Safety Clearances
The “safety clearance” is the minimum distance in air which is to be maintained between a live conductor and earth, or other equipment on which work has to be carried out.
There are many different values of safety clearances used by various utilities around the world. In practice, safety clearance is dervied by many different emperical relations not always depending on the actual system voltage. In some places, it is the legacy guidelines that depicts the clearance values.
Table of Contents
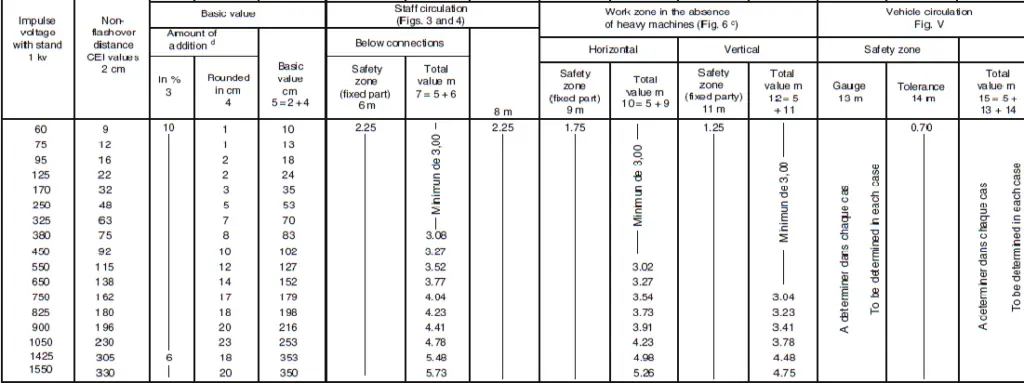
Table
The safety clearance is made up of Basic value and Safety zone.
Basic value
The basic value is basically the protective zone around the conducting parts whose value is a function of the impulse voltage withstand capacity of the substation. This protective zone ensures that adequate insulation is present so that flash over does not occurs during transient voltage surges. The basic value is usually the designed electrical clearance between phase and earth.
It is to be noted that the impulse voltage withstand capacity is a design basis and not the highest rated system voltage. For each impulse voltage withstand capacity, relative non-flashover distance is present. However, the highest rated system voltage can be related to a number of impulse withstand level and hence multiple non flashover distances can be eqauted.
Safety zone
Safety zone is basically a value that directly depends upon the personnel movement and nature of maintenance activities including various tools required on an electrical equipment. This calculated value forms a zone within which the risks related to electrical accidents are eliminated.
Calculation of the Basic Value
Under the fault condition, basic value assures that no flashover takes place in the equipment. For achieving this, the impulse withstand voltage of the substation is selected and corresponding non flashover distance in air is found out.
The non flashover distance thus found out is increased by a safety margin of 5-10% range. The margin is added to incorporate the manufacturing tolerance, installation inaccuracy, other geometrical errors. Various manufacturers have varied equipment sizes, this margin also takes care of this issue.
The basic value only holds the garunttee for no flashover if impulse withstand voltage is considered for its calculation and is never breached by any surges. This needes the substation to have properly sized equipments, capable of limiting the incoming surges, for example, lightning arresters and spark gaps with proper degree of protection.
Determination of the Safety Zone
The safety zone is basically the basic value as calculated above along with addition of distance due to the following factors.
- Personnel height
- Nature of equipment.
- Tools and access required for the maintenance of the equipment.
Movement of Staff
When there is no safety grills or screens fitted, the safety clearanance between the ground and lowest possible current carrying part must consider the free movements of the personnel.
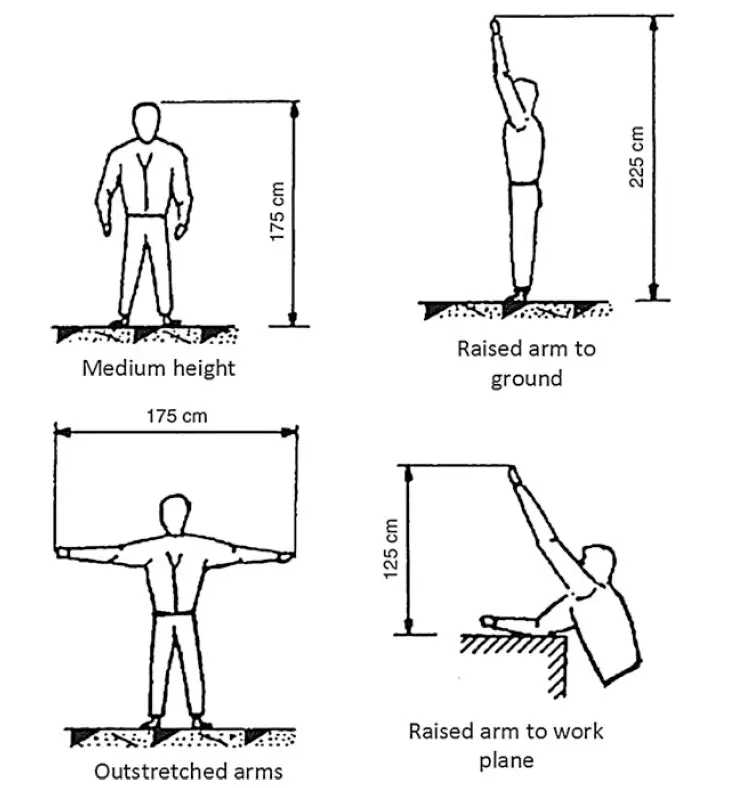
From the figure above, the minimum safety clearance should be equal to the basic value plus 2.25 m, which is the average height of a personnel raising hands on toes. However, corressponding to the impulse withstand voltages less than 380 kV, the basic value is very small, in such case a minimum basic value for the safety clearance for free movement of personnel has to be 3.0 m. The vertical distance between the base of any post insulator and the ground should be greater than 2.25 m. This will ensure safe working space below electrically charged equipments.
It is very essential to consider any insulator, live along its height with gradually decreasing voltage, where only the lowest metallic part which connects the base to structure is at ground potential.
The defined safety clearances are considered as highest accessible points from the ground. It is to be noted that climbing is not considered normal course of free movement. For example steps, or gratings even if they are provided.
When adequate safety clearance cannot be acieved, then free access to the live parts or equipments must be barred by the use of safety grills, gaurd rails and screens.
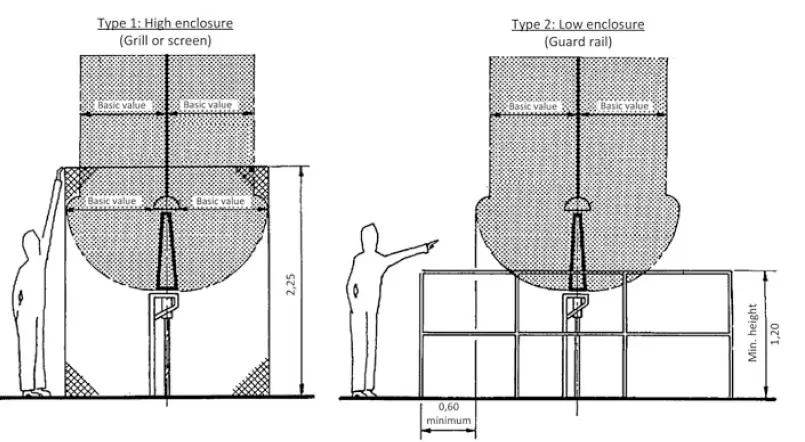
• For a high enclosure, a blocking grill of height equivalent to a personnel with raised arms that is 2.25 m and horizontally separated by the basic value.
• For a low enclosure, a blocking guard rail, 1.2 m in height along with horizontal separation of the basic value plus at least 0.6 m.
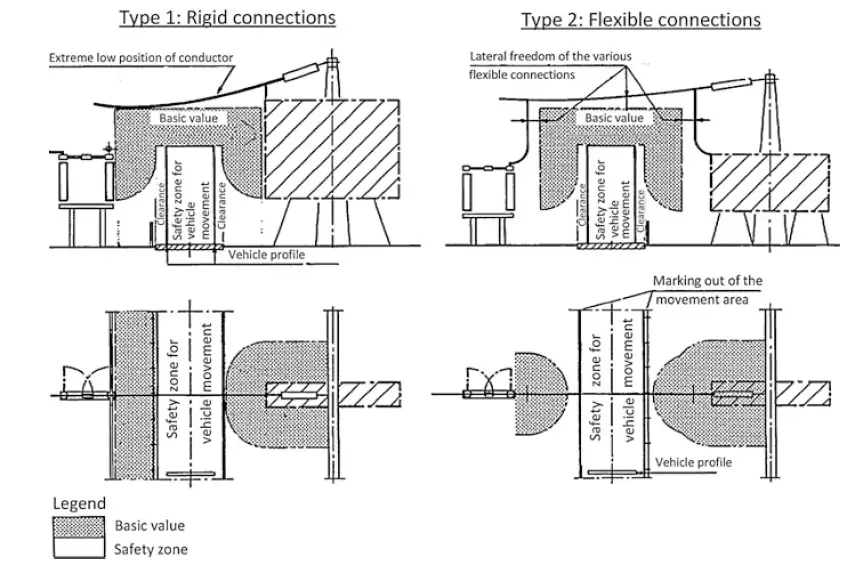
Movement of Vehicles
Some parts of the switchyard requires heavy machinery or vehicular movements for maintenance, overhauling of installation activites. For the tracks a horizontal as well as vertical safety clearance is required along with a margin of 0.7 m for unavoidable inefficient driving.
Work on Equipment or on a Conductor
In substation maintenance, situation arrives when an equipment has to be repaired or checked while keeping the adjacent circuit alive. Then the safety clearance or the distance from the live circuit to the equipment is derived using the same principles. It is basically the basic value along with an additional variable amount determined form the nature of equipment on which the work is carried out, posture of maintenance personnel and dimension of tools used in the process.
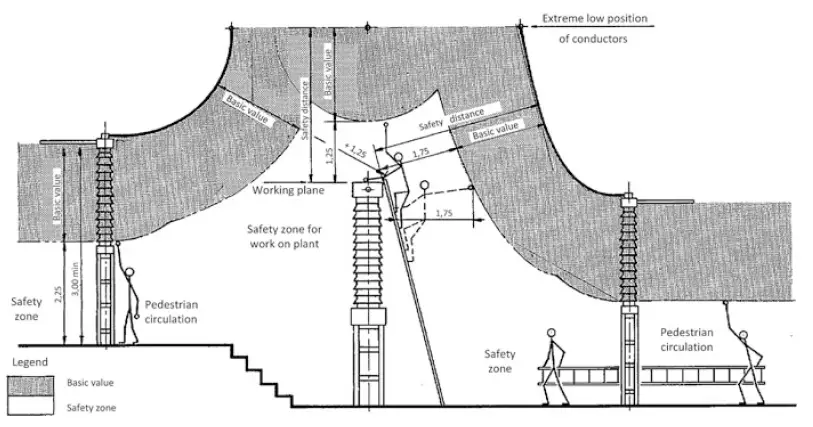
However, the value of the safety zone shall never be less than 3.0 m. The safety clearance is measured from the edge of the equipment that is worked on to the outmost periphery of the basic value of live conductor or equipment. It should be closely observed that the basic value zone of the live component under any situation is not penetrated.
For maintenance activities that includes use of portable equipments the safety clearance may be determined as follows:
• 1.75 m + Basic value, horizontally for a personnel with his arms outstretched.
• 1.25 m + Basic value, vertically above the working plane with arms outstretched.
This article is a part of the Safety and Earthing page, where other articles related to topic are discussed in details.

