Various circuit breaker types play a pivotal role in various types of electrical circuit based on complexity and other selection criteria, intended for protection of the circuit from overloads and short circuit faults. These devices automatically interrupts the electrical circuit, preventing the connected equipment damage. The circuit breaker can be reset after clearing the fault in the circuit and power can get restored with extension of limited operational resource.
The circuit breaker finds its application widely in domestic, commercial and industrial setup where reliability and electrical safety are critical. This article explores the major circuit breaker types as per the market standard with the construction and working based on specific application. Understanding the circuit breaker types helps in selection of the correct circuit breaker based on various selection criteria like voltage level, current rating, installation environment and other operational needs.
Table of Contents
Classification of circuit breaker types
Based on voltage level: Based on the level of voltage, the circuit breakers are classified as low-voltage, medium voltage and high-voltage circuit breakers depending on their operating range. The low voltage circuit breakers are used for protection of domestic and commercial circuits up to 1KV, while the medium voltage circuit breakers are installed in 1-33KV range setups and the high voltage circuit breaker extends from 33KV and beyond used in the power transmissions and substation networks.
Based on arc quenching medium: Arc is formed during the contact separation of the circuit breaker. Depending up on the medium used to quench this arc formed during circuit interruption, circuit breakers can be categorised as air circuit breaker (ACB), Oil circuit breaker (ACB), SF6 circuit breaker, and Vacuum circuit breaker (VCB). Each of them offers distinct features in terms of arc control, and insulation strength.
Based on installation: Circuit breaker types can also be categorized based on the installation area such as indoor installation circuit breaker (Miniature circuit breakers & Molded case circuit breakers) for domestic and commercial applications and outdoor installation circuit breakers such as air circuit breaker, SF6 circuit breaker for higher power application based on different current rating.
Low voltage circuit breakers
The low voltage circuit breakers are commonly used for domestic/commercial application in houses, offices and also in small industries. Various types of low voltage circuit breakers are discussed below:
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB): An MCB is a low voltage circuit breaker that provides circuit protection from overload and short circuits. It is capable of automatic tripping during faults and can be reset by flipping of the switch for circuit restoration without any part replacement unlike fuse. Commonly used for domestic application, it ensures continuous protection for small electrical loads such as lighting circuits, etc.
Molded case circuit breaker (MCCB): These are designed for higher current ratings compared to MCBs, typically ranges up to 2500 A. It offers circuit protection in commercial and industrial setup. The trip setting in these circuit breaker types can be adjusted, which gives the flexibility to use it for different load conditions. MCCBs have high durability and reliability, ideal for heavy duty applications.
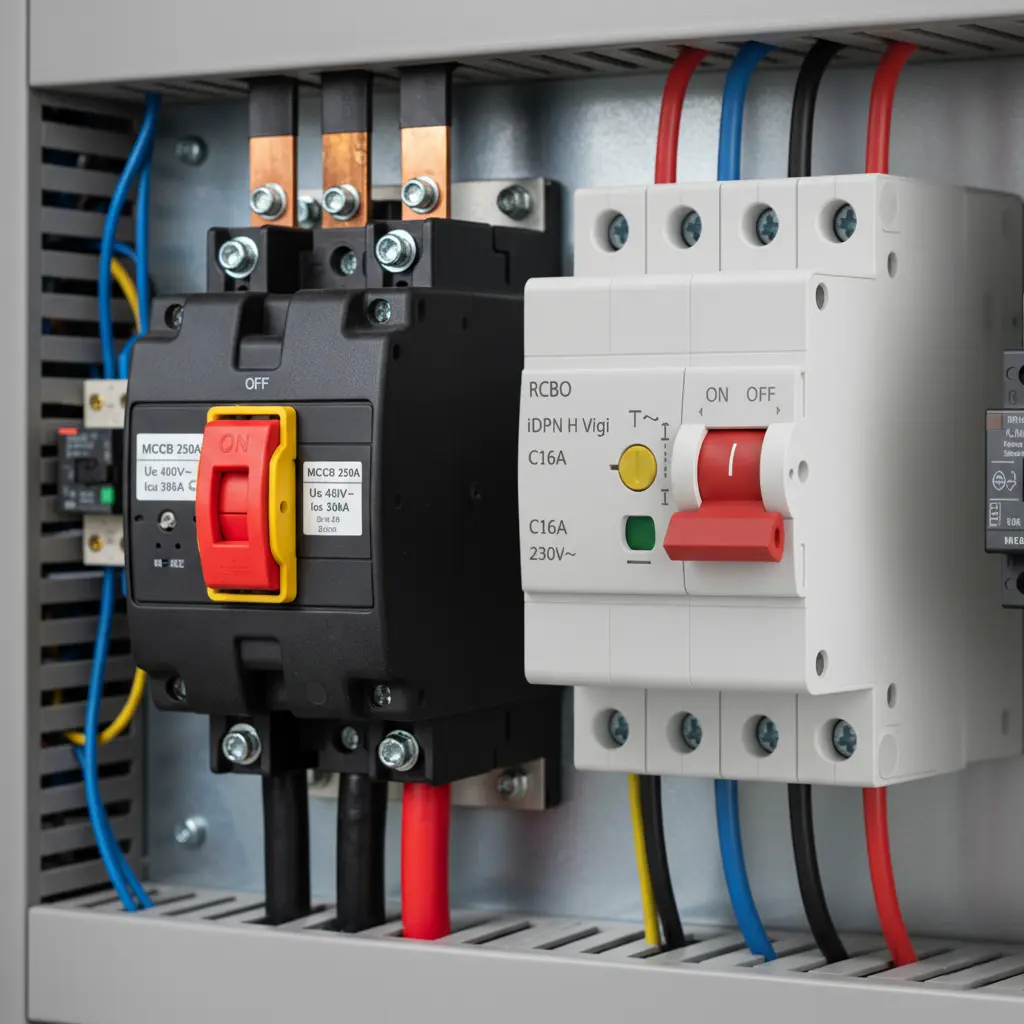
Residual current circuit breaker (RCCB/RCD): The RCCB, also known as RCD, provides detection of leakage current caused by failure of insulation or contact with other phase conductor. It interrupts the circuit instantly preventing hazardous electric shocks and risks of fire. RCCBs are essential for installation in damp and wet areas like bathroom and kitchen.
Residual current circuit breaker with overcurrent (RCBO): The RCBO is a comprehensive device used for circuit protection against overload, short circuit and earth leakage fault. The RCBO combines the function of both MCB and RCCB, thus, ensuring both equipment safety and personnel protection in a single unit. It is an ideal choice for modern residential and commercial electrical distribution system.
Medium voltage circuit breakers
Vacuum circuit breaker (VCB): A VCB uses high vacuum for quenching the arc produced during contact separation. These are highly reliable, compact and less prone to maintenance. These circuit breaker types are widely in use in medium voltage substation and other industrial setups because of high reliability and good dielectric strength.
Air circuit breaker (ACB): An ACB uses compressed air to cool down and extinguish the arc produced during circuit interruption. It is also used as a medium voltage switchgear for protection and control of circuit. Modern ACBs are equipped with electronic trip units for providing suitable protection setting, making them a good choice for power distribution system.
High voltage circuit breaker
Oil circuit breaker (OCB): The OCB uses insulating oil as the arc quenching medium and also as the dielectric medium. When the contacts of the breaker opens, the arc decomposes the oil producing various gases and thereby extinguishing in the oil. Though the OCB is an effective high voltage circuit breaker but it requires high maintenance as the oil gets contaminated soon making them less common in modern power system.
SF6 circuit breaker: The SF6 circuit breaker uses sulfur hexafluoride gas to quench the arc generated during circuit interruption efficiently and the gas provides superior insulation at high voltage ranges. The main advantages of using these circuit breaker types are the compact design it provides, lower maintenance compared to other circuit breaker types and excellent dielectric strength. These breakers are widely used in outdoor substation and transmission system for its high reliability and longer operational life.
Air Blast circuit breaker (ABCB): The ABCB also uses compressed air to blow the arc formed between the contacts when they separate. This circuit breaker is known for fast operation and quick reclosing making it ideal for high voltage transmission system. This circuit breaker has noisy operation and requires very high maintenance compared to other circuit breaker types.
Special purpose circuit breakers
Hydraulic- Magnetic Breaker: These circuit breaker type operates by using a magnetic coil and hydraulic delay mechanism thereby offering accurate temperature-independent protection. Common application of these circuit breaker type is found in marine, telecom and data centers, where stable consistent performance is required under varying ambient condition. These circuit breaker types provide reliable protection from overload and short circuit in a very rugged form factor.
Thermal Magnetic Breakers: This circuit breaker type combines two protection logics. One is the thermal method for overload protection and the other is the magnetic method for short circuit protection. The bimetallic strip reacts to prolonged overload conditions while the magnetic coil responds to sudden high current surge. These circuit breaker types are widely used in domestic and commercial system for being reliable and economic.
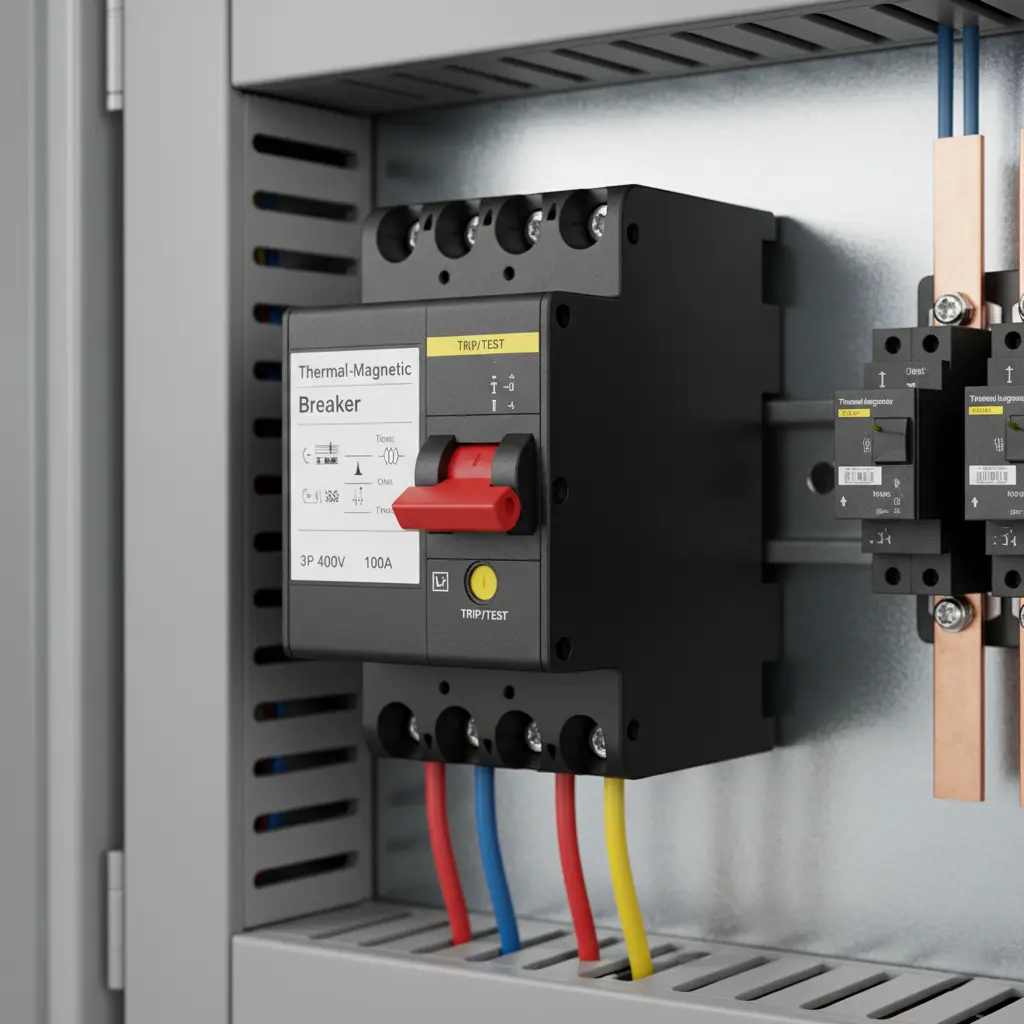
DC circuit breakers: These circuit breaker types are specially designed to disconnect a direct current circuit, which has no natural zero crossing. Thus, the extinction of arc is more difficult and challenging although achieved with the magnetic blowout or arc chutes. These circuit breaker type offers safe circuit interruption and protection to solar power systems, battery banks and other DC loads.
Recommended circuit breaker types by application
| Application Area | Relevant NEC Article | Recommended Breaker Type | Requirement / Description |
| Dwelling Units (Homes) | Art. 210, 240 | MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) | Protects branch circuits against overloads and short circuits; required for lighting and receptacle circuits. |
| Bathrooms, Kitchens, Garages, Outdoors | Art. 210.8(A) | GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) Breaker or Outlet | Mandatory for receptacles in wet or damp locations to protect against electric shock. |
| Bedrooms and Living Areas | Art. 210.12(A) | AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) Breaker | Required for protection against arc faults that could cause electrical fires. |
| Main Service Panel | Art. 230, 408 | MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) | Used as main disconnect or feeder protection device; must match service ampacity rating. |
| Commercial Buildings | Art. 215, 240 | MCCB or ACB (Air Circuit Breaker) | Provides feeder circuit protection and coordination with downstream devices. |
| Industrial Facilities | Art. 240.87, 240.92 | MCCB / VCB / ACB | NEC mandates arc energy reduction methods for breakers rated ≥1200 A; vacuum or air breakers often used. |
| Pools, Fountains, and Wet Areas | Art. 680 | GFCI Breaker | Required for all electrical equipment and lighting near water sources to prevent shock hazards. |
| HVAC and Motors | Art. 430 | MCCB or Thermal-Magnetic Breaker | Breaker rating must be based on motor full-load current; NEC allows up to 250% of FLA for protection. |
| Renewable Energy Systems (Solar PV) | Art. 690 | DC-Rated Breaker (MCCB or Specialized PV Breaker) | Must interrupt DC current safely; used for photovoltaic arrays, charge controllers, and inverters. |
| Generators and Emergency Systems | Art. 700–702 | MCCB / ACB with Interlock | Breakers must prevent backfeed and allow manual or automatic transfer switching. |
This article is a part of the Switchgear, where other articles related to switchgear are discussed in details.

