
Net metering meter is usually a bidirectional meter, which is used in grid substations, grid connected roof top solar systems and likewise installations where energy is imported as well as exported. The net energy meter is installed to measure the imported KWh and the exported KWh, while it also calculates the net energy for the purpose of billing.
Table of Contents
Why is the bidirectional measurement needed?
In installations like a grid substation, it has often more than one feeder on the high voltage side. Among them, some may import the energy while via some feeders energy can get exported if the demand on the LV side is not high enough. In such a case every feeder must be equipped with a net metering meter or a bidirectional meter to precisely measure the imports and exports of energy and also the net energy.
In solar installations, during the day time or sunny hours, solar energy is efficiently converted into electrical energy and is utilised for the domestic consumption and if generation exceeds the consumption, energy is exported to the grid. Likewise, during night or cloudy days, the installation imports energy from the grid. And this export and import of energy is recorded by net metering meter or bidirectional meter.
Working principle
The working of a net metering meter or bidirectional meter is same as a static energy meter but with a direction of energy flow included. The working can be divided in to:
Input sensing: The net metering meter or bidirectional meter uses current transformer and potential transformers to sense the voltage and current in both directions of the power flow. The instrument transformer’s polarity and phase sequence must be maintained properly as the direction determination depends largely upon the vector relationships of current and voltage.
If the power factor is positive the meter records import and otherwise export. Hence, the phase angle must be correct. If the CT polarity (S1-S2 or P1-P2) is reversed, the load current which is normally lagging is seen as leading and the meter interprets the normal import as export.
If the PT polarity is reversed, the voltage vector rotates by 180°, this flips the cos ϕ and results into incorrect direction sensed and wrong power factor.
If the phase sequence is wrong, the meter will compare the R phase voltage to different phase’s current and so with other phases. This will make the phase angle calculation meaningless and the vector summation will become invalid.
DSP computation: The digital signal processor of the meter continuously samples the instantaneous voltage and current from all the phases and computes the active energy, reactive energy, and apparent energy. It applies the sign-based power calculation to classify the flow of energy as import or export, thereby ensuring bidirectional metering.
Direction: The meter determines the direction of flow from the sign of the real power which is computed continuously from the sample voltage and current input. The core logic is that for positive real power P > 0, the meter reads as import, for negative real power P < 0, the meter reads as export. This sign convention allows the bidirectional or net metering meter’s firmware to decide the increment of energy registers either Import KWh register or Export KWh register.
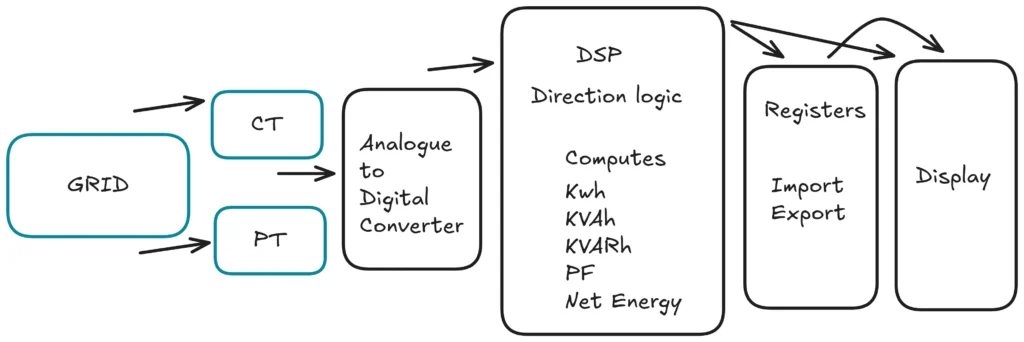
Memory: The bidirectional meter’s memory maintains all billing data, divided into multiple secure registers. Among the essential ones for the net metering meter are import KWh, Export KWh and net Kwh (Import-Export).
Display: The meter is equipped with a LCD display which scrolls through several parameters like real time voltage, current, KW, power factor, import/export energy and net energy.
Application of the bidirectional meters
The net metering meters are mostly used in
- Feeders connecting solar generating station to substation.
- Rooftop solar and distribution utility’s interface metering.
- Used for metering solar energy injection from distributed generators.
- Used for substation feeders where both import and export of power is possible.
This article is a part of the Metering page, where other articles related to the topic are discussed in details.

