The optical port of energy meter is basically a non contact type communication interface, which uses infrared light signals to transfer data between the meter and an external device via a probe or optical head.
The energy meter’s casing has an in built infrared LED transmitter and an infrared photodiode, which is the receiver. The optical head magnetically attaches to the port, which converts the electrical signal from the external device to infrared light pulses and vice-versa for the meter to read.
Table of Contents
Why is the Optical ports of energy meter used instead of electrical ports?
Optical port of energy meter offers many advantages over the traditional electrical ports like the RS-232 or RS-485 for meter reading and are listed as:
Galvanic isolation: The optical port of energy meter provides complete galvanic isolation, which provides safety to the personnel by eliminating the risk of shock and damage from voltage surges or ground loops. The galvanic isolation is absent in the electrical ports and to achieve it, it requires an additional external isolation circuits.
Sealed protection: The optical port of energy meter allows it to be environmentally sealed fully, which provides tamper proofing and longevity by maintaining the ingress protection rating and protecting the internal circuitry from getting environmental damages. The electrical ports require cut outs and special terminal connectors which must be again sealed for protection against dust and moisture.
Data Integrity: The optical port of energy meter is immune to electromagnetic interference and radio frequency interference, which increases the reliability by ensuring data transfer in electrically noisy environments. The electrical ports are not immune to the noise and interference as the optical port of energy meters.
Security: The data transfer from the optical port of energy meter essentially is done via very short range of sight and it requires specific and expensive probe or optical head, which repeals unauthorized physical access and manipulation. However, for electrical port, the communication can be easily tapped into with normal tools.
Components involved in the process of reading
The components involved in the process of reading from the optical port of energy meter are broadly classified as under:
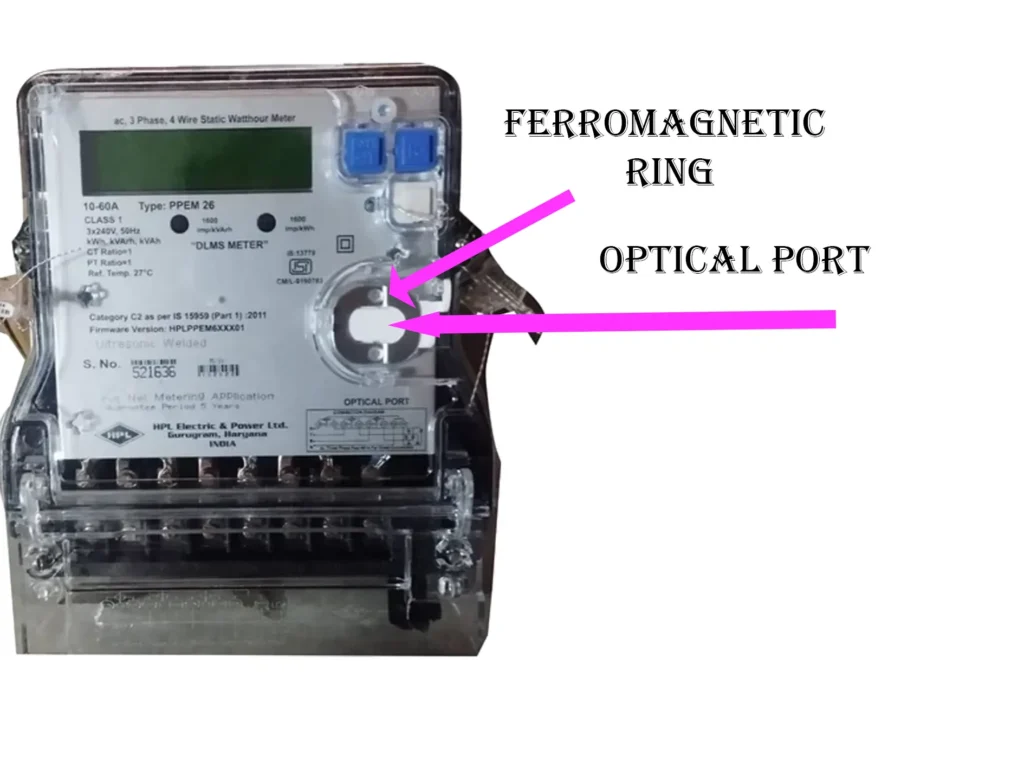
Optical port of energy meter
It is the contactless interface which is built into the meter’s casing. The optical port of energy meter is composed of the following:
Infrared LED transmitter: It is a light emitting diode which converts the energy meter’s electrical signals (data) derived from the digital signal processor into pulses of infrared light for further transmission to the optical head or probe.
Photodiode or IR receiver: It is a semiconductor element often made from silicon or indium gallium arsenide, which converts the incoming infrared light pulses from the optical head or probe to electrical signals that can be processed by the meter’s internal circuitry.
Ferromagnetic ring: It is a metal ring which is embedded around the port, which provides a secure magnetic attachment point for the optical probe ensuring proper alignment of the port and probe for the communication of light to get established.
Sealed housing: The port design is such that it is integrated within the meter’s housing, leveled with the surface of the meter’s body neither protruding out, nor recessed deep. It helps to maintain the IP rating of the meter adding to its longevity while making it tamper proof.
The optical head or probe
It is the external device which is connected to the optical port of energy meter to establish communication between the energy meter and the reading device. The optical head comprises of the following:
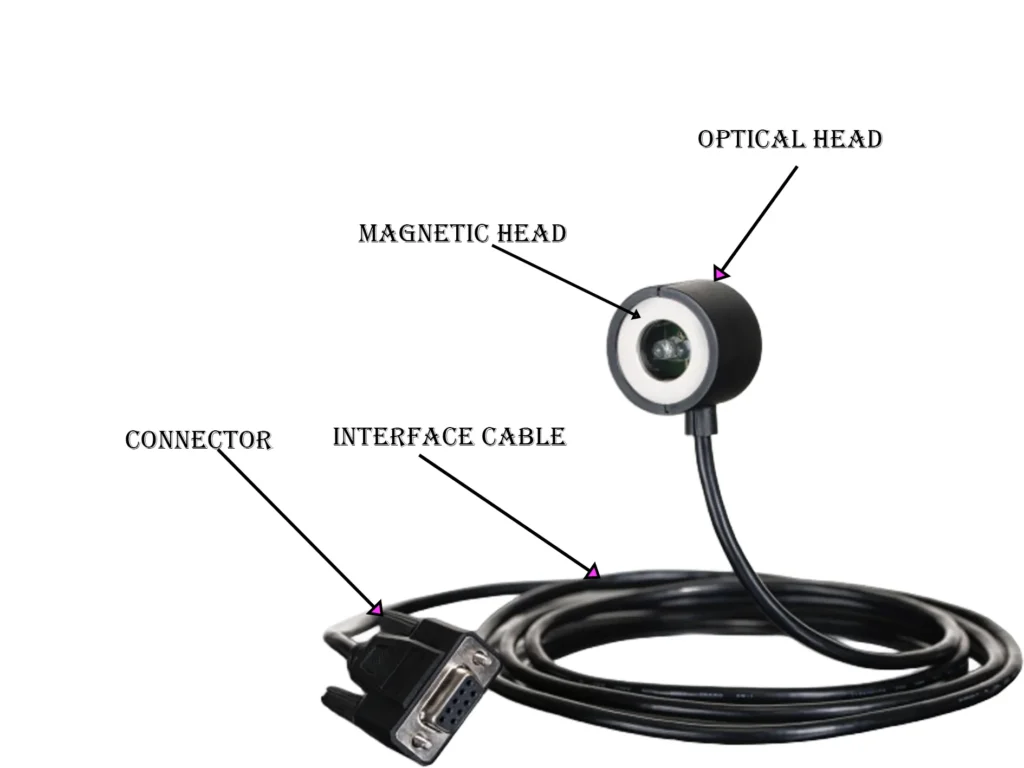
Optical transceiver: It is the core of the optical head which consists of an Photodiode sensor to receive the infrared pulses from the optical port of energy meter, which converts the optical signal to analogue current. The signal then passes through the transimpedance amplifier which converts the photodiode current to measurable voltage. The comparator or signal shaper converts the analogue signal to clean digital pulse in binary which is then passed through UART level transmitter for a compatible output with serial communication channel.
The transceiver also has an infrared LED transmitter to send commands and data to the meter in form of infrared light pulses for example sign in request and configuration data. The command is generated by the reading device which is typically of 5V approximately and is converted to binary by the head circuitry. LED ON sends logic 1 as IR pulse and LED OFF transmits logic 0 as no IR pulse.
Magnetic head: This is the physical attachment head typically made of neodymium that connects to the ferromagnetic ring of the optical port of energy meter snapping a secure and properly aligned connection to establish a precise communication route.
Interface cable: It is the component that connects the optical head to the reading device. The interface cable has USB to UART converter IC that allows the electrical data to be converted into USB data packets. It also ensures proper bund rate, signal parity and framing while providing power to the optical head electronics.
Reading Device
It is the device which is used for initiating the command, interpret the data and store the results, usually a laptop with a specialized software which is responsible for initiating the communication protocol and negotiating the parameters.
Meter Reading software’s workflow
Select the correct communication protocol: Before the beginning of communication, the software must choose the correct protocol stack DLMS/COSEM which is used in almost all modern electronic meters or Legacy IEC 1107, used for old static meters or manufacturer’s proprietary protocol.
Password entry: After the selection of the protocol, the software authenticates with the meter. Typical authentication layers in meters are Low level security(LLS) with simple password with read only access or High level security (HLS) often required for billing data and meter configuration. Some also have multiple security levels, where level 0 has no authentication, level-1 for public reading, level-2 password protected and level 3-5 for utility and manufacturer access.
Select the Data Object: The software displays an Object Identification System tree (OBIS) which essentially contains measurable parameters and event parameters.
| OBIS Code | Standard DLMS/COSEM Meaning | Category |
| 1-0:1.8.0 | Total Active Energy Import (A+) | Billing Register |
| 1-0:2.8.0 | Total Active Energy Export (A-) | Billing Register |
| 1-0:32.7.0 | Voltage (L1) | Instantaneous Value |
| 1-0:31.7.0 | Current (L1) | Instantaneous Value |
| 1-0:14.7.0 | Frequency (Mains) | Instantaneous Value |
| 1-0:90.x.x | Tamper Events | Abstract/Status Objects |
| 1-0:99.x.x | Load Survey Profile | Profile Generic Object |
| 1-0:96.x.x | Meter ID, Time, Firmware | Abstract/Status Objects |
Engineers often selects the billing registers, load survey blocks, tamper and event logs and power quality parameters.
Exporting Data: Once the desired data is selected the software exports the data in CSV or XML or JSON or PDF formats or even encrypted formats. The export includes the meter serial number, reading time stamp, and OBIS values.
This article is a part of the Metering page, where other articles related to the topic are discussed in details.

