
A power transformer is basically a static device which is used to transfer bulk electrical energy from one circuit to another with the help of electromagnetic induction. The primary purpose of power transformer is to alter the voltage level of the electrical energy source by either stepping up or stepping down such that the energy generated can be transmitted over long distances with increased efficiency with reduced losses and can be used safely in the load centers.
Working principle
The power transformer also works on the fundamental principle of electromagnetic induction which is governed by the Faraday’s law. As a alternating voltage is applied to the primary winding of a transformer which results in the flow of alternating current through it. This flowing current produces the alternating magnetic flux in the core of the transformer, which ensures an efficient magnetic coupling between the primary and the secondary winding of the power transformer.
It is this time varying flux, that induces the electromotive force, EMF in the secondary winding of the transformer, according to the Faraday’s law and the process is known as mutual induction, which forms the basis of energy transfer in a transformer. The magnitude of induced voltage in the secondary is proportional to the number of turns in that winding. The ratio of the secondary voltage to primary voltage is equal to the ratio of number of turns in the secondary winding to the number turns in the primary. It is by proper selection of this turns ratio, a transformer can step up or step down voltage levels as required.
As the secondary winding is connected to the load, current flowing in the secondary winding produces a secondary magnetic flux, which opposes the primary. In order to maintain the core flux at a constant value, the transformer automatically draws additional current from the source side or primary side. It is in this way the power is transferred from the primary circuit to the secondary circuit.
Major components of power transformer
Power transformers that are used in substations are basically electro mechanical systems, which are designed according to well established international standards as IEC 60076 and IEEE C57. Each major component of the power transformer has a clear defined function which contributes to its electrical performance, insulation integrity, efficient cooling, ensuring long term reliability.
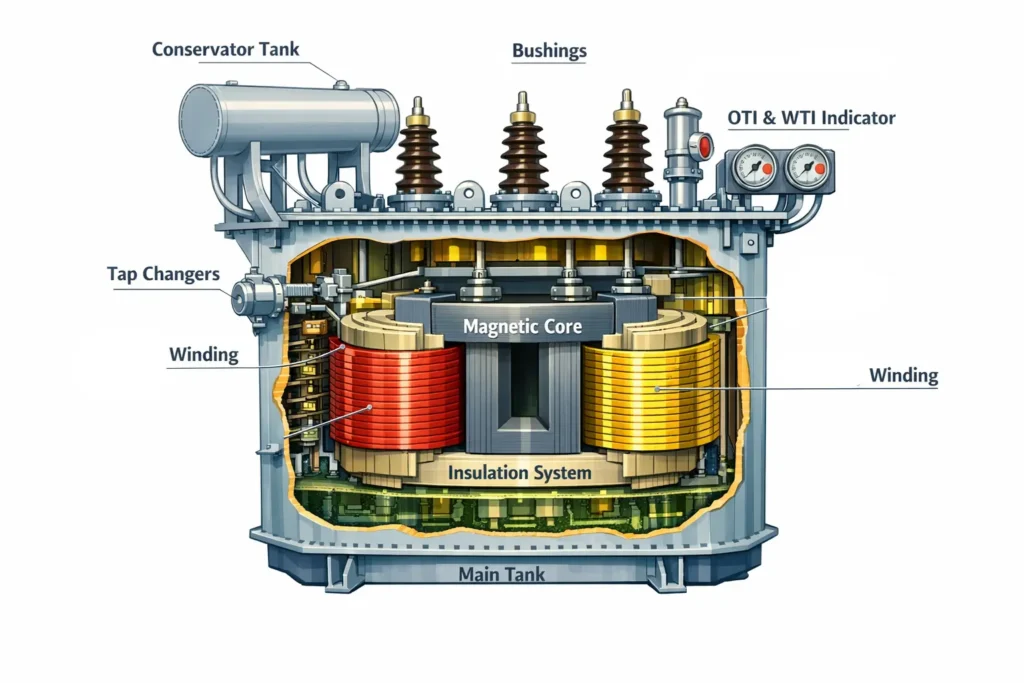
Magnetic core: The magnetic core of the power transformer provides low reluctance path for the alternating magnetic flux which enables the electromagnetic induction between the windings. The magnetic core is built from laminated silicon steel sheets with high magnetic permeability and low hysteresis loss. The laminations are insulated form each other to reduce the eddy current losses. The most common core construction in power transformers includes core-type and shell type designs with step lap joints to reduce the no-load loss and noise.
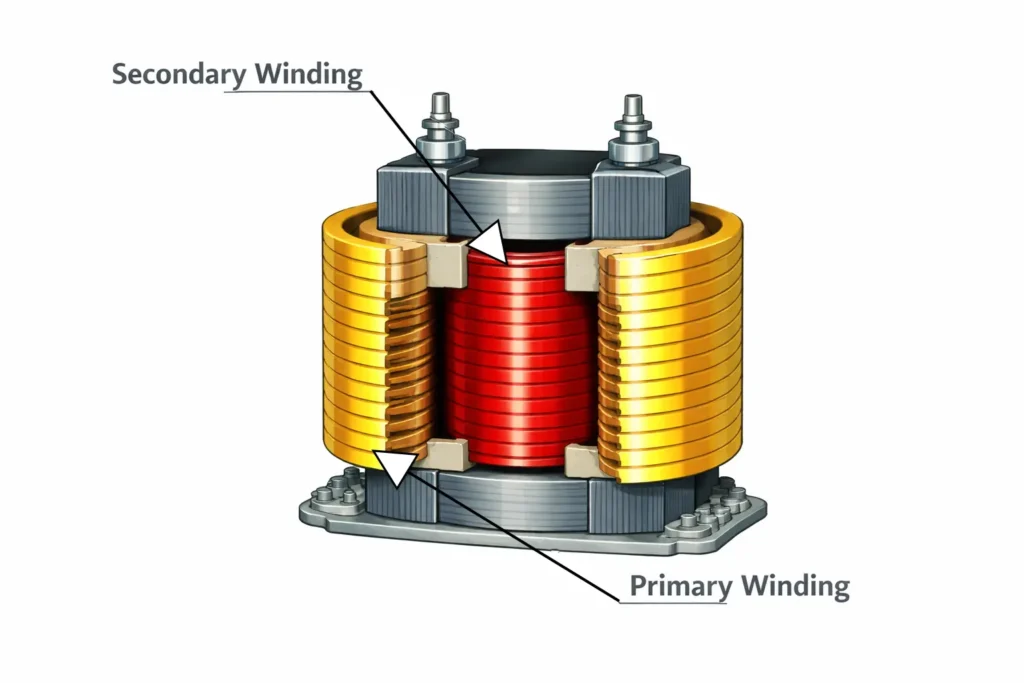
Windings: The windings of the power transformer carries the electric current which produces the magnetic flux required for energy transfer. The windings are made from copper or aluminum conductors, which is selected based on the current rating, required mechanical strength and economic considerations. Windings are arranged as primary, secondary and even tertiary in multi voltage transformers. Common configuration includes cylindrical, disc and helical windings.
Insulation system: The electrical insulation in power transformers ensures the electrical isolation between the windings, windings and core, winding and earth while ensuring the thermal endurance. Most power transformers are oil immersed, which consists of cellulose materials insulation like kraft paper and press board along with the transformer oil. This power transformer oil serves as a dielectric insulation medium along with being a medium for heat transfer.
Tap changers: The tap changers in power transformers are used for regulating the output voltage of the transformer by changing the effective turns ratio of the transformer. The tap changers of power transformers are of two types. The off load tap changers require the power transformer to be de-energized before changing of the taps. While, the on-load tap changer, OLTC allows the tap change, altering output voltage under loaded condition of the transformer, without causing interruption in power supply.
Bushings: The bushings of the power transformers facilitates the passage of the conductor safely through the transformer’s main tank for external termination. The high voltage bushings of the power transformers are basically oil impregnated type or resin impregnated type, designed to withstand electrical stress, environmental conditions and mechanical load.
Main tank, Conservator and accessories: The main tank of the power transformer houses the magnetic core and windings, filled with the insulating oil. The conservator is provided at the top at elevated level from the main tank which accommodates for the oil expansion and contraction because of the temperature change. The conservator makes sure that the main tank remains always filled with the oil.
A breather is attached to the conservator which contains silica gel makes sure that the air entering the conservator is dry to prevent moisture ingress. Safety and monitoring accessories like pressure relief valve, oti and wti temperature indicators ensures safe operation and fault detection.
Cooling System: The cooling system in power transformer dissipates the heat generated in the core and windings to maintain a permissible operating temperature. As per the IEC the cooling system of power transformers are designated as
ONAN (Oil Natural Air Natural) where oil and air circulate naturally and is used for smaller ratings of power transformers.
ONAF (Oil Natural Air Forced) is where the air is forced to circulate via use of fans and the oil circulates naturally. It increases the cooling capacity.
OFAF (Oil Forced Air Forced), the oil and air both are forced to circulate by the use of oil pumps and fans. It enhances the cooling rate and are used for higher rated power transformers.
OFWF (Oil Forced and Water Forced) here the transformer oil is forced to circulate and water-based heat exchangers are used for enhanced cooling capacity. The water is also forced via water pumps. This type of cooling system is used for very large power transformers and indoor installations.
The selection of cooling system directly influences the power transformer’s rating, overload capability, and life of the insulation.
This article is a part of the Transformer page, where other articles related to the topic are discussed in details.


This highlights the crucial role of power transformers in ensuring reliable and efficient voltage transformation across transmission and distribution networks. Proper design, quality insulation, effective cooling, and regular maintenance are key to achieving long-term performance and minimizing losses. Source: EMR Global