A proper understanding of switchgear vs switchboard is essential in the design of modern power system as both Switchgear and switchboard are central components to the electrical power transmission and distribution system as they provide the necessary control, protection of circuits and the isolation.
Switchgear includes circuit breaker, isolator, in conjunction with necessary relay and fuses housed in metal enclosure for it’s operation, which is designed to interrupt fault and ensure safe maintenance of the power equipment. A switchboard on the contrary, serves as a panel, which contains bus to distribute power form one or more sources to various load circuits via protective devices installed for the protection of the circuits.
Table of Contents
Switchgear vs switchboard
| Parameter | Switchgear | Switchboard |
| Function | Controls, protects, and isolates power equipment from faults | Distributes power from source(s) to various distribution circuits |
| Primary Purpose | Fault interruption and system protection | Power distribution and load management |
| Voltage Level | 3.3 kV and above | below 1 kV applications |
| Components | Circuit breakers, isolators, relays, contactors, and fuses | Switches, busbars, fuses, meters, and circuit breakers |
| Protection Capability | Auto fault detection and interruption | Limited protection |
| Location | Common in Electrical substations | Installed in commercial buildings, offices, and load centers |
| Construction | Enclosed in metal cabinets; often arc-resistant and compartmentalized | Panel-type construction with front-access wiring and instruments |
| Operation | Manual, automatic, or remote-controlled | Mostly manual or semi-automatic operation |
| Cost | Higher due to complex protection and control mechanisms | Lower; primarily a distribution component |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized inspection and testing | Easy to maintain and operate |
Definition
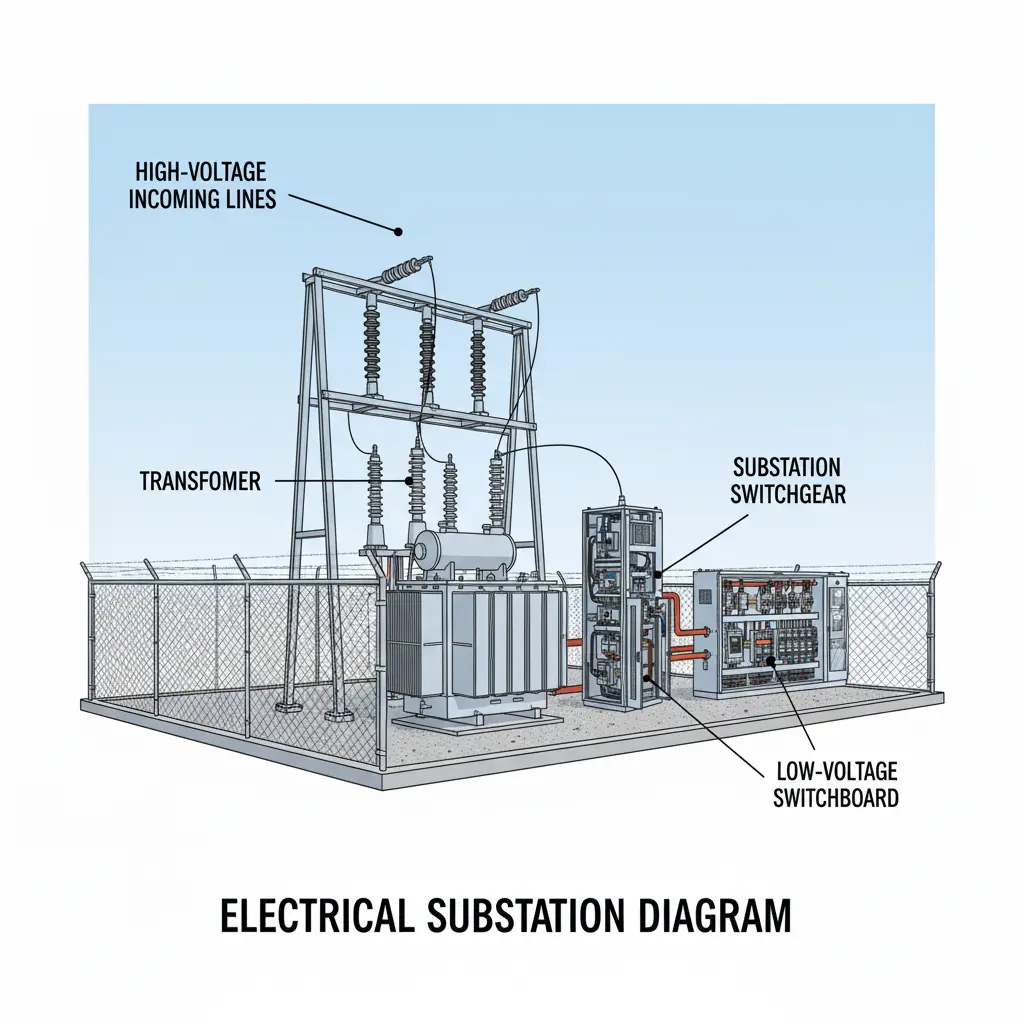
Switchgear: It is basically the combination of electrical devices intended for controlling, achieving protection and isolating circuits and equipment in the power system. While differentiating switchgear vs switchboard, the switchgear primarily focuses on protection and interruption of the electrical circuit during a occurrence of fault by the help of circuit breaker, relay, isolators and fuses. Switchgear makes sure that the fault in the system is not propagated to essential and expensive power equipment and it gets cleared with minimum interruption in the entire power network. These are commonly found in transmission, generation and distribution substations. Modern switchgear are more compact and intelligent compared to the older counterparts, with improved reliability and safety in operation and maintenance.
Switchboard: It is essentially a electrical panel designed to distribute power from incoming source(s) to various branch circuits ensuring safety and efficiency. In the context of switchgear vs switchboard, the switchboard primariliy handles the distribution of power only. Switchboard includes busbar, switches, fuses and circuit breakers for managing the electrical load across various output. Switchboards are more commonly found in industrial and commercial areas as it acts as the central point for collection of power and diverting it to various lighting, electrical machine and auxiliary systems. Modern switchboard houses digital meters for monitoring the power with labelled outputs for ease of operation and maintenance.
Components of switchgear
Circuit breakers: With reference to switchgear vs switchboard, the switchgear circuit breaker are basically the switching device, used for making and breaking the high voltage electrical circuits. These circuit breakers are equipped with arc chambers and arc quenching media for channelling and quenching the arc generated during contact separation. The breaker closing and opening is controlled by a mechanism box which is often spring/pneumatic operated. The switching of the circuit breaker is governed by the various associated relay which can sense faults.
Isolator: With respect to switchgear vs switchboard, the isolators are mechanical switching device used to disconnect a circuit physically during maintenance or inspection. This device only operates under no load condition unlike the circuit breaker. The primary objective of the isolator is to make a visible break in the circuit for preventing accidental energization of the circuit during ongoing maintenance activities.
Relay and contactor: Concerning switchgear vs switchboard, the relay is that equipment in the switchgear which detects the faults / abnormal conditions in the power system based on various numerical logics. The relay gets the input from current and voltage transformer and based on these input it generates a trip output if any abnormalities is detected. This output is transmitted to the trip coil of the circuit breaker and upon receiving the signal the circuit breaker trips.
While the contractor controls the switching of the electrical load based on predefined logics.
Current and voltage transformer: The current transformer is used to reproduce a minimal proportional value of the higher actual current flowing in it’s primary circuit. As the higher currents in the primary circuit cannot be measured directly hence to proportionally minimize the magnitude current transformer is used.
The voltage transformer is also a instrument transformer used to step down the high voltage into a minimal measurable level. Both the CTs and the VTs provide current and voltage input to the relay.
Control panel: In relation to switchgear vs switchboard ,the control panel of the switchgear houses various relays for centralised control, supervision and monitoring of the power system. It also contains switches, meters, indicators other than relays along with a control circuit and voltage and current inputs for real time fault management.
Components of switchboard
Busbar: Relating to switchgear vs switchboard, the busbar is the most important component of the switchboard as it is the junction of the incoming power from source(s) and the outgoing power in various distributed circuits. It is usually made of thick metallic strip of copper or aluminium. A properly sized busbar reduces heat generation and energy loss. It is the largest conductor in the entire switchboard.
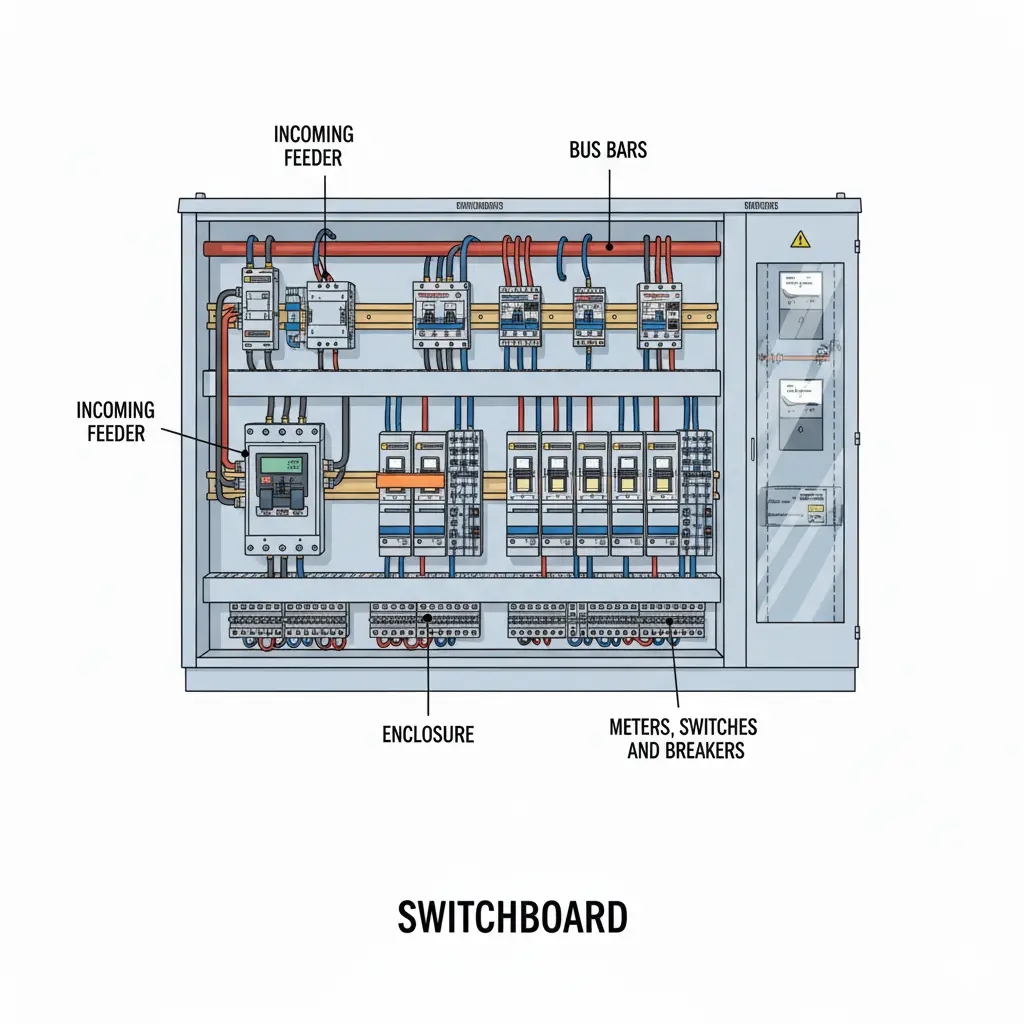
Incoming and outgoing Circuits: In context to switchgear vs switchboard, the incoming and outgoing feeders in a switchboard is basically the entry and the exit of the electrical power. The incoming feeders collects electricity from the main supply or transformers and the outgoing feeders distributes the same. Safe power routing and efficient load sharing is dependent on these circuits.
Meters and Circuit breakers: Meters, fuses, circuit breakers in a switchboard is used for monitoring, protection and control of the electrical circuits. Meters measures the voltage and current, while fuse and breakers provide the automatic circuit protection from overcurrent and short-circuit. Pertaining to switchgear vs switchboard, It may be noted that breakers in switchboard are usually MCBs or MCCBs.
Enclosure: The housing of the switchboard provides a physical protection to the busbar and associated feeder’s wiring. The enclosure saves the connections from dust and moisture and also from accidental physical contact. Thus, it improves the reliability safety and ensures longer life of the connections.
This article is a part of the Switchgear, where other articles related to switchgear are discussed in details.

