
A mobile substation is a temporary arrangement of compact assembly of all the essential components of a power distribution system, mounted on a transportable platform. The setup of this type of substation is easy and quick, done primarily to provide emergency power to areas that cannot be conventionally supported electrically by the existing grid. For example, disaster-hit areas, construction sites, event sites, etc.
Table of Contents
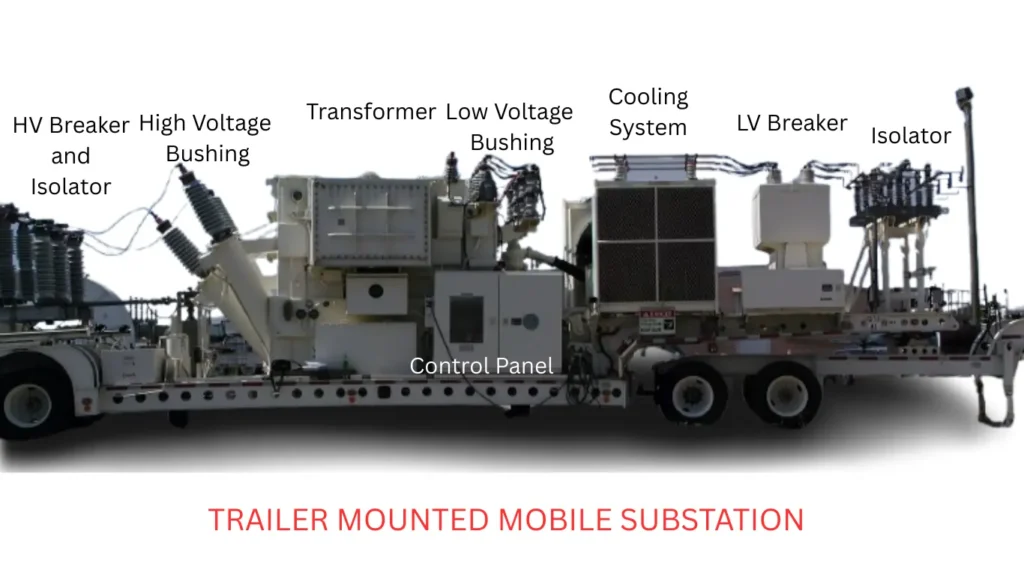
Components of a mobile substation
The main components of a mobile substation are
Power Transformer: A step-up / down transformer is needed for the voltage transformation, which is usually compact and designed for transportability. The transformer of a mobile substation is often oil-cooled, hence the cooling arrangement is critical in design.
High voltage Switchgear: It is used for the control of power flow and interruption of the high voltage circuit during any fault.
Low-voltage Switchgear: It is used for the control and interruption of the low-voltage distribution circuit in the event of any fault and prevents its further propagation.
Protection system: The protection system includes main and auxiliary relays, like earth fault and overcurrent relay, differential relay, etc, embedded in the control and relay panel. Besides the relay, a surge protection system is also integrated in the mobile substation. The mobile substation can have a SCADA system for remote operation, along with communication equipment based on optical fibre technology and GSM or satellite.
Auxiliary systems: The auxiliary system includes portable earthmats, with earthing rods and cable to ensure proper earthing of the system, a Fire protection system with extinguishers and fire detectors. For auxiliary power supply, a battery bank, UPS, and a diesel generator are used.
Connection interface: The high-voltage side utilizes cable connectors and bushings for cable termination, while on the low-voltage side, a flexible busbar arrangement is present for load-side power distribution connection.
Metering system: Secondary inputs from the current and potential transformers are utilized for the purpose of recording the parameters of the power flow.
Transport and mechanical structure: All equipment of the mobile substation is mostly trailer-mounted, while sometimes they are skid skid-mounted or transported inside a container. Most designs utilize a hydraulic system for lifting with a weather protection enclosure.
Mobile substation utilizes all the equipment as a conventional substation does, but is designed modularly for ease of transportation. Also, it can be designed according to specialized needs in various voltage ranges, power ratings, grid codes, etc, following the regulatory standards.
Types of mobile substation
Trailer-mounted substation: These substations are compactly designed for faster mobility and transportation. Mounted on a trailer, it can be towed by special trucks. They can be properly aligned with the high voltage lines by rotating and have a high degree of flexibility.
Skid-mounted substation: These substations are mounted on skids for easy and fast deployment, requiring minimal civil works such as ground levelling. It can be easily lifted by cranes and placed on the levelled ground.
Containerized substation: These substations are placed inside a container, which is a weather-proof design. The equipment inside is kept safe from outside pollution. The container can be moved by road, rail, or sea. This design is suited for areas with a high level of contaminants and humidity, like ports.
Benefits of Mobile Substation
Minimum deployment time: This type of substation comes fully assembled and factory tested and can be put into service in a few hours. With minimum deployment time, the power outage time during emergencies is greatly reduced.
Portable: The mobile substation is portable and flexible, which makes it easy to transport to various locations via land, sea, or air. It can serve various locations over time, which are already overloaded.
No civil works required: Unlike conventional substations, it requires almost no civil works, such as foundations, etc., minimizing the erection time and cost.
Emergency Power and Disaster Recovery: It provides power in case of emergencies like natural disasters. When the conventional substation fails, it reestablishes power to critical facilities like hospitals, water supply, etc. During any equipment failure of the conventional substation or any planned maintenance work, utilities can use the mobile substation to service the load and reduce the outage.
Grid Expansion Support: It can temporarily service the load during the construction of a substation or a bay expansion, and can support seasonal load demands like large festive events, mining sites, and defence installations.
Reliability: Mobile substations can essentially maintain the power without disruption in hospitals and other essential service industries. It enhances the grid stability during peak demand.
Reusability: It can be reused at different locations, making it a cost-effective investment for the utilities.
Limitations of mobile substation
Capped Capacity: To manage the portability, mobile substations cannot have high capacity, which otherwise would make them bulky. Hence, these substations cannot service higher load or industrial loads for a longer time.
Temporary Solution: These are designed as temporary and emergency solutions and hence are not suitable for long-duration use (months).
Higher Cost: The cost per unit capacity of these substations is higher compared to the conventional substations. The transportation and setup also add to the cost.
Logistical issue: Though the substation is mobile and can be deployed anywhere, it needs road access and a special truck. Also, the deployment in remote, hilly, and flood-affected areas can be delayed because of logistical issues.
Redundancy Limit: Since only a small number of these substations are in the utilities’ fleet, too many outages can still overwhelm the response.
Applications of mobile substations
Utility Application: The utility service providers keep a fleet of these substations to deploy during emergency situations like natural disasters, planned maintenance, bay extension, and construction works. These substations can also be used for providing reactive power compensation, voltage, and frequency control.
Renewable energy Application: Renewable energy projects often get completed before the completion of the grid substation. In such a stage, these substations can be used to evacuate the power generated and can be transformed and transmitted accordingly. Before the grid synchronization of renewable projects, mobile substations can be used for various testing of voltage transformation and protection systems. During the outage of the conventional grid substation, mobile ones can be used to evacuate the generated power.
Data Centers Application: Data centers require high availability of electricity; hence, mobile units can provide a reliable and secure supply of power.
Industrial power Application: Mobile sub-stations can be used to power the industries that require a high availability, a reliable source of power with greater quality and efficiency. The mobile units can also be used for backup or to power the critical industrial processes in mines, paint, oil & gas, chemical industries, etc.
Application in port: The ships at ports burn diesel to power their necessary equipment, which is very inefficient and also produces pollution because of high carbon emissions. Mobile sub-stations are used to supply power to these ships when docked at port. Because the mobile units can be moved and are not rigid, they help secure better connectivity with the ships at the port.
This article is a part of the page Substation Guide.

