Earth switch in electrical system is used for the personnel protection during the maintenance of the component of the system. It is among the most important component for the maintenance and is also known as grounding switch. Earth switch enables the residual or induced electrical charge to dissipate to the ground by providing a low impedance path.
Earth switch is primarily used to ground sections of a circuit or equipment which is already isolated from the live system. The ground connection ensures, no dangerous potential, which would have been fatal for maintenance personnel, exists in the section of circuit or equipment under maintenance.
Earth switch are most commonly installed as a component of air insulated switchgear, AIS substation and gas insulated switchgear, GIS substation across the transmission and distribution networks. These switch are also interlocked with the disconnector or isolator and circuit breaker, which prevents any unsafe switching operation.
Table of Contents
Function of Earth switch
The primary function of a this switch is to properly ground the de-energized component of a circuit. The switch basically functions a conductive link between the ground and the part of the circuit to be grounded. It ensures the following
Discharge of stored energy: Electrical Equipment such as transformer, long transmission line, busbar can sometime retain capacitive or induced voltage, even after disconnection. The grounding switch safely discharges this residual charge.
Personnel protection: During maintenance of the grounded equipment or section of circuit, maintenance personnel may accidently touch the conductive part of the circuit/equipment. Earthing ensures that the potential difference between grounded equipment/circuit is zero. Hence, preventing any electrocution.
Protection from induced voltage: High voltage parallel circuit or circuits crossing can induce voltage in the already discharge line. The grounding switch ensures that these induced voltages are safely grounded.
System integrity: The grounding switch ensures no accidental energization occurs during the maintenance works or testing of equipment, thus preventing accidental operation while maintaining system stability.
Grounding switch basically transforms the isolated circuits into grounded circuits.
Main components
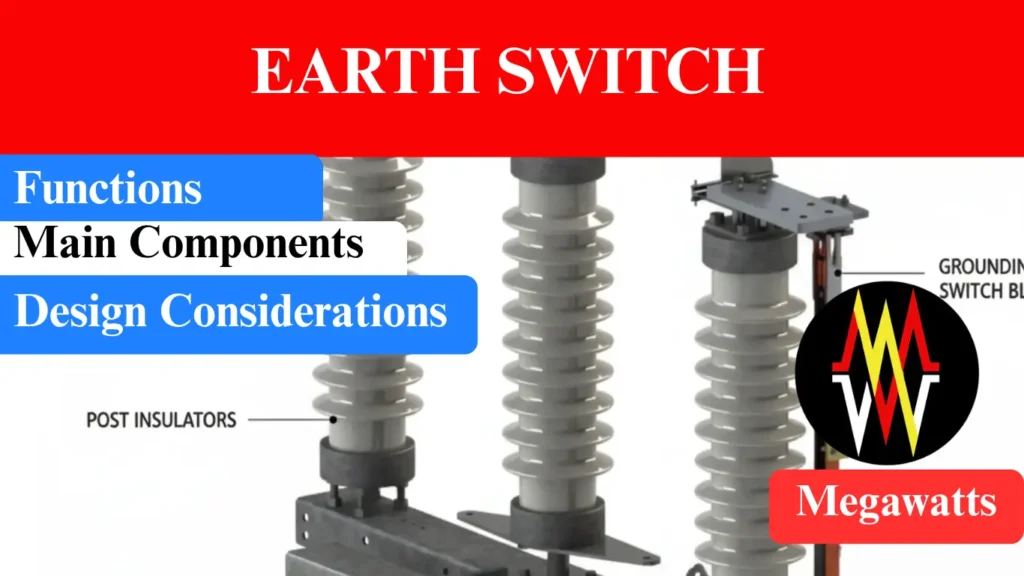
Fixed and moving contact: Earth switch basically have these contacts, the moving contact glides in the fixed contact (fixed in the isolator) to establish earthing connection. The other side of the earthing switch is connected to the grounding grid. The contacts are generally made from high quality copper or silver plated alloy, which ensures low resistance and long operational life.
Earthing blade: It is the part of the moving contact which physically connects the conductor to the ground. While designing it is to be ensured that the blade must withstand the short time current rating without any deformation.
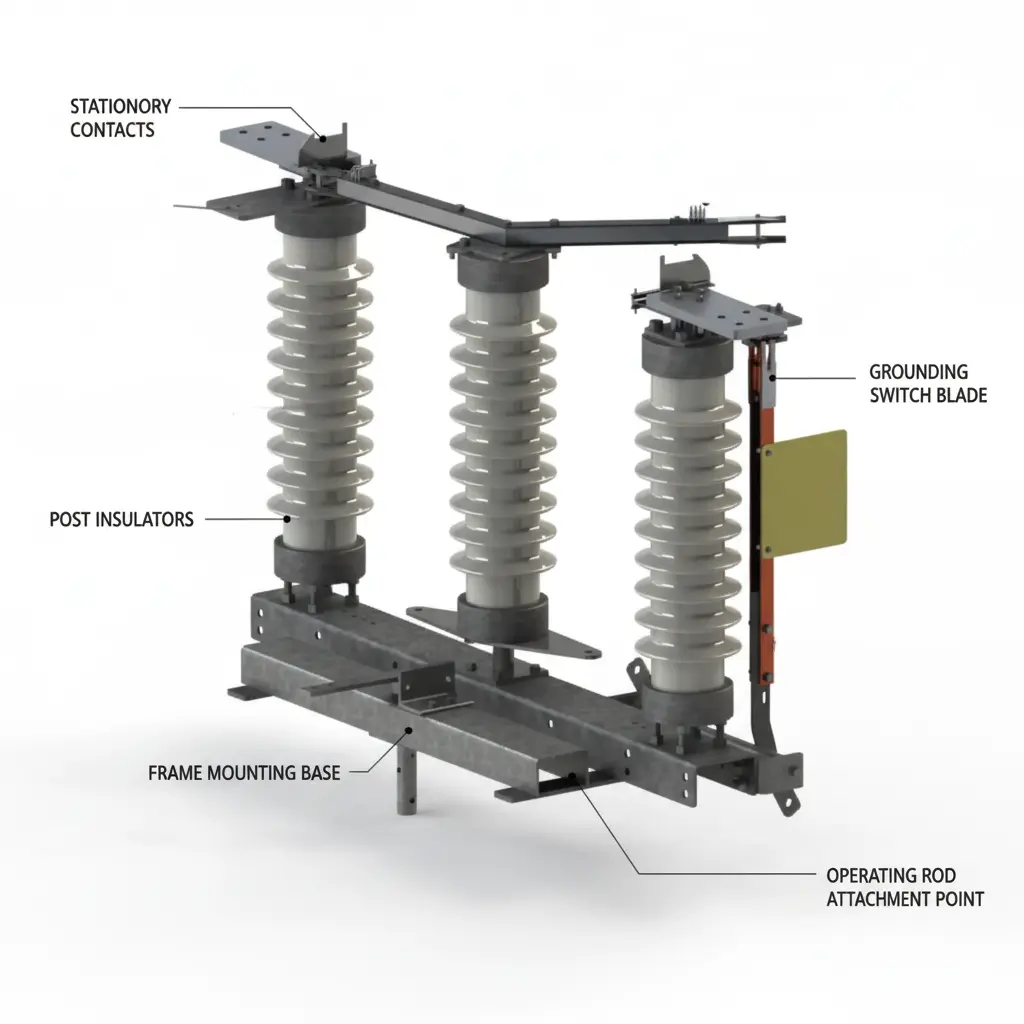
Operating mechanism: The switch can be operated manually, mechanically or electrically via motor. A motor connected to a gear and pinion rotates the operating rod of the earth switch, which gives motion to the earthing blade to swiftly move into the fixed contacts at the disconnector.
Interlock: Earth switch has both mechanical and electrical interlocks. The mechanical interlock prevents the grounding switch to close on to a charged circuit or the mechanical interlock will stop the isolator to get closed with grounding switch connected to the circuit, preventing accidental operation. While the electrical interlock is via the auxiliary relay which stops the closing operation of the associated circuit breaker, if the grounding switch is connected in the circuit. These interlocks are in compliance with IEC 62271-102 and IEEE C37.32 standards.
Mechanical indicator: It manual operating handle or the motorized panel gets a mechanical indicator which provides visual confirmation of the switch’s position specially in the GIS type. In AIS type switch the connection is directly visible.
Grounding terminal: The other end of the earth switch is bolted to the grounding terminal of the switchyard’s grounding grid which provides a low impedance path for the discharge of all sorts of unwanted charges in the circuit during maintenance.
Design considerations
Following are the important factors to be considered while designing a earth switch
Short time current rating: The earthing blade must withstand the short time current rating which is the highest fault level in the substation typically for 1 or 3 seconds as specified without any physical deformation.
Adequate insulation: The earth switch in open position must have enough insulation so that it can withstand the system voltage.
Low contact resistance: The contacts must be so designed that it offers minimal contact resistance for effective grounding of charges.
Environmental stress: It must operate reliably under all environmental stresses such as dust, humidity and temperature without requiring maximum maintenance. The GIS grounding switches are however inside protective enclosure and remain safe from these stresses.
Types of earth switch
These switches are categorized based on operation capabilities
Manual earth switch: These are operated by hand using a lever or a handle. These are simple mechanism and are cost-effective. These switches are suitable for low and medium voltage level distribution circuit applications where manual control is sufficient.
Motorized earth switch: These switches re used in high voltage systems above 33KV transmission level circuits with automated substations. These switches are can be operated remotely via motor drive whose control is often integrated with the substation SCADA. It is best suited for quick grounding operations and sites where manual access is limited and unsafe.
High speed earth switch: It is a type of grounding switch specially for GIS application which closes at a very high speed usually 8 to 15 milliseconds to instantly discharge the residual charge, which if slowly discharged can cause arcing and damage of insulation. It is operated by a spring charge or pneumatic mechanism.
Operating sequence
The operating sequence of these switches are discussed in the following to prevent dangerous situation.
- Firstly isolate the circuit to be grounded from the live bus by operation of circuit breaker and then operation of the disconnector.
- Secondly, verify that the circuit is disconnected with voltage detectors.
- Now, close the earth switch, connecting the circuit / equipment to the ground.
Maintenance
Routine maintenance of these switches includes
- Visual inspection for any sign of corrosion, loose connection and mechanical wear.
- Contact resistance testing to ensure low resistance during grounding
- Lubrication of the mechanical gears and linkage for smooth operation.
- Periodic operation to test the manual and motor function and also check alignment.
Application
Earth switch are used commonly of AIS and GIS substation for grounding of the transmission line for maintenance of the substation equipment / switchgear or transmission line. They are also used in distribution lines and substations for earthing.
This article is a part of the Switchgear, where other articles related to switchgear are discussed in details.

