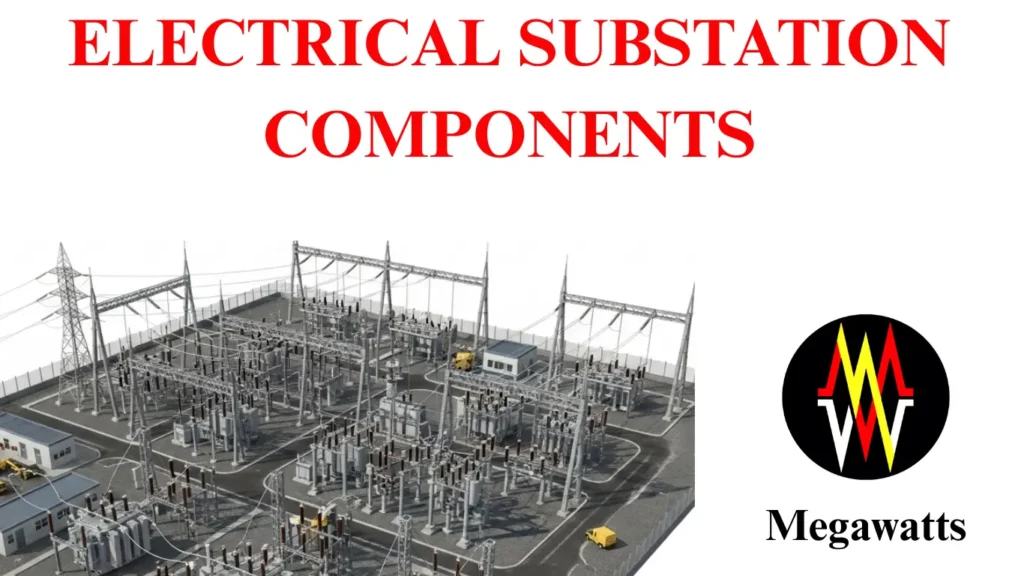
An Electric substation is a part of the power system, which is utilized mainly for the transformation of voltage, either stepping up or down, depending upon the type of substation, either a generation substation or a transmission substation, respectively.
Table of Contents
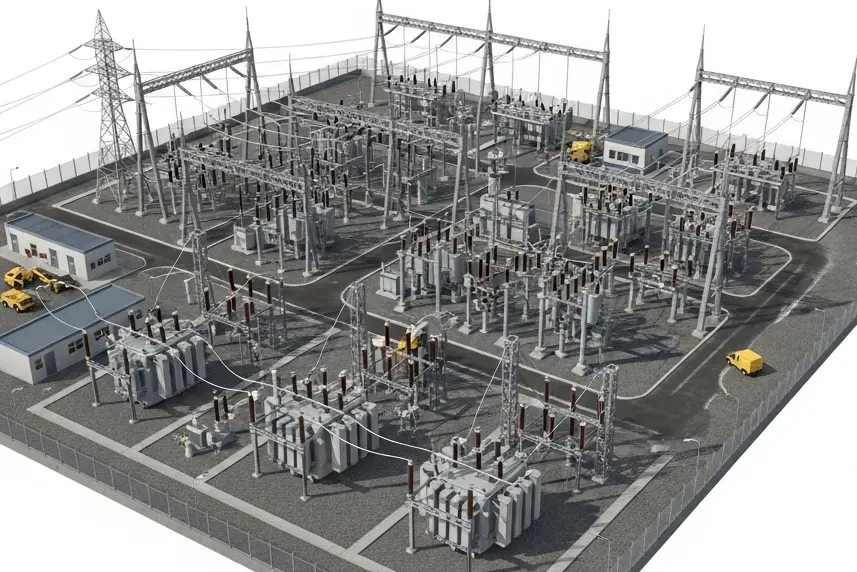
Main electrical equipment of a substation
The main electrical substation components are:
Power Transformer: It is the main electrical substation component that is used to transform the power. Power transformation in this device is achieved by stepping up or down the voltage, based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, transferring the electrical energy between two or more windings without changing the frequency of the power system. The power transformers are generally designed to operate at 99% efficiency or higher, this is possible as it involves no moving parts.
At the generating substations, the generated electrical power is approximately 11 to 15 KV. For the transmission of this generated power over long distances with minimal loss, the voltage is stepped up to a higher level with the help of a power transformer to a range of 132/220/400 KV. However, for distribution of power, the voltage is stepped down in grid substations to 33KV level with power transformers.
Busbar: These are conductors or bundle conductors that serve as a common electrical junction within the substation. The high-voltage busbar collects bulk power from the incomer bays and distributes it to the transformer bay or even to the outgoing feeders. The low-voltage busbar collects the transformed power from the transformer and distributes the same to the outgoing distribution feeders. They are connected to the substation gantry via insulators and are designed to carry large fault currents. Depending on the flexibility and reliability of operation and maintenance, various busbar designs are opted in a substation, like a single main and transfer bus, a double main and transfer bus arrangement, etc.
Circuit breaker: A circuit breaker is an electrical substation component that operates to make or break a circuit. High-voltage electrical circuits involve large flashings during sudden disconnections of fault current or load current; these flashes are being constricted inside the circuit breaker via various technologies and designs. There are various designs of interrupters based on the arc interruption methodologies, like Vacuum circuit breaker uses vacuum to interrupt the arc, and gas circuit breakers involve quenching the arc in a gaseous medium.
It may be noted that this electrical substation component circuit breaker is not a protective device but a circuit interrupting device; the protection from fault is achieved by various functions of relays, and energization of these relays trips the breaker.
Isolator: These are the electrical substation components, which disconnect a circuit completely, and through their switching, the circuit is physically disengaged. It is used for maintenance and inspection only. It may be noted that the isolators are not designed to interrupt the load current or fault current, unlike a circuit breaker. Isolators are generally used on both sides of a circuit breaker, transformer, or busbar, serving as an added physical gap during maintenance for the additional safety of the personnel.
Current Transformers: These electrical equipment in a substation step down the high current flowing in the circuit proportionally to a lower measurable value for metering and protection purposes. The current transformer in the substation can have multiple cores and multiple ratios. Each core is used for a different purpose, like one for metering, the others for protection. The metering core prioritizes accuracy under normal operating conditions, whereas the protection core demands high accuracy at the higher fault current values and abnormal conditions without getting saturated.. This electrical substation component can be classified as live and dead types based on the placement of the tanks.

Potential Transformer: A potential transformer is an electrical substation component that accurately steps down the high voltage of the system to a proportional low voltage of 110 V range. It provides an accurate replica of the primary voltage while maintaining an isolation of the secondary side measuring and protection devices connected.
Lightning Arrester: A lightning arrester is an electrical substation component that provides protection to all equipment of the substation from traveling lightning surges or switching surges. These are basically made of metal oxide plates, which resist the flow of current at a nominal voltage but provide a low resistance path for the surges to be safely grounded. The lightning arresters are placed on both sides of the transformer and are also the first equipment in any feeder. Since the switching surges are more predominant at and above 220 KV, the lightning arresters are also called surge arresters. This electrical substation component enhance the grid reliability and asset life, thus also reducing outages.
Capacitor bank and reactors: Capacitor banks and reactors are essential electric substation components which is used for reactive power compensation and managing the voltage level. A capacitor bank is a group of capacitors connected in series or parallel, used to supply reactive power. By compensating for inductive load, the capacitor bank improves the power factor of the system while also maintaining healthy system voltage.
The reactor is an electrical substation component which is basically an inductive coil, which is used to absorb reactive power and limit the short-circuit current, and it also helps to reduce harmonics. The shunt reactor, connected to the line bay, is utilized to counter overvoltage during lightly loaded conditions.
Protection system: The protection system is the most vital part for the electrical substation components, which includes various main and auxiliary relays like overcurrent relay, differential relay, distance relay and many more. The auxiliary relay is the one that upon getting a certain input, provides multiple outputs example is the master trip relay 86. These relays function under DC voltage, which is supplied from the battery bank of the substation. These relays work as a group and monitor the power system parameters. Once an abnormal condition is sensed, the main relay picks up and sends a trip signal to the contact multiplier relay 68, which then trips the circuit breaker and causes the faulty section isolation.
Auxiliary system of substations
These are the electrical substation component systems without which the substation can function, but with them, the substation can function more reliably, safely, and efficiently. These are:
DC system: This is basically the heart of the protection system of the substation and also the control and SCADA system. This system of battery and charger also provides power to critial lighting sources during emergency.
Fire protection system: The power transformers are mandated to have fire protection system to supress fire immediately if any cases of fire immerges.
Lighting and HVAC: The lighting system is essential for operation in the dark hours while the HVAC system is essential for electronic equipment cooling inside the control room.
This article is a part of the page Substation Guide.

