In context to DLMS?COSEM, DLMS stands for Device Language Message Specification and COSEM stands for Companion Specification for Energy Metering. The set of specifications for the standard for global smart metering and data exchange is defined by DLMS/COSEM. It is a two part framework which makes sure that different smart devices such as meters and sensors can communicate seamlessly with the central utility system.
DLMS sets the communication rules, services, and message structure for exchanging data. It provides services like GET (read meter data), SET (write data or configure) and ACTION (remote connect or disconnect). DLMS is basically media agnostic and it can run over any physical communication channel like TCP/IP (Ethernet, GPRS, LTE).
Table of Contents
COSEM is basically the data model and the structure, it defines what is being communicated. COSEM standardise the data inside the meter using a object oriented approach. Every piece of information in the meter like the total energy consumed, current voltage, meter’ clock, billing date is modelled as COSEM object. Each COSEM object is given a unique identifier called an OBIS code Object Identification System. For example, 1.0.1.8.0.255 universally means Total active energy import.
By standardising the data model and using OBIS codes any Head End System (HES) built to communicate with DLMS/COSEM can automatically understand the data from the meter even if the make is different.
DLMS/COSEM Layered Architecture
COSEM object model: This is the core object model which specifies how the parameters are organised into objects. Each COSEM object has an interface class (IC), attribute and method.
The interface class defines the object type. For example, IC3 is for register for single value like voltage, KWh, IC7 is profile generic like load survey tables, IC8 is clock for meter’s time and etc.
Each object has data field called as attributes for storing data. For example, IC3 register may include attributes like Value, Scaling factor and Unit (Ampere, Volt, Wh,..), IC8 clock can have attributes like current time, time zone offset and DST rules.
Methods are basically the operations that can be performed on the object. For example, IC8 (Clock) the operation can be “set time”, for IC 7 (profile generic) the operation can be “capture data”, for ID3 (register) the operation can be “reset value”.
Putting together Object = Interface class + Attribute + Method. For example, voltage register has IC3 as interface class, attributes like value = 230, unit = V, and scale = 1. The methods/operation can be “reset”. This makes the voltage readable by any DLMS software.
OBIS Codes: OBIS codes are standard addressing system used to uniquely name and locate every COSEM object in any compliant device. The structure of OBIS code includes 6 byte identifier, usually represented by six dot separated numbers: A.B.C.D.E.F.
| GROUP | FUNCTION | EXAMPLE |
| A | Medium | 1= Electricity, 7 = Gas, 8= Heat |
| B | Channel | 0 = Default or 1,2,3 for multi channel |
| C | Quantity | 1 = Active Energy, 3 = Reactive Energy, 32 = Voltage |
| D | Type | 8 = Cumulative, 7 = Instantaneous |
| E | Measurement | 0 = Total, 1 = Tariff |
| F | Time period | 0 = Monthly, 1 = Daily, 255 = Absolute Value |
The OBIS code 1.0.1.8.0.255 identifier total cumulative active energy import. This universality guarantees interoperability.
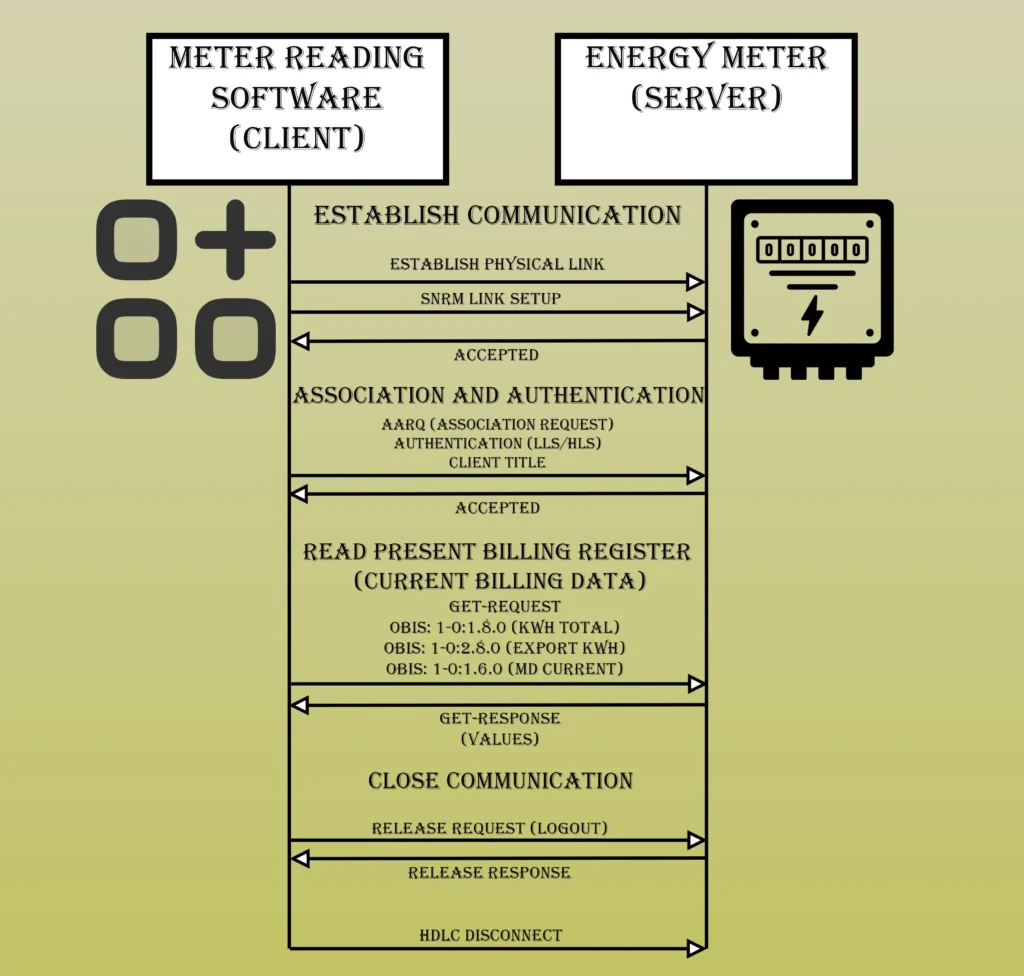
DLMS Protocol Layers: The DLMS primarily defines three upper layers which are Application, Presentation and Session over various lower layer communication profiles.
The function of the application layer contains DLMS services or commands which are used to communicate with the COSEM objects. These services are based on client server model.
GET: It requests the value of an attribute.
SET: It writes a value to an attribute.
ACTION: It starts a method or operation.
The presentation layer handles the data encoding and security. It uses A-XDR encoding which standardise the complex data structures of the meter like time stamp, load profiles and are converted into byte stream ensuring identical interpretation among all devices. This layer is also responsible for encryption and authentication.
The session layer manages the application association, which is the logical connection between the client HES and the server meter. It is responsible for handshake, negotiation of communication parameters and session termination.
Logical name vs short name referencing: The two ways to address COSEM objects within a DLSM message are logical name referencing and short name referencing.
| Feature | Logical Name referencing | Short Name referencing |
| Identifier | 6-byte OBIS code | 2-byte short name |
| How it works | The DLMS request contains full 6 byte OBIS code and attribute index number for specifying exact data points. | The meter assigns condensed 16 bit address for most frequently accessed data points |
| Advantage | Universal interoperability and requires no knowledge | More Efficient and faster |
| Usage | Mandatory for all modern meters for AMI system. | Mostly used for legacy system where speed over the narrow band is critical. |
Integration of DLMS/COSEM
The successful integration of DLMS/COSEM across all utility system defines a functional smart grid.
DLMS in AMI: The DLMS/COSEM is the base communication protocol for the entire AMI network. Every smart meter is basically a DLMS server, providing standardized data access to AMI system components like Head End System (HES) or Data Concentrators, which acts as DLMS clients. It defines the application layer but is independent of the underlying communication media like cellular LTE, PLC, etc, allowing the utility to use a mix of communication technologies based on geography, maintaining a consistent data interface.
DLMS not only enables the meter reading but also controls the crucial functions related to the AMI like remote configuration, load limiting and firmware updates.
Head End system: The head end system is the IT application layer which interacts with all meters connected. The HES must incorporate a robust DLMS/COSEM client stack for managing millions of secure application association with the meters. The primary job of the HES is to poll the meters for energy data, load profile, instantaneous values and receive the event notifications from the meter like tamper events and power outages. The HES can also issue control commands.
The HES translates the raw DLMS message to structured data before passing it to MDMS, Meter Data Management System.
MDMS Meter Data Management System: It is the enterprise application which handles massive volume of collected meter data via the HES. The MDMS performs the following:
The translated time stamped data is received from the HES and then is processed by the MDMS. The MDMS performs validation, estimation and editing to ensure the data is complete and accurate before it being used for billing or analysis.
The standard DLMS/COSEM data with OBIS code simplifies the MDMS functions as it allows the MDMS to compare and analyse the consumption pattern across different meters types, zones and communication channel without any need of complex translators.
The validated data is packaged by the MDMS and sent to billing system for revenue collection.
This article is a part of the Metering page, where other articles related to the topic are discussed in details.

