Battery sizing is a critical engineering process which is used to determine the required capacity of a battery system, which has to ensure uninterrupted power supply to protection system, control system and communication equipment of the substation during normal and emergency operating conditions. The battery system must support the essential loads such as relay, circuit breaker tripping and closing, substation SCADA and emergency lighting backup for a specified duration. Proper battery sizing ensures the DC system reliability and operational safety. Accurate battery sizing prevents premature failure, voltage collapse and loss of critical functions during blackouts.
Table of Contents
System Description and load classification
Accurate battery sizing begins with precise understanding of the DC loads to be supplied by the battery. These loads are grouped based on their behaviour during normal operation and during AC supply failure.
Continuous Load
Continuous load is that DC load which remains energized for the entire battery duty cycle (time) including normal operations and during the AC failure. It typically includes the indication lamps, trip circuit supervision relay, bay control units, communication system and other panel electronics. In IEEE battery sizing methodology, continuous load forms the base load curve and is applied for full backup duration having the highest impact on the total battery capacity.
Momentary load
Momentary load is basically the short duration, high current demand that occurs only for brief interval of time, usually during the switching or fault condition tripping. Typical example includes circuit breaker trip coils, closing coil, DC motor operated isolators. IEEE standards treat momentary loads separately from continuous loads because momentary load imposes peak current stress on the battery. These loads influences the battery’s discharge rate capability and sizing of inter cell connectors, cables.
Emergency load
This load refers to the DC loads that are energized only during abnormal or emergency conditions such as AC supply failure, system faults or protection operations. These includes emergency lighting, fire protection system. In battery sizing calculation, emergency loads are added to continuous load profile for the specified backup period to ensure that the battery can sustain critical system function until the restoration of normal AC power.
Battery Duty Cycle
The battery duty cycle represents the complete anticipated electrical loading profile that the DC battery system must support after the loss of AC power, from the instance of the AC failure till the backup period or till AC power is restored. It shows how much current the battery must deliver and at what time each load occurs and for what period are the loads connected.
The duty cycle or the load cycle of the battery combines continuous, momentary and emergency load into a single operational scenario, which reflects the worst credible operating condition of the substation.
Steps of battery sizing for 220V
Data
1. Type of battery = Valve Regulated Lead Acid type
2. Nominal Battery Voltage (NBV) = 220 V
3. No of cells = 220/2 = 110 Nos As each VRLA cell has a voltage of 2 V (approx.)
4. End cell voltage after discharge (for Discharge Rate of C10) = 1.8 V
5. Load cycle considered
a. Continuous load (Control & Relay Panel) = 10 hours
b. Emergency load (Lighting) = 1 hours
c. Momentary load (Simultaneous Tripping) = 1 min
6. Average electrolyte temperature = 24 Deg.C.
7. Load Determination
Panel manufacturer’ data
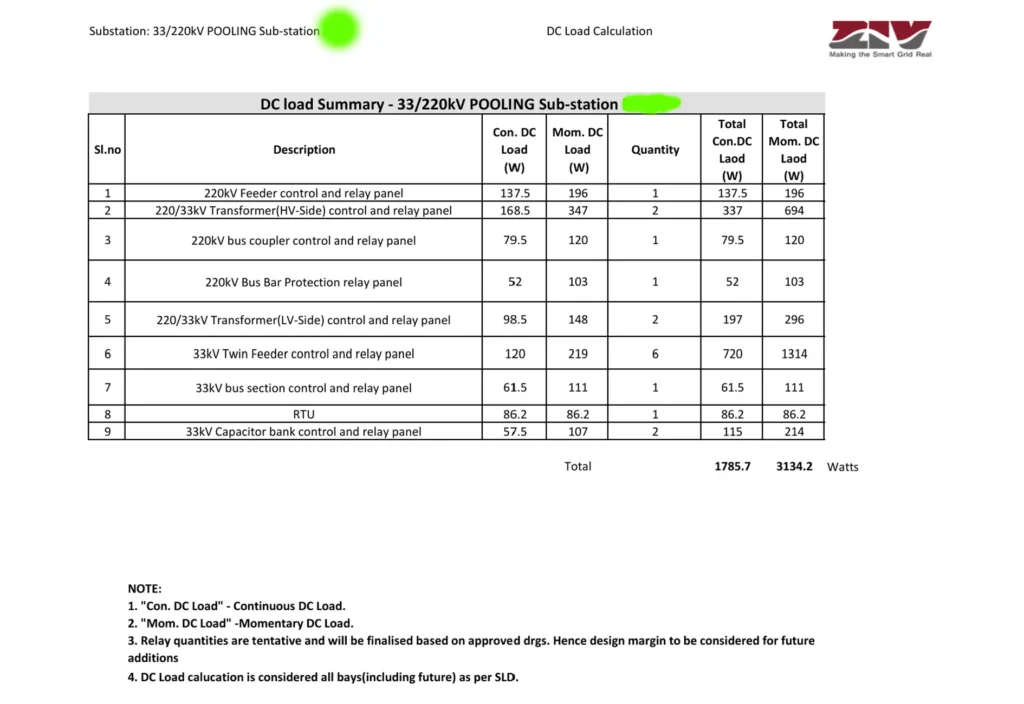
Continuous Load calculation
| Sl | Equipment / Panel | Quantity | Load per Unit (W) | Total Load (W) |
| a | 33 kV Twin Feeder Control & Relay Panel | 6 | 120 | 6 × 120 = 720 |
| b | 33 kV Bus Section Control & Relay Panel | 1 | 61.5 | 1 × 61.5 = 61.5 |
| c | 33 kV Capacitor Bank C&R Panel | 2 | 57.5 | 2 × 57.5 = 115 |
| d | 220/33 kV Transformer LV Side C&R Panel | 2 | 98.5 | 2 × 98.5 = 197 |
| e | 220 kV Line C&R Panel | 1 | 137.5 | 1 × 137.5 = 137.5 |
| f | 220/33 kV Transformer HV Side C&R Panel | 2 | 168.5 | 2 × 168.5 = 337 |
| g | 33 kV Bus Coupler Panel | 2 | 200 | 2 × 200 = 400 |
| h | 220/33 kV Transformer RTCC Panel | 1 | 79.5 | 1 × 79.5 = 79.5 |
| i | Switchyard SAS Panel (RTU) | 1 | 52 | 1 × 52 = 52 |
| j | Synchronizing Panel | 1 | 86.2 | 1 × 86.2 = 86.2 |
| k | Battery Charger | 2 | 200 | 2 × 200 = 400 |
| l | Fire Fighting System | 2 | 15 | 2 × 15 = 30 |
| m | PLCC & FOTE | 2 | 240 | 2 × 240 = 480 |
| n | Miscellaneous DC Loads | — | — | 0 |
| Total Load a+b+c+d+e+f+g+h+i+j+k+l+m+n | 3095.7 W |
Total continuous load current (L1)
= Total continuous load / Battery voltage = 3095.7 /220 = 14.07 A
Emergency load calculation
| Sl | Emergency Equipment | Quantity | Load per Unit (W) | Total Load (W) |
| a | Emergency DC Lighting | 8 lamps | 100 | 800 |
Total load duration selected by client as is 1 hour, as all substation breaker can be opened and control room emergency can be handled within this time period.
Emergency load current (L2) = 800/220 = 3.64 A
Momentary load calculation
Based on data from circuit breaker manufacturing sheet and panel’s manufacturer
| Sl | Equipment / Operation | Bays / Qty | Load per Unit (W) | Total Load (W) |
| a | 33 kV VCB – Closing Coil | 1 bay × 1 coil | 250 | 250 |
| b | 220 kV CB – Closing Coil | 1 bay × 1 coil | 330 | 330 |
| c | 33 kV VCB – Trip Coil | 7 bays × 1 coil | 250 | 1750 |
| d | 220 kV CB – Trip Coil | 4 bays × 1 coil | 330 | 3960 |
| e | 33 kV Twin Feeder C&R Panel | 6 | 219 | 1314 |
| f | 33 kV Bus Section C&R Panel | 1 | 111 | 111 |
| g | 33 kV Capacitor Bank C&R Panel | 2 | 107 | 214 |
| h | 220/33 kV Transformer LV Side C&R Panel | 2 | 148 | 296 |
| i | 220 kV Line C&R Panel | 1 | 196 | 196 |
| j | 220/33 kV Transformer HV Side C&R Panel | 2 | 347 | 694 |
| k | 33 kV Bus Coupler Panel | 2 | 300 | 600 |
| l | 220/33 kV Transformer RTCC Panel | 1 | 120 | 120 |
| m | Switchyard SAS Panel (RTU) | 1 | 103 | 103 |
| n | Synchronizing Panel | 1 | 86.2 | 86.2 |
| o | Battery Charger | 2 | 360 | 720 |
| Total momentary load a+b+c+d+e+f+g+h+i+j+k+l+m+n+o | 10744.2 |
Total momentary current, L3 = 10744.2/220 = 48.84 A
Load Determination
Continuous load considered for 10 hrs = 3095.7 W
Emergency load considered for 1 Hr = 800 W
Momentary load considered for 1min = 10744.2 W
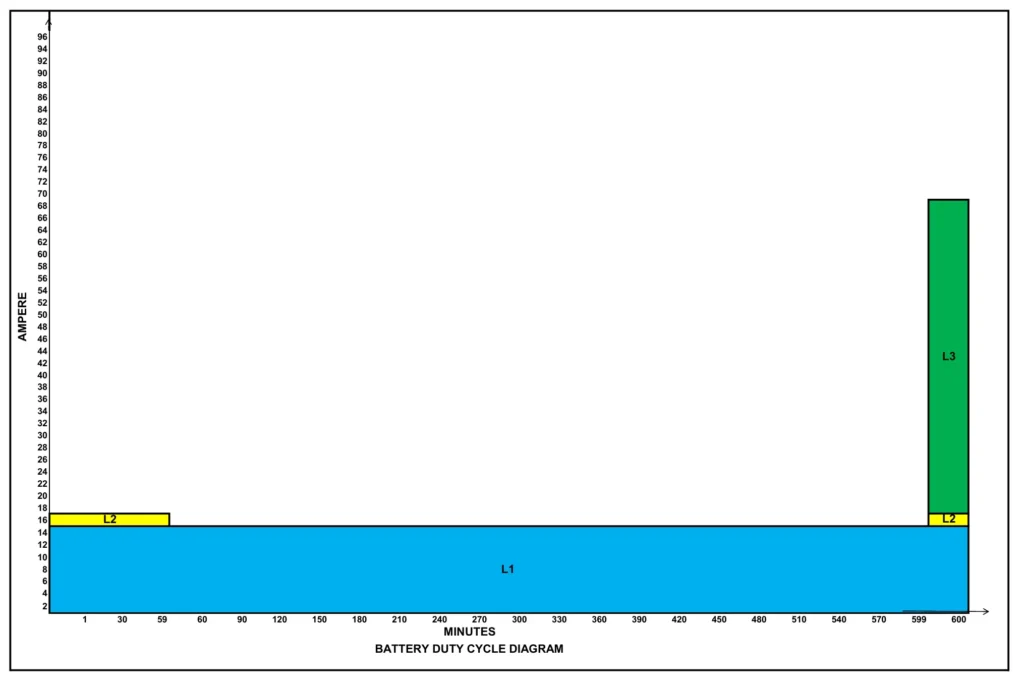
Calculation from the duty cycle
| Period | Loads | Load Current (A) | Duration (Minutes) |
| 1 | L1+L2 = A1 | 17.71 | 59 |
| 2 | L1 = A2 | 14.07 | 540 |
| 3 | L1+L2+L3 = A3 | 66.55 | 1 |
The battery capacity is calculated as below
| Period | Load | Change in load (Amp) | Duration of Period(minute) | Time at the end of section(minute) | Capacity factor | Required section size |
| Section-1 For first period only, If A2 is greater than A1 go to section-2 | ||||||
| 1 | A1 | A1-0 = 17.71 | M1 = 59 | T = M1 = 59 | 2.4 | 17.71 * 2.40 = 42.49 |
| Section-1 Total | 42.49 | |||||
| Section-2 For first two periods only, If A3 is greater than A2 go to section-3 | ||||||
| 1 | A1 | A1-0 = 17.71 | M1 = 59 | T= M1 + M2 = 599 | 10 | 177.077 |
| A2-A1 = -3.64 | M2 = 540 | T = M2 = 540 | 9.6 | -34.909 | ||
| Section-2 Total | 142.168 | |||||
| Section-3 First 3 periods only | ||||||
| 1 | A1 | A1-0 = 17.71 | M1 = 59 | T = M1+M2+M3 = 600 | 10 | 177.077 |
| 2 | A2 | A2-A1 = -3.64 | M2 = 540 | T = M2+M3 = 541 | 9.6 | -34.909 |
| 3 | A3 | A3-A2 = 52.48 | M3 = 1 | T = M3 = 1 | 1.2 | 62.98 |
| Section-3 Total | 205.141 | |||||
The capacity factor is found out from the battery manufacturer’s discharge curve as is shown below for time at the end of section 1 that is 59 minutes.
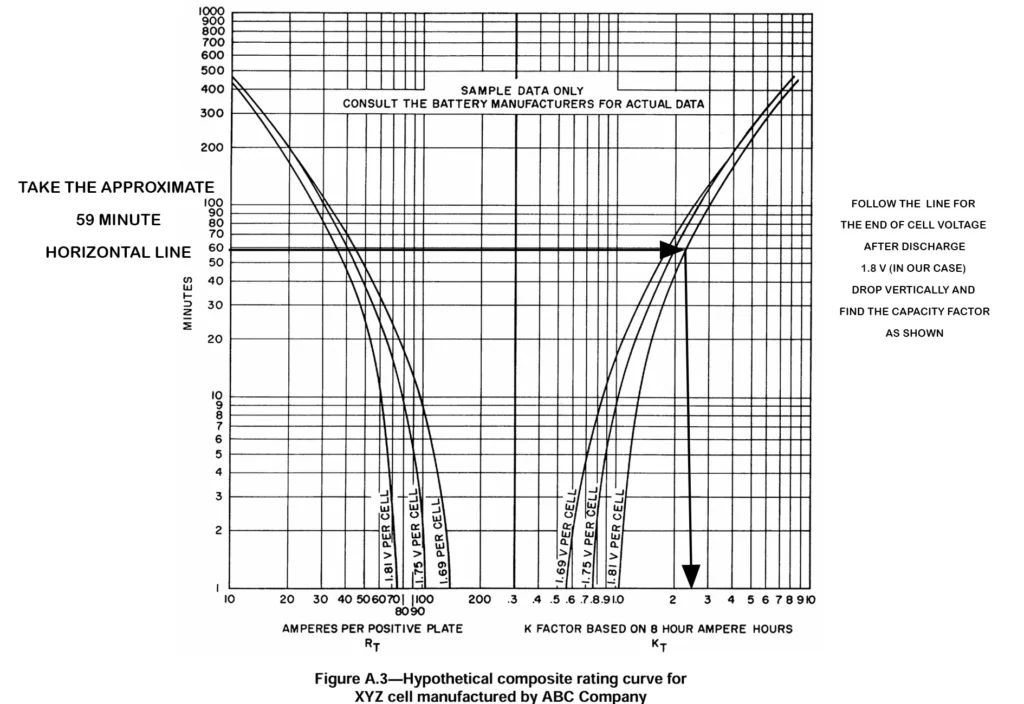
From the above table we find that the maximum section size is 205.141. Hence, this value is considered for further calculations.
Considering,
Design margin = 1.1 As per IEEE -485
Aging factor = 1.25 As per IEEE -485
Temperature correction factor = 1.01 As per IEEE -485
Required battery capacity = 1.1 x 1.25 x 1.01 x 205.141 = 284.88 AH
Selected battery capacity = 300 AH.
Determination of battery charger capacity
Online Float charger rating
Float charger rating = 1.2 x DC average Load
Average DC load = Area of the load cycle / Time of the load cycle
= (A1 x M1 + A2 x M2 + A3 x M3) / (M1 + M2 +M3)
= (17.71 x 59 + 14.07 x 540 + 66.55 x 1) / (59 + 540 + 1)
= 8709.24 / 600 =14.51A
Therefore, float charger rating calculated = 1.2 x 14.51 = 17.41 A
Chosen float charger rating = 30 A
From the above calculation it is seen that the charger’s rating is sufficient.
Offline Boost charger rating
Boost charger rating = 10% of the AH load.
=0.10 x 300 = 30 A
Chosen boost charger rating = 45 A
From the above calculation, it is seen that the chosen boost charger capacity is sufficient since chosen rating > calculated rating.
The battery sizing calculation concludes the size of the 220 V battery bank as 300 AH and float cum boost charger rating at (30+45) = 75 A.
This article is a part of the Energy storage and reactive power compensation page, where other articles related to the topic are discussed in details.
Reference

