
A single phase meter is used in homes, small commercial shops and lightly loaded installation that accurately measures the electrical energy consumption in a 230 V or 120 V, two wire systems (phase and neutral). It’s basic job is to record every unit of electricity drawn so that the electrical utilities can bill correctly. The single phase meters has shifted from old electromechanical technology to modern digital and smart meter technology that offers better accuracy with temper detection and remote reading and control.
Table of Contents
Construction of single phase meter
Based on construction the single phase meter can be of two types
Single phase meter (Electromagnetic)
Voltage coil: It is made of fine enamelled copper wire, wound with high number of turns around a soft laminated core. This coil is insulated with varnish, tape and paper spacers, fitted in the upper section of the meter with neutral and phase terminals brought out for connection.
Current Coil: The current coil is made with thicker, low resistance copper wire with fewer number of turns. It is wound on a magnetic core positioned around the aluminium disc. The rigid coil is well anchored to the base plate, designed to handle high load current with minimal thermal stress.
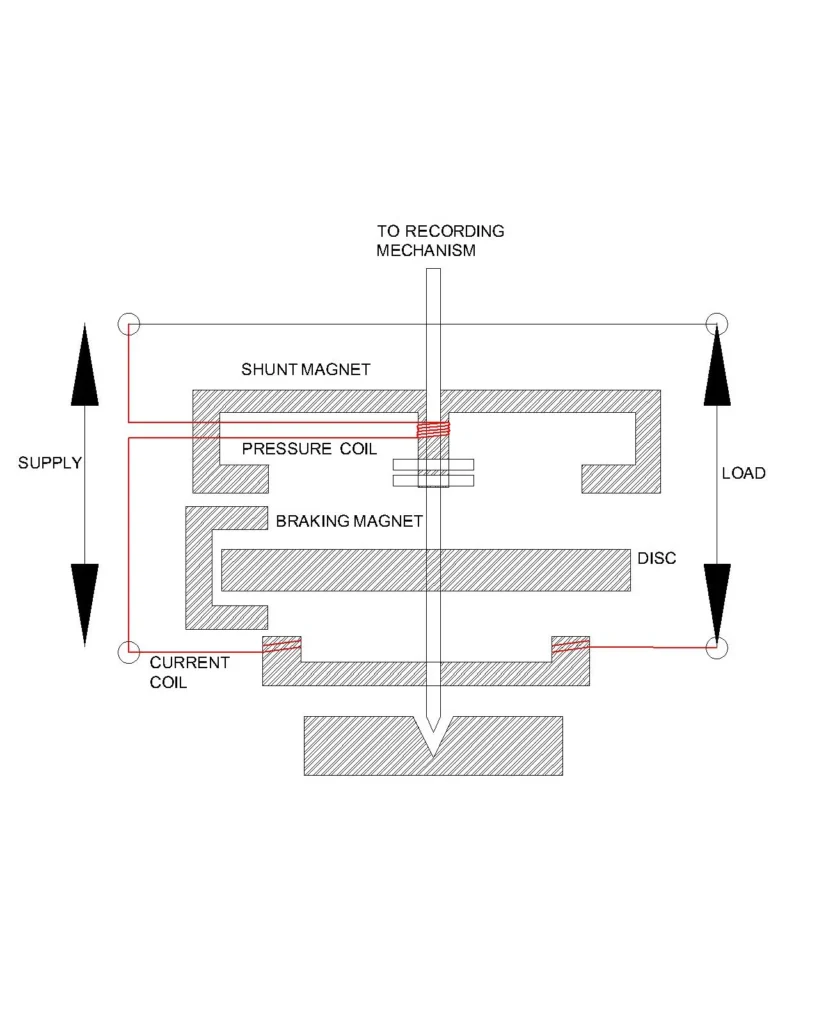
Aluminium Disc: It is a single piece, light weight aluminium disc machined to precise thickness. It is mounted on a vertical spindle with a low friction bearing. The surface of the disc is polished and calibrated.
Permanent magnet: An U shaped permanent magnet made of AlNiCo or similar alloy, is fixed close to the disc edge with adjustable screw that sets the braking gap. It is mounted on an insulated support to avoid magnetic distortion.
Gear train and KWh register: It is a series of precision moulded plastic or metal gears mounted on stainless steel shafts. The gear train drives the mechanical number register with rotating drums, which is enclosed in a dust protected housing and calibrated for accurate unit counting.
Single phase meter (Static Type)
Current sensing element: For low load meters a manganin or copper shunt is used as a thick metal strip machined to accurate resistance and bolted to the PCB. For higher ratings, a miniature current transformer is used which is a toroidal core wounded with enamelled copper wire and encapsulated with epoxy resin for stability.
Voltage Divider: It is built from high precision metal film resistor placed in series on the PCB. The resistors are mounted with accurate creepage distance and coated with insulated varnish. It is designed to step down the voltage to a signal level.
Analog to digital converter: It is a silicon IC integrated on the motherboard. It is surface mounted with multiple pins, supported by protective components like capacitors, filters and isolators.
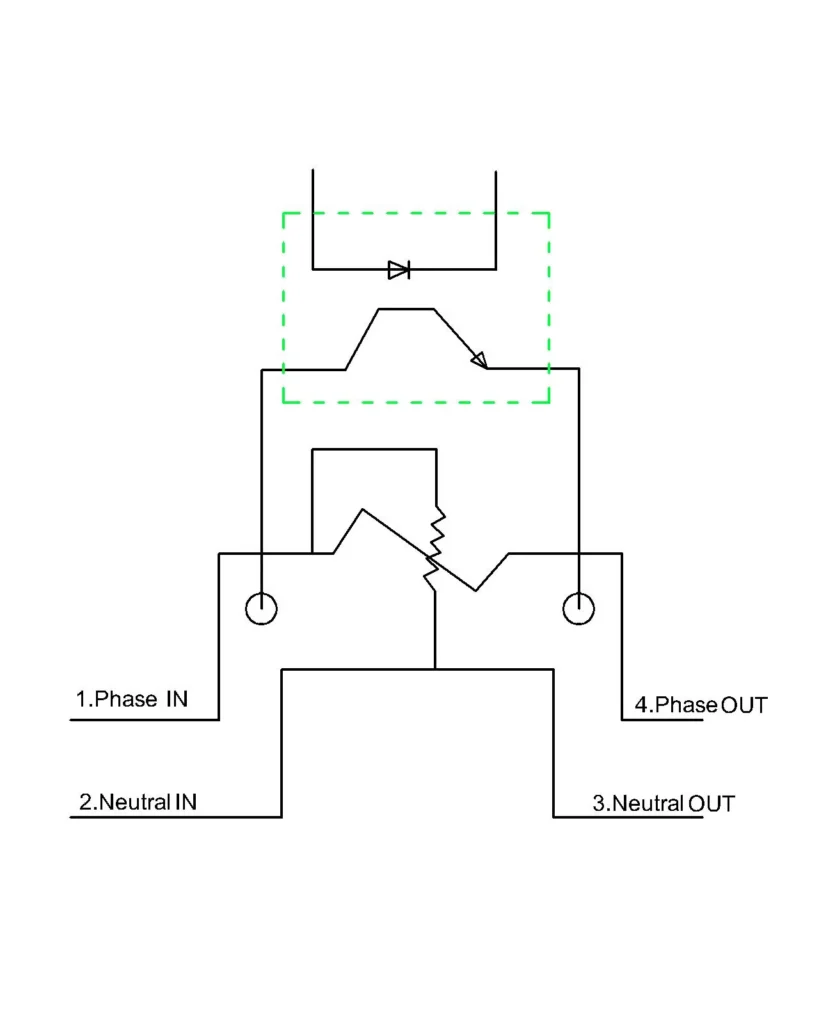
Energy computation IC: It is a dedicated metering chipset which is soldered directly on the PCB. It contains internal digital signal processing blocks, calibration register and metering algorithms.
LCD display: It is basically a dot matrix LCD module mounted on the front panel connected through a flex cable or pin header to the meter’s micro controller unit. It often includes backlight and protective transparent window.
Tamper detection: For the tamper detection, the static meters uses magnetic sensors, tilt sensors and cover open microswitch mounted on the PCB. In some cases, conductive tracks are printed on the inner side of the front cover, when someone tries opening it, the loop breaks and the MCU logs a tamper event.
Working principle
Electromechanical single phase meter: The voltage coil produces a magnetic flux proportional to the supply voltage and the current coil produces a flux proportional to the load current. Both fluxes interact and create operating torque which acts on the aluminium disc and rotates it. The speed of rotation is based on the V x I x power factor. The permanent magnet provides the breaking torque for steady rotation while the gear train rotates the cylindrical mechanical energy registers to record the disc rotation and thus accumulates the total energy in KWh.
Static or Electronic single phase meter: Here, the CT or the shunt senses the load current and the voltage divider scales the supply voltage. Both these signals are fed to the analogue to digital converter ADC for digital conversion of the analogue signals and fed to the metering IC, which calculates the real time power and energy. The LCD display shows the cumulative KWh and other electrical parameters. Accuracy is higher in the static meters as there are no moving parts and no frictional losses.
Installation Requirements
The single phase meters must be installed on a rigid non combustible board. The phase conductor must be routed through the meter properly at phase in and phase out terminals, while ensuring the neutral is terminated properly and is never bypassed. It is to be taken care of that all terminals have the recommended torque to avoid any loose connection and creation of hotspots. Mounting the meter to a height of 1.5 to 1.7 m from the ground for easy accessibility for readings and inspection. The meter must be sealed properly to avoid tampering.
This article is a part of the Metering page, where other articles related to the topic are discussed in details.

