
A maximum demand meter is a special type of meter used by the utilities to measure the highest average power demand in KW or KVA that is drawn by a consumer during a specific time interval or repeating blocks (15 minutes/ 30 minutes/ 1hour). Along with the measurement of energy, KWh, these meter measures the highest load or power demand that is put on a system during the billing cycle.
Table of Contents
How is Maximum Demand measured?
The maximum demand meter continuously tracks the load and calculates the average load over a specific time or repeating block of time called as integration period.
For example the integration period is 30 minutes. If the load varies from 100 to 150 KW in 30 minutes, the maximum demand meter averages it. If in the billing cycle, in some separate block of 30 minutes, the demand averages to 180 KW, then that becomes the new maximum demand for the billing cycle.
Purpose of using Maximum demand meter
Utilities design the substation, feeders, breakers or cables based on the peak load that the consumer impose. The design is not depended upon the monthly energy consumptions. If a consumer(s) creates high peaks, it affects all the electrical equipment and hence the utility has to strengthen the network capacity, upgrade the equipment to handle higher thermal and fault stress.
Because of uneven loading, the system becomes less efficient. Hence, the utilities, checks the maximum demand using maximum demand meter to charge the heavy consumers pay for the peak capacity and not just the units consumed.
Types of Maximum demand meters
Mechanical demand meters or indicators: These meter uses thermal and pressure sensing elements to measure the load which is averaged over the demand interval. A drag type mechanism moves the pointer of the meter proportional to the heat developed by the load. The maximum position thus attained during the billing cycle is held by a red or different coloured pointer, which remains fixed until manually reset by the utility staff. These meters cannot store the data and are slow, prone to drift and tampering.
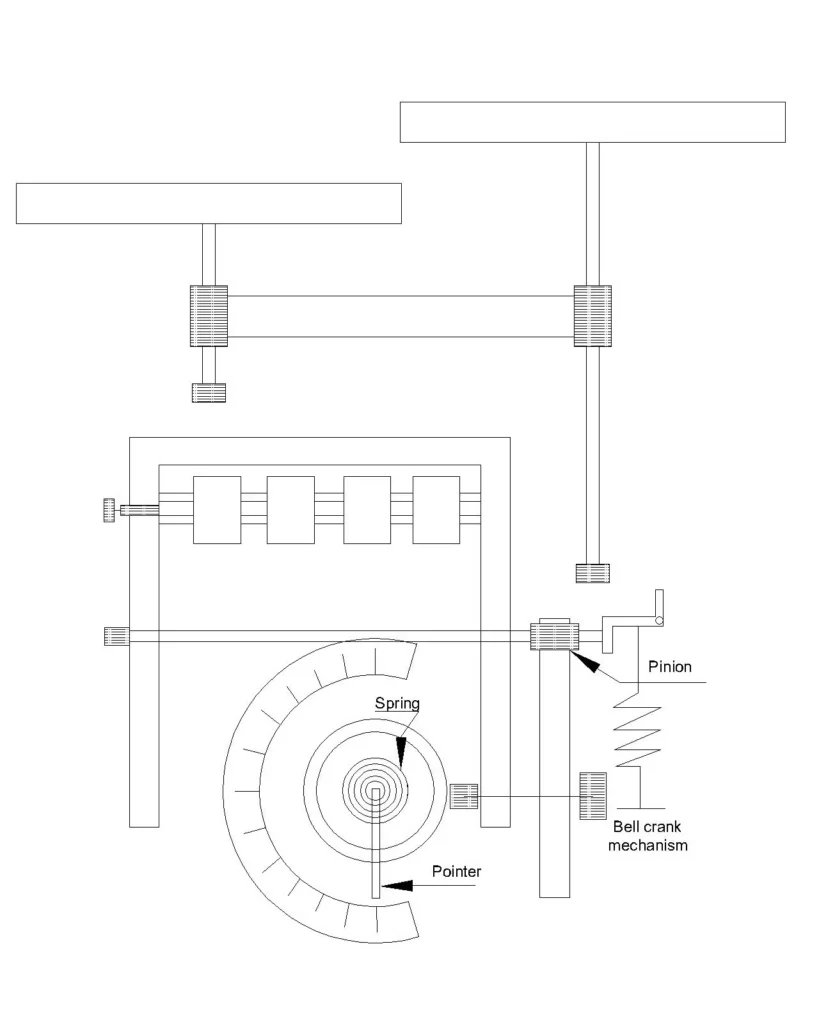
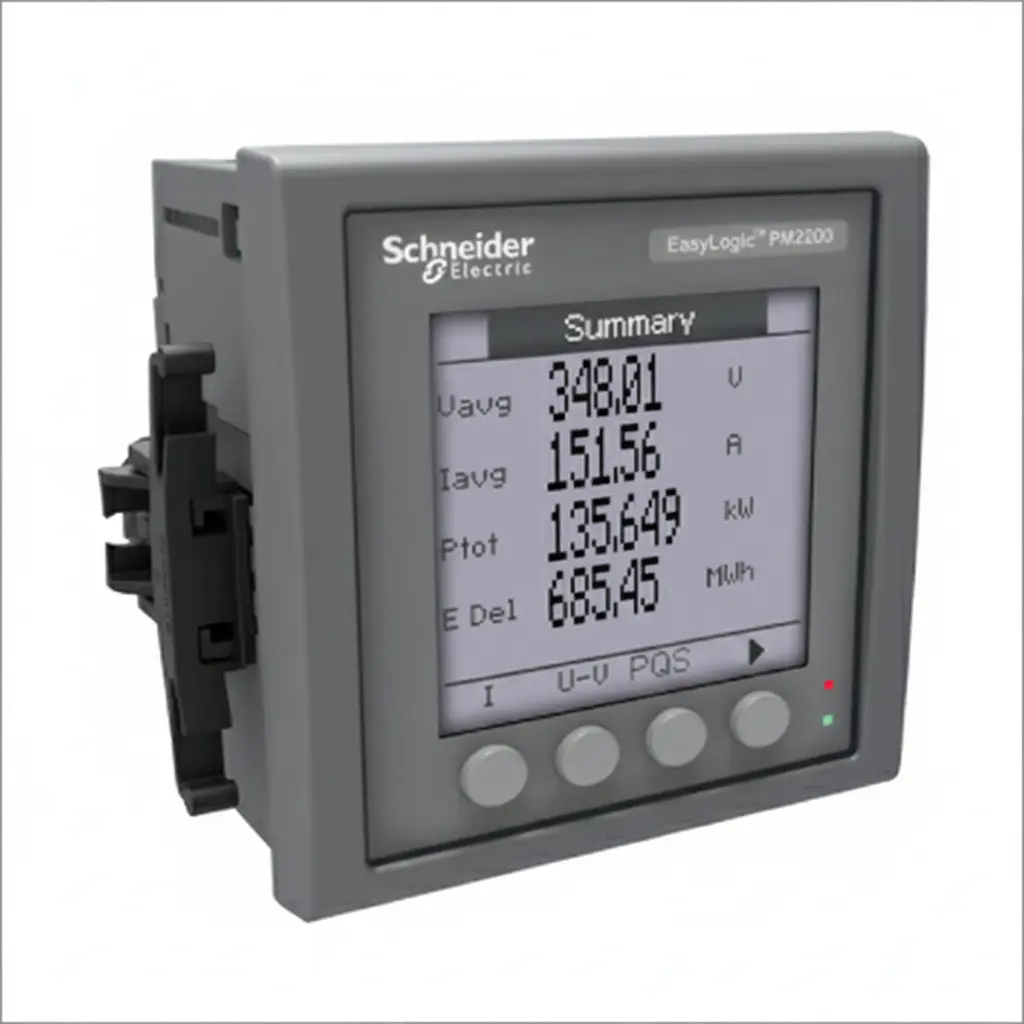
Digital maximum demand meter: These are static meters, which uses solid state sensors with an ADC and microcontroller to calculate the maximum demand. This meter usually records KW/KVA along with power factor, load profile and logs the events. These are integrated with a real-time clock which controls the integration period. It can store and reset the maximum demand in each billing cycle with the support of internal memory, communication port. It also supports tamper detection and is much more accurate and stable than the mechanical type.

Smart or AMI based maximum demand measurement: Smart meters with Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) system includes the functionality of maximum demand metering within itself. These meters essentially includes cloud connectivity for remote access to stored data, with real time demand forecasting. These meters communicates instantly with the utility’s SCADA system and is integrated with prepaid and other demand response programs.
Working principle
The modern meters continuously samples the voltage and current via the ADC channel. The internal microprocessor calculates the instantaneous power using the formula
P = V x I x Power factor
Over the integration period the meter stores multiple power readings which is used to compute the average demand.
Average Demand = Σ (multiple Power readings within the integration time) ÷ Integration time.
The highest average thus recorded in the entire billing cycle is stored as the maximum demand.
In mechanical meters, it is the heat built-up or the magnetic drag that moves the pointer proportional to the average load, while in static meter it is the microcontroller which performs the averaging and maintains the load profile logs with time stamps.
Advantages
- The maximum demand meter helps consumers to understand their peak loadings.
- It allows the consumers to optimize the power consumptions or load managements and avoid maximum demand penalties.
- It assists the utility in planning the feeder and transformer capacity.
- It enables operational efficiency tracking during the energy audits.
Applications
- It is used for commercial and industrial setups with fluctuating loads like welding, compressor use, motor use, etc.
- It is widely used in malls, hospitals and large offices.
- Used in cold storages, IT parks and manufacturing units.
- Used in any installation, which is billed under demand based tariff.
This article is a part of metering page, where other related articles are discussed in details.

