A solid state relay is basically a switching device that has electronic components like thyristors, TRIACs or transistors for achieving the control of electrical loads without moving parts. It functions similar to an electromechanical relay but with faster switching, longer lifespan and higher reliability in zones of vibrations.
The solid state relay offers fast, silent and reliable operation with increased durability because of absence of contacts arcing and mechanical wear. Hence they are ideal for industrial automation, heating control, lighting solution and motor application also.
Table of Contents
Construction of Solid-state relay
The solid state relay basically uses semi conductor components in place of mechanical contacts as used in electromechanical relays. The structure of the solid-state relay can be divided in to three main groups: input circuit, isolation circuit, and output circuit.
Input Circuit: The input circuit in a solid state relay is that part of the structure of the solid state relay which receives the control signal in form of low voltage DC typically between 3-32 Volts form an external source such as a PLC, micro controller or a manual switch. When the control signal is applied, an LED is activated with in the solid state relay, which serves as primary triggering device.
Isolation circuit: Next in the structure is the isolation circuit which is usually an opto isolator or photo coupler. It forms the barrier between the primary side and the secondary side or the load side of the solid state relay. The opto isolator provides the electrical isolation between the low voltage control circuit and the high voltage load circuit, protecting the sensitive electronics from high voltage transient surges. The isolation circuit has a LED on the input side and a light sensitive device like a photo diode, photo transistor or phototriac on the output side of the circuit.
Output circuit: The output circuit is the third in the structure and contains a power switching device, typically a TRIAC or SCR pair or MOSFET depending on the Solid State Relay design operation (AC or DC). The output circuit switches the load current based in the signal received through the opto isolator.
TRIAC: Triode for Alternating current is a bidirectional semiconductor used for switching or controlling AC loads like lighting, heating loads and motors. The TRIAC can conduct current in both direction. TRIAC is ideal for low-medium current AC switching applications.
SCR Pair: The silicon controlled rectifier conducts current in one direction only. It is used for switching high power AC load. By connecting two SCR pair in anti parallel configuration or back to back configuration, conduction can be achieved during both positive and negative halves of the cycles. Compared to a TRIAC, SCR pair offers better thermal performance and can handle higher current.
MOSFET: The Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor is a fast acting switch, controlled by voltage which is ideal for application in low -medium DC solid state relay. It offers low resistance, high switching speed and better efficiency.
The entire structure of the solid state relay is enclosed in a heat resistant, insulated casing with terminals extrusions for control, load and common connections.
Additional components of Solid state relay
Snubber circuit: It is a protective resistor-capacitor network which is connected across semiconductor devices in solid state relays. It supresses the voltage spikes and limit the switching transient surges. It prevents false trigger, provides reduction in electromagnetic interference and enhances the longevity as it minimises the stress on the semi conductor components of the relay.
Heat sinks: It is used for dissipating the heat generated by the semiconductors during the conduction state. The heat sink provides the path for thermal energy transfer from the relay body to the surrounding air. It prevents the malfunction of the relay components and enhances the operational life by reducing the overheating.
Varistors: The metal oxide varistors protect the relay from voltage surges and transients. They offers high resistance to normal voltage but rapidly reduces the resistance during overvoltage condition, clamping the excess energy. It saves the relay from lightning strikes and switching surges.
Working principle
The working principle of the solid state relay is based on the optical coupling and semiconductor switching. When small control voltage is applied as the input in relay’s terminal, the LED in the input circuit emits the light. This light is transmitted across the opto isolator to the output side of the relay ensuring physical disconnection and galvaniv isolation of the control and the load circuit.
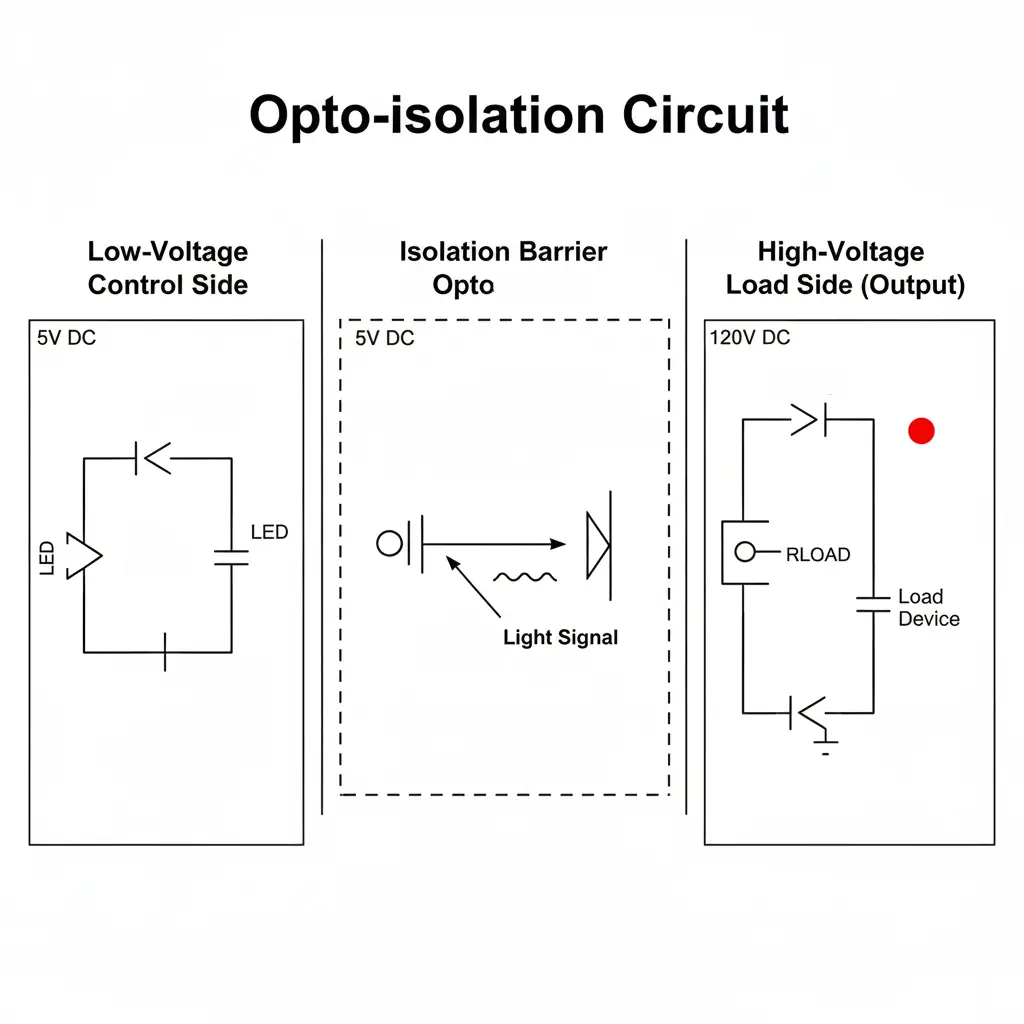
On the secondary side (Load), the photo sensitive element detects the incoming light from the input circuit’s LED and activates the corresponding semiconductor switch. A TRIAC or SCR pair for AC switching application and a MOSFET for DC switching application.
Once the switching is triggered, the semiconductor allows the current to pass through the load circuit, completing the connection and turning the load ON. Upon removal of the control signal from the input circuit, the LED stops emission of light, the photo sensing element also goes inactive, ceasing the semiconductor’s conduction turning the load OFF.
Additional circuitry like the zero cross detection can ensure the switching operation during the zero voltage of the AC wave form, which minimises the switching transient. Snubber circuits and thermal cut offs can prevent the damage under overloading conditions.
Solid state relay wiring
Input side: Connect the positive terminal of the DC control source (PLC / Microcontroller / Switch) to the positive input terminal of the SSR and negative of the source to the negative terminal of the SSR. It may be noted that the voltage range is from 3-33 Volts depending upon the relay model and care must be taken of the polarity during solid state relay wiring as polarity change may not trigger the input circuit’s LED.
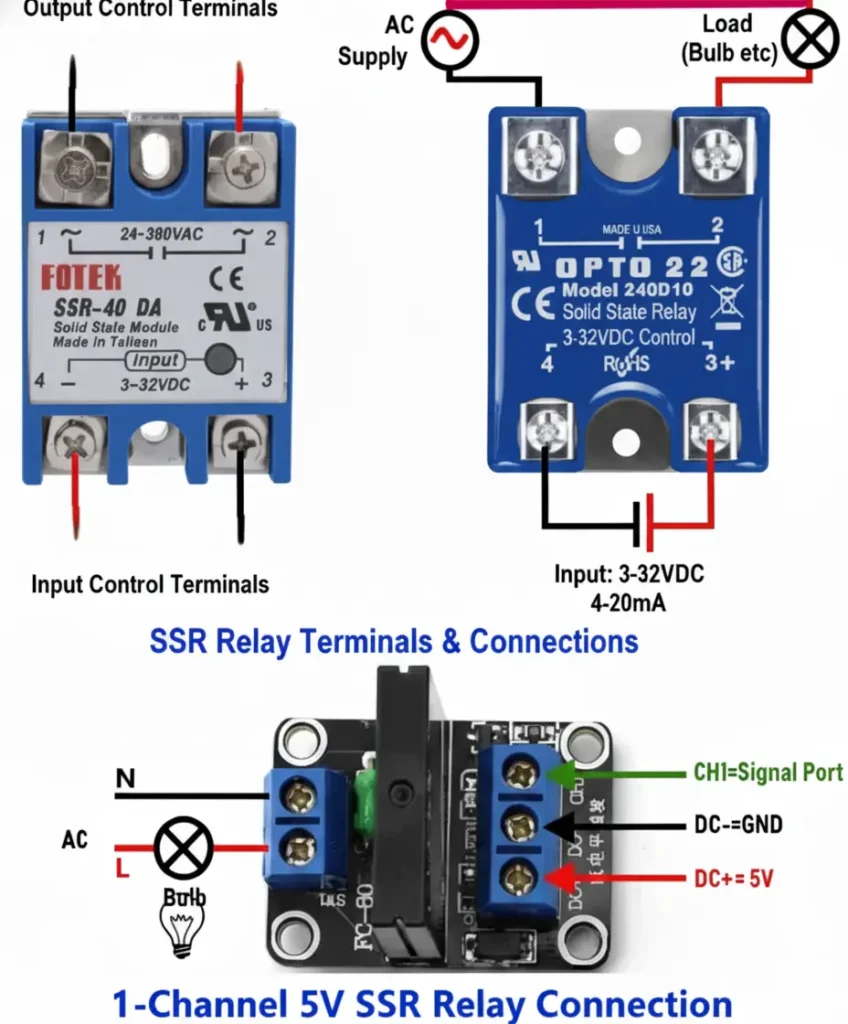
Output side: For DC loads connect the terminals marked as “+” and “_” to the positive and negative terminals of the DC load. However for AC load, connect one terminal to the Load and other terminal to the neutral across the AC supply.
Applications
Industrial automation: Solid state relay (SSR) ensures fast and reliable switching in automated control systems enhancing the precision of the process, operational safety and longevity of the equipment
HVAC Control: It is used for the control of HVAC system and heating elements as it provides smooth, noise free and efficient thermal controlled operation.
Lighting and motor control: SSR makes rapid and arc free switching which improves the performance and reduces maintenance, thereby extending the service life significantly.
Test equipment: SSR provides precise control and isolation in test setup and power circuit which ensures accurate measurement and equipment safety.
Advantages
- The solid state relay are maintenance free and reliable.
- It offers faster response time.
- It offers arc free operation with no contact bounce.
- It offers excellent service in harsh environment with high vibrations, where electromechanical relay is not suitable.
Limitations
- This relay is sensitive to overvoltage and heat.
- For high current application, it requires a heat sink.
- The initial cost is higher compared to mechanical relay.
- Leakage current is present in OFF state as the semiconductors are not perfect insulators.
This article is a part of the Protection System, where other articles related to the protection of electrical equipments are discussed in details.

