional behaviour of the CT is correct by simple observation of the relay response and current flow through the protection scheme. Any incorrect ratio connection or polarity will result in abnormal relay pickup and non operation of the relay which can be thus detected during the test.
Relay pickup current accuracy
The injected current at which the relay starts to operate is compared to the set pickup value. This confirms that the relay senses the current correctly and operates with in permissible tolerance limits.
Relay operating time
The time taken by the relay to issue a trip command after pickup is measured and checked against the relay’s time-current characteristics and settings.
Trip coil operation
The test confirms the continuity and health of the trip circuit, including the auxiliary relay, wiring and trip coil energization.
Circuit breaker tripping performance
The opening of the circuit breaker is observed to verify proper operation and satisfactory tripping response under simulated fault condition. It also indirectly confirms correct relay logic, healthy trip circuit and mechanical ability of the breaker to open the contacts.
Thus the primary injection test mainly verifies the relay pickup current, relay operating time, trip circuit continuity, correct wiring and polarity and overall protection system integrity.
This article is a part of the Testing and commissioning page, where other articles related to topic are discussed in details.

