In context of circuit breaker vs fuse, overcurrent protection provides safety cushion to electrical circuits from excess current flow in the circuit, caused by short circuit, or overload thus increasing system reliability and preventing equipment damage in the electrical installation.
Protective devices interrupts the fault instantly as it is detected, minimizing equipment damage, decreasing the risks of fire and preventing electric shock, thereby maintaining electrical safety while extending system lifespan in domestic and industrial sectors.
Considering circuit breaker vs fuse, both fuse and circuit breaker are essential protective components that detect overcurrent and isolates the faulty circuit from the power source, thus limiting fault propagation into the power system, ensuring safety of operation while maintaining uninterrupted power to other circuits.
Table of Contents
This article aims to provide in depth comparison between both (circuit breaker vs fuse), explaining the functions, benefits and ideal application for correct selectivity of device for effective electrical protection.
Comparison Table circuit breaker vs fuse
| Parameter | Circuit Breaker | Fuse |
| Basic Function | Automatically interrupts current flow during faults | Melts and breaks the circuit when current exceeds limit |
| Reusability | Can be reset after tripping | Must be replaced once blown |
| Response Time | Slower (mechanical operation) | Faster (milliseconds) |
| Type of Protection | Overload and short-circuit | Overcurrent only |
| Operation | Automatic or manual | Automatic only |
| Maintenance | Low (resettable) | High (replacement needed) |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application Area | Residential, industrial, and commercial panels | Small appliances, electronics, and basic circuits |
| Reliability | High and consistent | Depends on fuse quality and replacement accuracy |
| Safety | Safe reset and manual isolation possible | Replacement can be hazardous under load |
Detailed explanation of comparison parameters
Basic function: In relation to circuit breaker vs fuse, a circuit breaker is a device which automatically disconnects power when overload or fault occurs in the connected circuit and can be manually or automatically reset to restore the services. An electrical fuse on the other hand, uses a thin metal conductor which melts when current exceeds the limit in a circuit, causing a permanent disconnection of the circuit from power supply until replacement.
Safety: Concerning circuit breaker vs fuse, circuit breakers enrich the electrical safety as it allows the faults to be cleared and power to be restored through simple reset mechanism without direct contact to the live parts of the circuit. In contrast, replacing a fuse element which are under load can expose user to electric shock or risks of arc flashing making the circuit breaker a safer choice in the modern power system.
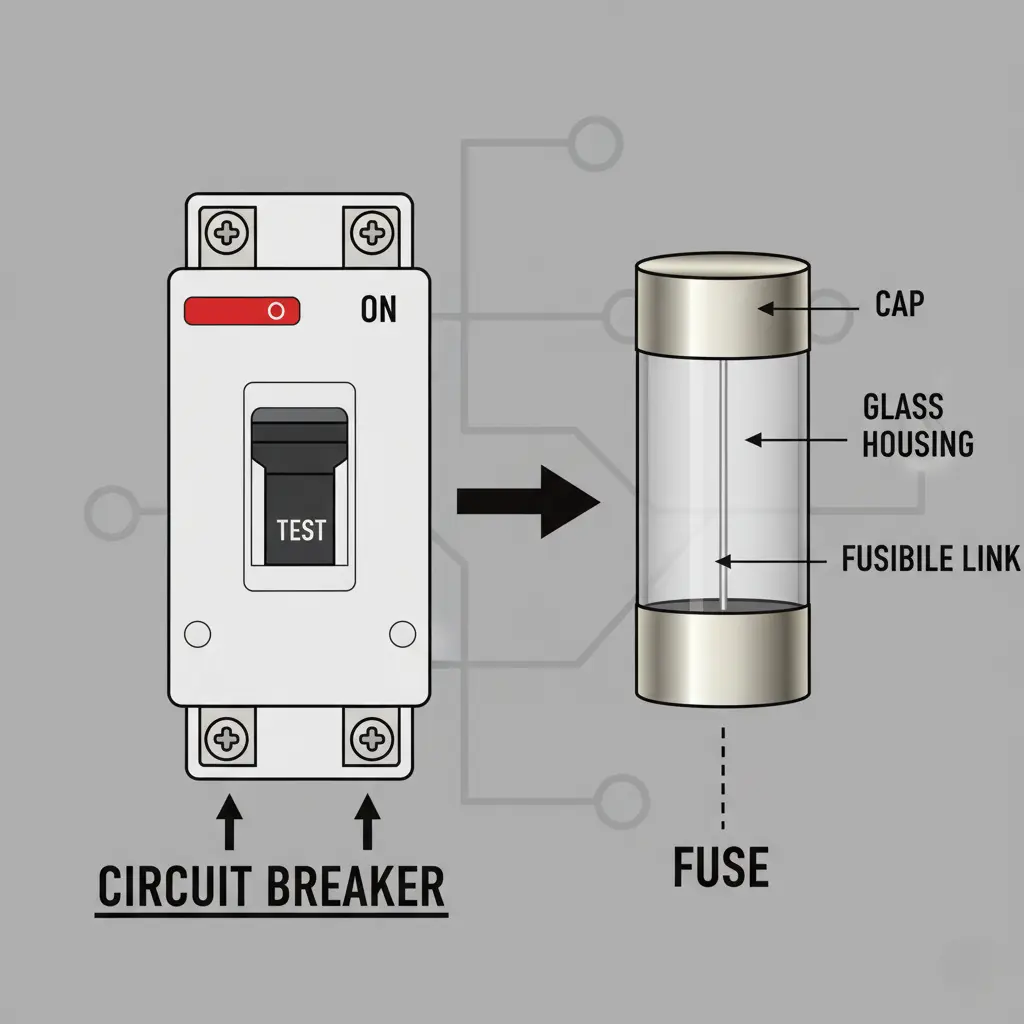
Reusability: Considering circuit breaker vs fuse, circuit breakers are advantageous because it offers reusability as its inherent function. Once the fault in the circuit is identified, checked and cleared, it can be easily reset to restore the power without any replacement of parts. Fuses, however, are single use devices that melts away once the fault is encountered in the circuit. After finding and fixing the fault in the circuit, the fuse needs the element replacement to resume normal operation and circuit protection.
Response time: Concerning circuit breaker vs fuse, the response time of fuse is almost instant to overcurrent, typically within milliseconds, because the fuse element melts immediately when current exceeds the elements rated limit. Circuit breaker on the other hand is slightly slower due to mechanical involvement of tripping mechanism, but it still reacts quickly to provide dependable protection to the connected circuit against overload and short circuit in most electrical systems.
Type of protection: Within the framework of circuit breaker vs fuse, circuit breakers provide comprehensive protection, detecting both overload and short circuit conditions in an electrical circuit, there by automatically disconnecting the power to prevent equipment damage or fire hazard. While fuse essentially provides protection against overcurrent by melting of the fuse element when current exceeds the safe limits, making fuse ideal for simple, smaller and low power circuits where advanced circuit protection is not required.
Operations: Circuit breakers can be operated both in auto mode, while encountering fault and manually for system maintenance and control, thus offering flexibility of operation and control. While fuse operates automatically when current flow in the circuit exceeds the rated limits of the fuse element and it cannot be manually reset. Once a fuse is blown, it requires fuse element replacement for circuit restoration.
Maintenance: From the perspective of circuit breaker vs fuse, circuit breaker requires very less maintenance, only involving periodic inspection, testing and tightening of terminal connections to ensure proper and safe operation. Fuses, however, requires higher maintenance compared to circuit breakers, since the fuse element requires replacement after each encounter with a fault, thus increasing downtime, adding to maintenance costs and additional effort while maintaining this electrical protection.
Cost: Circuit breakers are costly because of their advanced design, mechanical components and reusability features, making it a long-term investment for large system. However, fuses, in contrast are less costly, simple device, providing a economical choice of circuit protection for small scale or temporary applications which prioritizes the low initial cost over reusability.
Applications: As it pertains to circuit breaker vs fuse, circuit breakers are commonly used in residential distribution panels, industrial plants and electrical substations as well for providing a system level protection and easy restoration of electrical circuits after clearing the faults. On the other hand fuses, are better suited for protecting small electronic devices, control circuits and simple panels where low power equipment like chargers and adapters are in use which needs quick and simple fault isolation.
Reliability: Circuit breakers perform consistently and reliably through precise tripping mechanisms and accurate coordination with other protective devices, making it suitable for complex protection circuits of power systems. Fuses relies heavily on correct rating selection and proper replacement after each fault occurrence. The overall reliability of the fuse is always at stake if the maintenance and rating selection is poor.
Conclusion
Both fuse and circuit breaker play a pivotal role in protecting the electrical circuits and connected appliances from overcurrent conditions like overload and short circuit. Circuit breakers are best suited for modern electrical installations requiring frequent operations with enhanced safety and easy resetting after the fault occurrence. Fuse in contrast, provides a low-cost solution with very fast response time making them ideal for small, simple and temporary circuits. The choice between a fuse and a circuit breaker depends ultimately on the complexity of the electrical circuit which is influenced by safety requirement and maintenance practice preffered.
This article is a part of the Switchgear, where other articles related to switchgear are discussed in details.

