PILC cables (Paper Insulated Lead Covered) are cables that has been used in the power industry, traditionally. PILC cables had a wide application in medium voltage power transmission and distribution system. These cables has oil impregnated paper insulation which is enclosed in lead sheath, resulting in excellent moisture resistance and mechanical protection. This cabling tech was developed in early 20th century, was most reliable standard of cabling before the development of polymer insulated technology. PILC cables were used extensively in underground power networks ensuring safety and durability in the delivery of energy. Although use of PILC cable is phased out and replaced by newer XLPE and EPR cables, it remains a significant milestone in electrical engineering.
Table of Contents
Construction
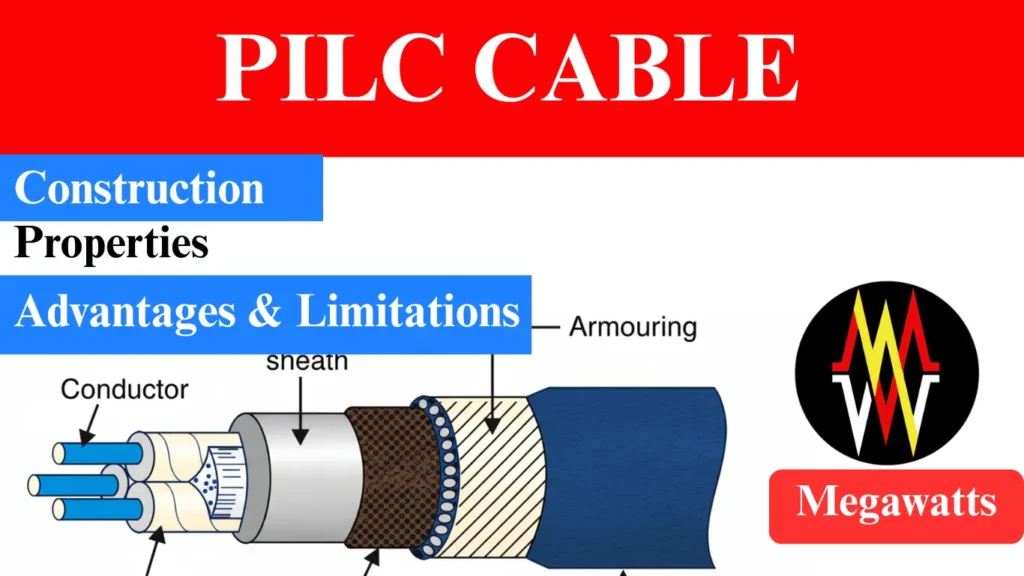
Core conductor: PILC cable uses copper or aluminium conductors with a cross section area of 10 to 1000 mm2. Copper offers a higher conductivity of around 58 MS/m, while aluminium provides slightly lower conductivity of around 36 MS/m. Stranding of conductors are done for achieving flexibility and compact shape. As per IEC 60228, these cables are also rated up to 33KV.
Paper insulation: The insulation of PILC cables comprises of 20 to 40 layers of kraft paper with a thickness of 0.08 to 0.12 mm. The insulation is wrapped around the conductor, impregnated with mineral oil or synthetic compound for achieving a dielectric strength of 6 to 10 KV/mm. The kraft paper ensures low dielectric loss and a high breakdown voltage.
Lead sheath: The lead sheath which is around 1.5 to 3 mm thick, encompasses the insulated core of the cable. It repeals moisture and provides mechanical protection and screening to the cable against all interference. The lead sheath has a tensile strength of 18 to 25 MPa, offering excellent corrosion resistance in buried condition.
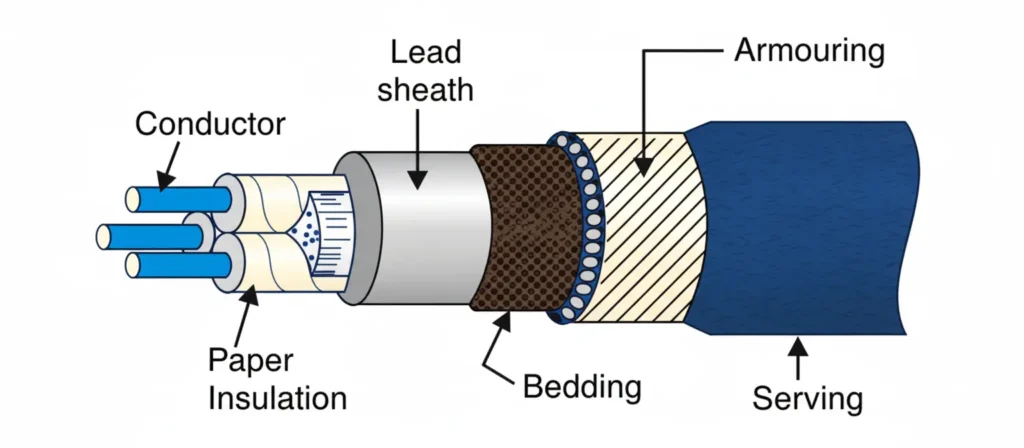
Bedding layer: On top of the lead sheath, a layer of bituminous material or PVC compound is laid, which is usually 1 to 2 mm thick. The bedding layer is applied for cushioning and protecting the lead sheath from the armouring. The bedding layer also prevents the galvanic corrosion as it is chemically inert.
Armouring: It is used for mechanical protection with use of steel wire or tape type armour. The wire diameter ranges from 2 to 4 mm, depending on the cable size. The armour resists the mechanical impacts and tension during the installation adding tensile strength of 800 N/mm2. Non magnetic armour is used for single core cables as because of single magnetic field, the magnetic armour heats up resulting in power loss.
Outer sheath: The protective outer layer or sheath of the PILC cable, also called as the serving of the cable. It is basically made up of jute yarn impregnated with bitumen compound or extruded PVC 1.5 to 3 mm thick. This layer protects the cable from moisture intrusion, surface abrasion and termites. The PVC sheath enhances the flexibility of the cable allowing it to withstand harsh environment.
Working principle
The PILC cable (Paper Insulated Lead Covered) transmits electrical power through its conductors, insulated with oil impregnated paper layers. The paper is the main dielectric medium where as the insulating oil (mineral oil) is the viscous compound that fills the air gap between the layers of paper. The filled air gap prevents ionization and increases the dielectric strength. The combination of paper and the viscous compound make the insulation uniform with a stable performance under the voltage stress. The lead sheath ensures moisture proof barrier, protecting the insulation from humidity and contamination while maintain the dielectric strength over time.
The metallic armour protects the cable against various mechanical forces and also provides a return path to the fault currents. PILC cables basically operates up to a voltage level of 33KV carrying high current depending up on the size of the cable. Despite the heavy construction of these cables, it offers a very good reliability in underground and substation application.
Types of PILC cables
Single core: Single core PILC cables contains one conductor with impregnated paper insulation covered by a lead sheath. These cables are used for high current applications, with minimized magnetic field effects, suitable for underground and substation application with medium voltage levels.
Multi core: It houses multiple conductors, each insulated with impregnated paper, collectively enclosed in a lead sheath. These cables are cost effective for low to medium voltage, commonly used in distribution networks up to 11 KV.
Belted type: Belted type PILC cables have individual insulated conductors wrapped with an additional paper belt layer which provides mechanical strength and insulation. These cables are prone to dielectric stress concentration at high voltage levels and hence are suited up to 11KV. These cables are simpler and economic compared to other types.
Screened type: These PILC cables includes metallic screens around each conductor and also above the cable to control the electric stress. These cables are used above 11 KV voltage level with a better dielectric performance and with minimal inter core discharge, with a uniform electric field distribution.
Pressure type: These cable uses pressurized gas or oil which prevents void formation in the insulation. The constant pressure keeps the paper fully impregnated which improves the dielectric strength allowing higher voltage applications up tp 275 KV for long distance high voltage transmission.
Properties
Operating voltage range: PILC cables operates from a voltage level of 1.1 KV to 33 KV with reliable insulation and mechanical strength. However, pressurised oil or gas cable can operate till 275 KV.
Insulation resistance and dielectric strength: Oil impregnated paper insulation offers high resistance ( > 106 MΩ·km) and a dielectric strength between 6 to 10 KV/mm, which ensures a low current leakage and stable performance under voltage stress.
Temperature limits: The oil impregnated paper insulated lead covered cables can withstand a continuous operation temperature of 70 °C and can withstand short circuit temperature of 160 °C for 5 seconds without any physical degradation.
Bending radius: The lead sheath and armouring of the PILC cable provides a stronger protection but flexibility of the cable, the typical bending radius reduces to 12 times the cable diameter.
Advantages and Limitations
| ADVANTAGES | LIMITATIONS |
| The cable offers excellent moisture resistance. | The cable is heavy with limited flexibility. |
| The cable offers high dielectric strength. | The cable’s lead is not corrosion free and is impacted by fatigue. |
| The cable has a long service life under normal conditions. | The cable termination and jointing are tough. |
| Suitable for underground installations. | It is replaced by XLPE and EPR cables. |
Comparison: PILC vs XPLE cable
| Parameter | PILC Cable | XLPE Cable |
| Insulation | Paper impregnated with oil | Cross Linked Polyethylene |
| Sheath | Lead | Extruded PVC or PE |
| Weight | Heavy | Comparatively Lighter |
| Installation | Difficult as the cable is less flexible. | Easier as the cable is comparatively flexible. |
| Maintenance | Maintenance is difficult as termination and jointing is complex. | Installation is simple. |
| Voltage Range | Up to 33 KV | UP to 400 KV |
This article is a part of the Cables and Conductors, where other articles related to the topic are discussed in details.

