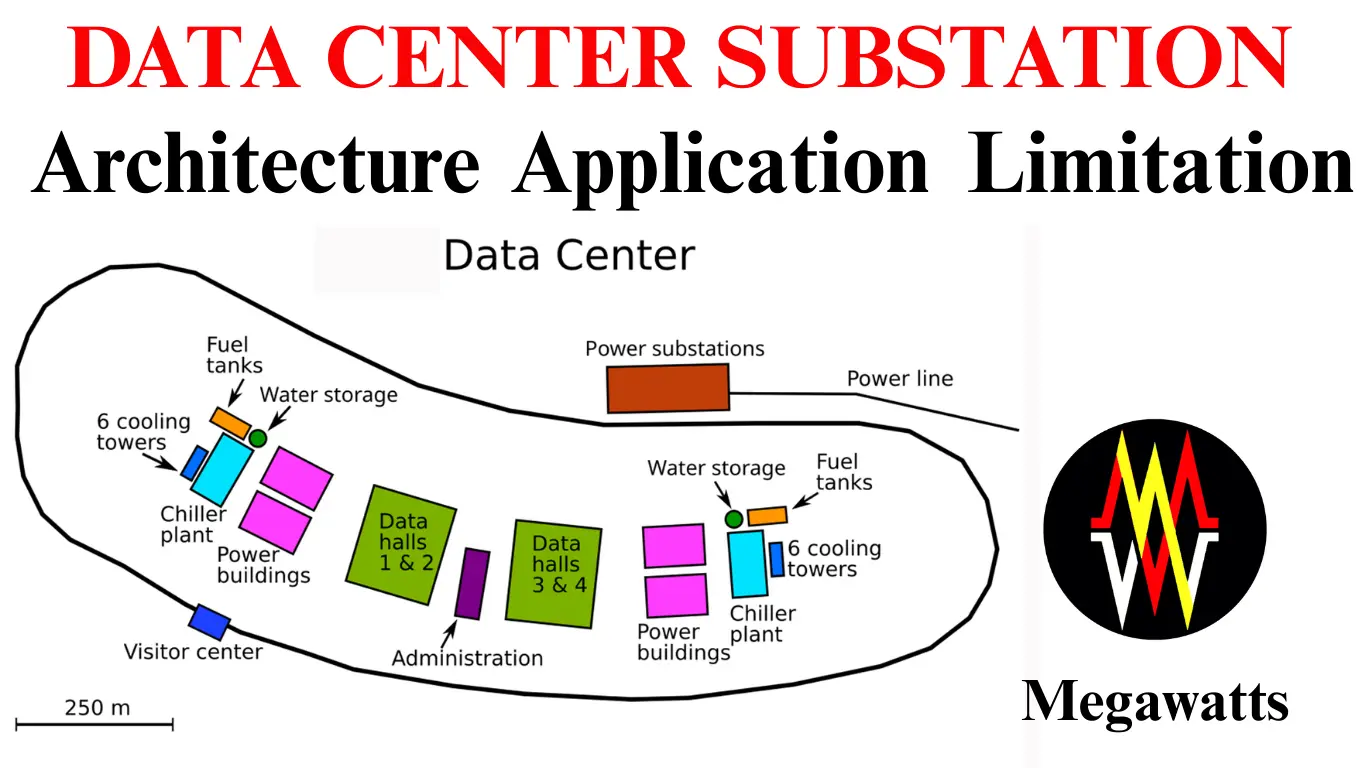
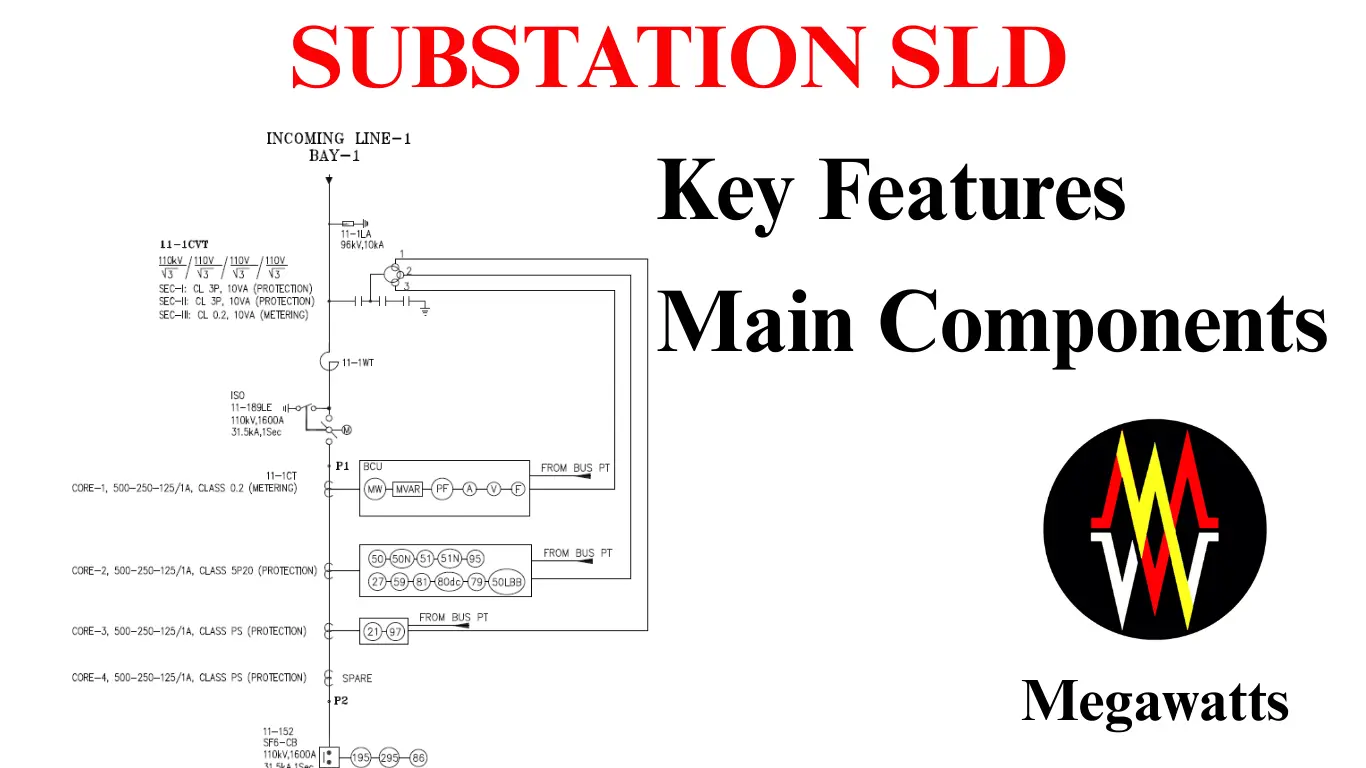
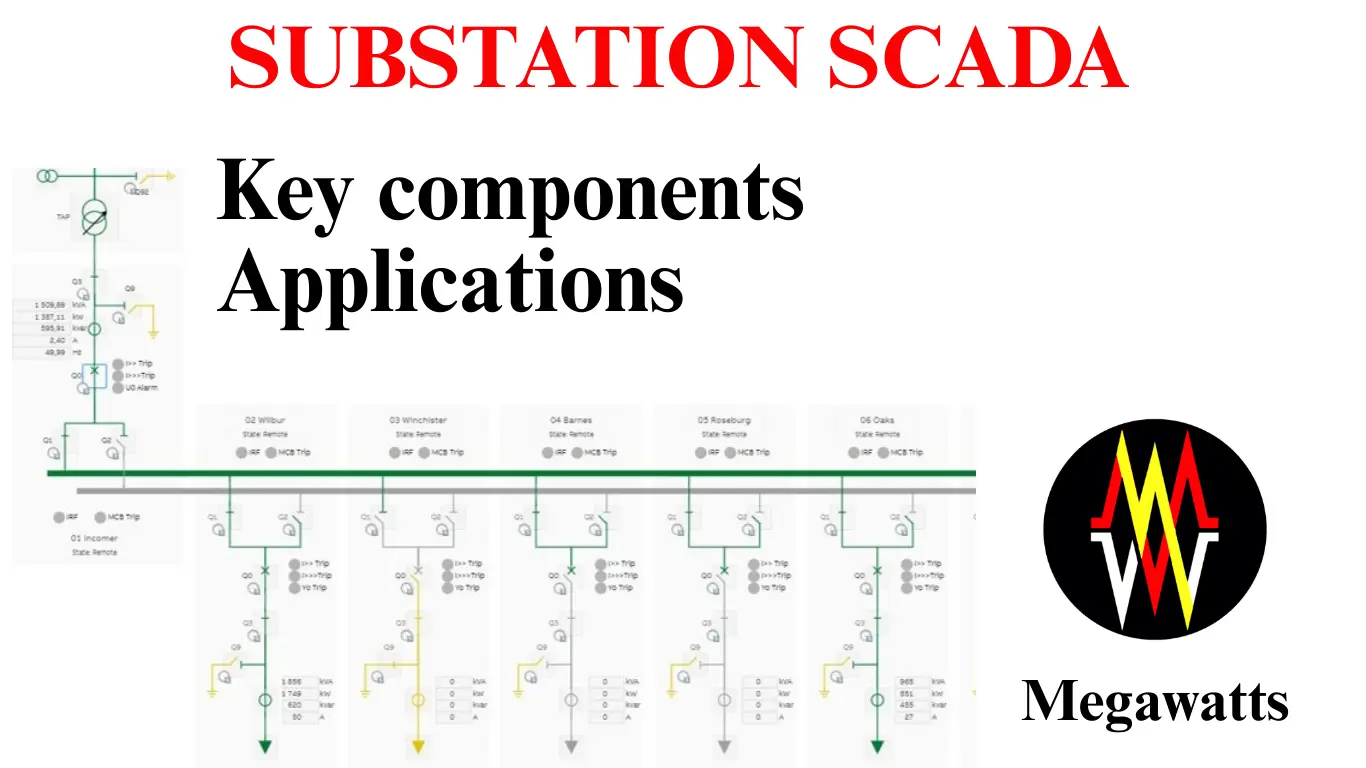
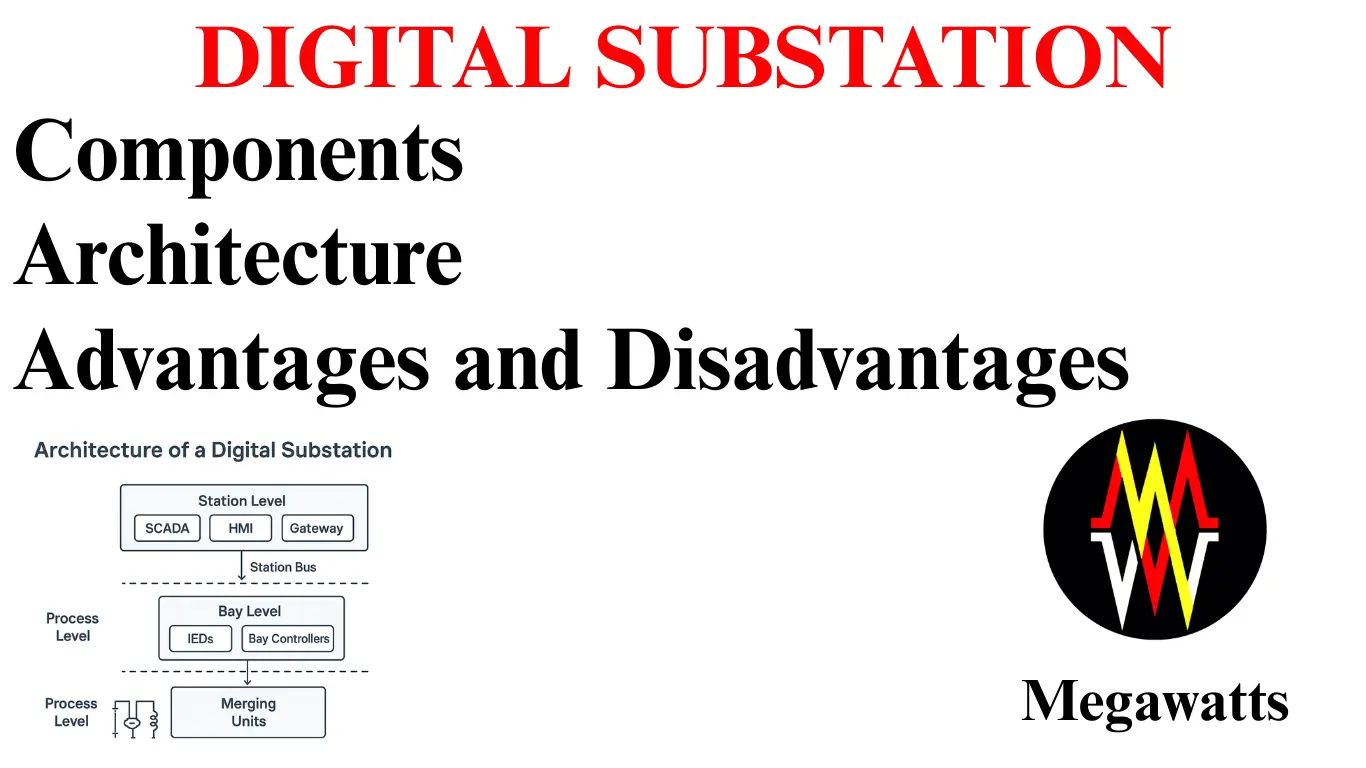
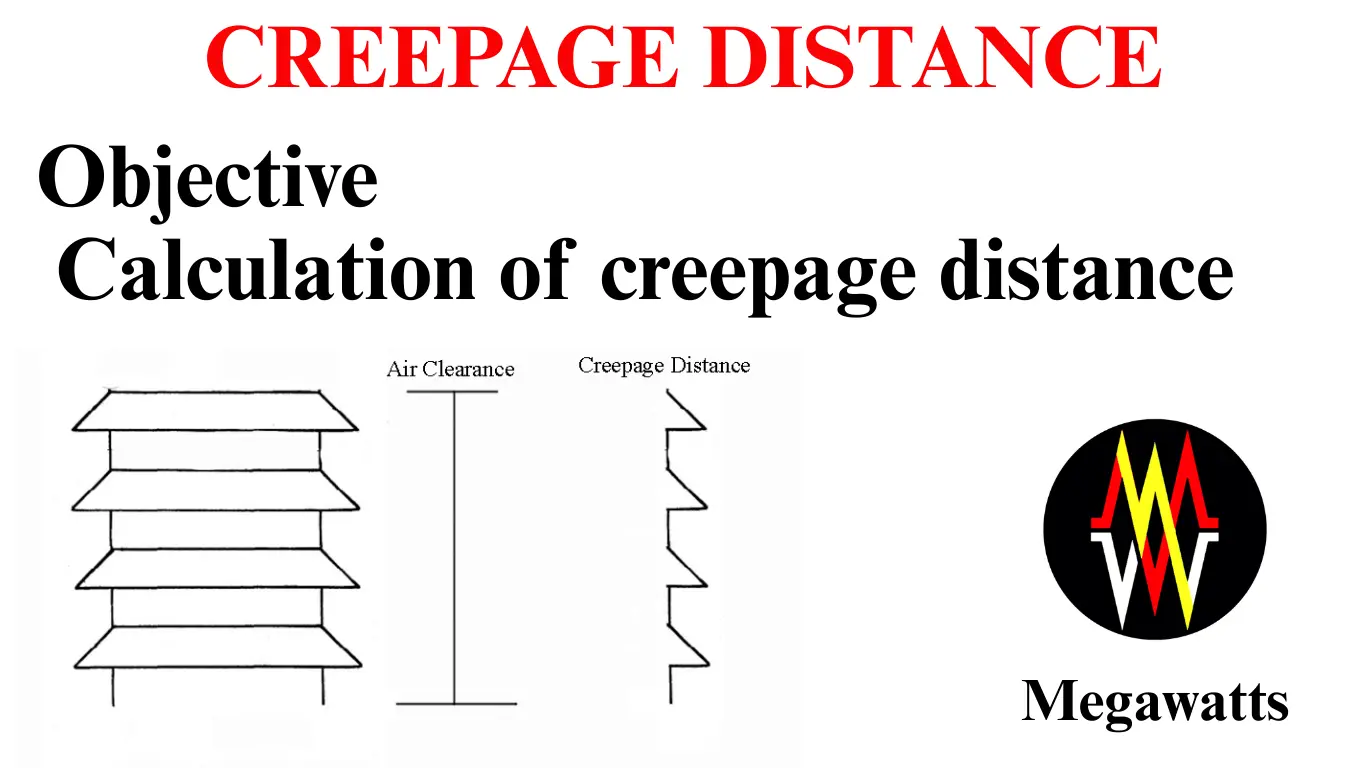
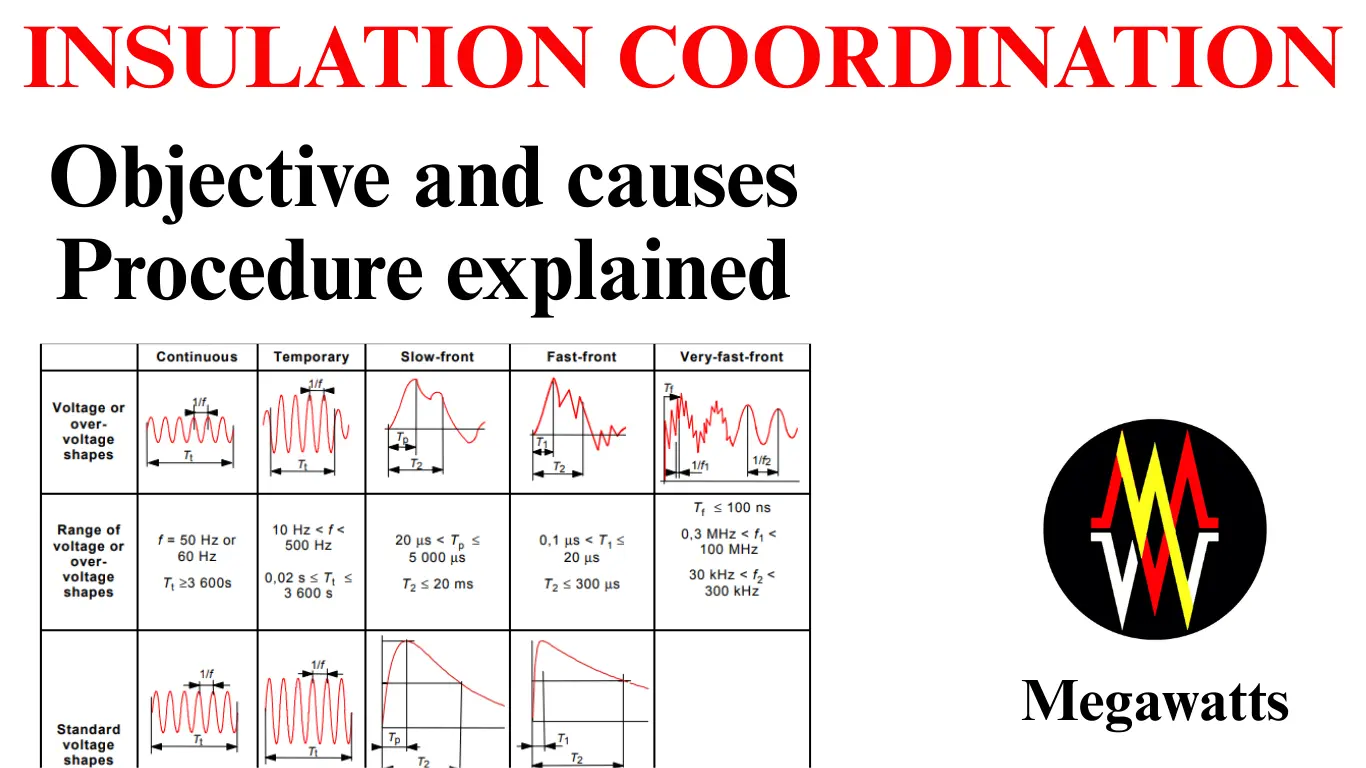
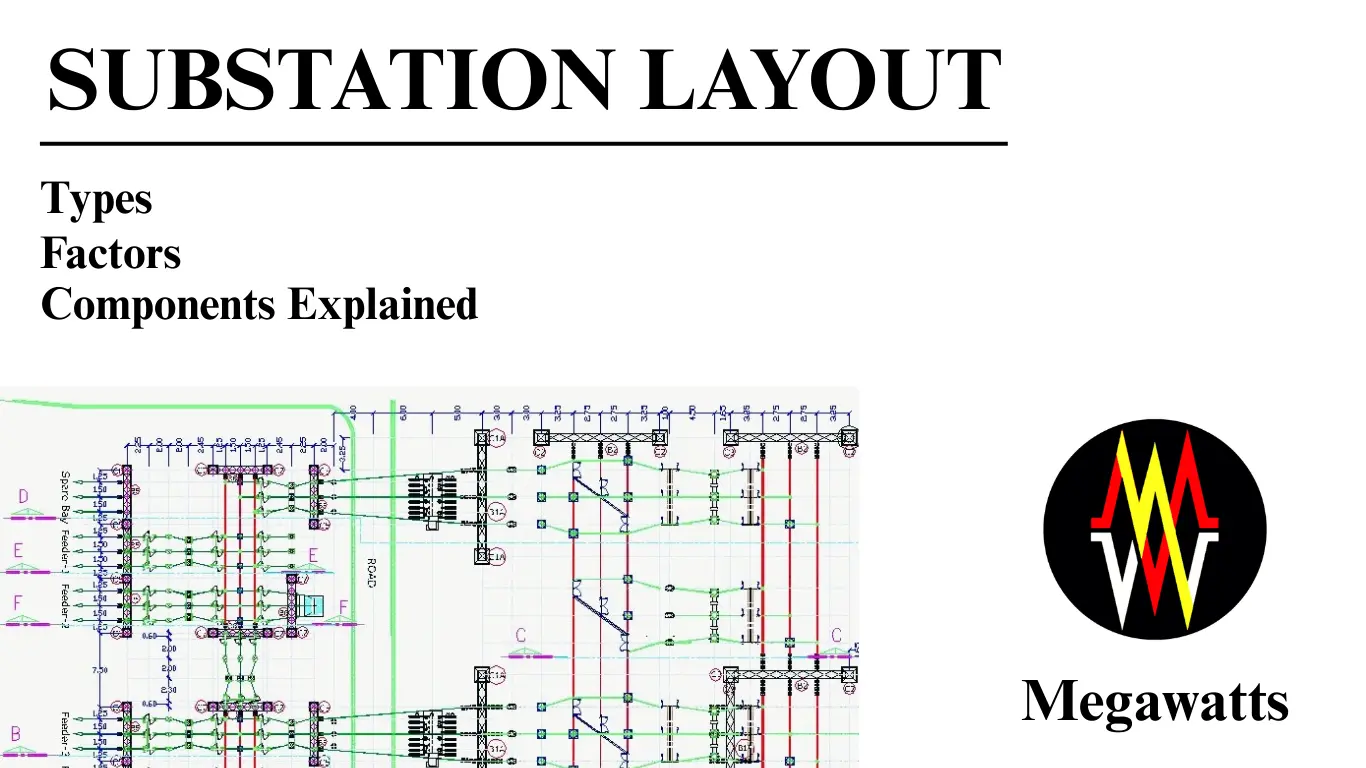
UNDERSTANDING DATA CENTER SUBSTATIONS: Ensuring Efficient and Resilient Power
Data center substation is among the special types of substations, which are specially designed for highly reliable, high power quality, and uninterrupted power supply to critical IT processes in the data center. These substations stress majorly on the importance of redundancy of power supply with reliability to various …