
Residual current device is a device used in electrical circuits which protects humans from electrical shock and electrical fire as well which may be caused because of current leakage. The device is placed between the phase and neutral wire for monitoring and detection of any unbalance in current there by, causing the isolation of the circuit upon detection in milli seconds. This quick action of the device help save fatal injuries to humans. It enhances reliability and electrical safety.
Table of Contents
Construction and Working Principle
The residual current device works on the principle of current differential between the current flowing through phase conductor and returning through the neutral wire. Under normal operating conditions, the current entering the circuit is equal to the current leaving the circuit via neutral wire. The magnetic field thus produced because of the current entering and leaving are equal and opposite, each nullifying the other.
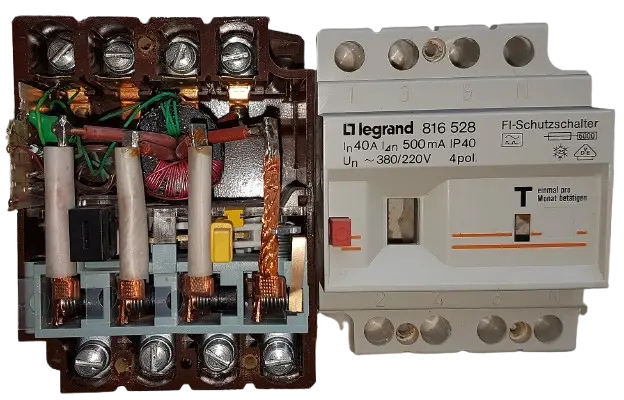
The RCD houses a core balance current transformer CBCT or a toroidal coil. The live and the neutral conductor passes through the magnetic core and generate a net magnetic flux, which is zero, when the currents are balanced. Hence, no voltage gets induced in the secondary winding.
But whenever, there is a leakage current, like accidental touching of the phase wire, insulation failure, leading current through unintended path causes an imbalance between live and neutral currents. It is this imbalance current that generates the magnetic flux in the core balance current transformer CBCT, which induces a voltage in the secondary winding of the transformer, activating the trip relay mechanism.
The trip relay mechanism upon activating via the secondary induced voltage, causes the mechanical trip mechanism to activate which isolates the circuit instantly and disconnects the load from the supply. The entire tripping mechanism takes approximately 30 ms from initiation to isolation. The RCDs are very sensitive devices and usually rated in milli amperes (mA). The standard rating for personnel protection is 30 mA and for fire and equipment protection it is 100-300 mA.
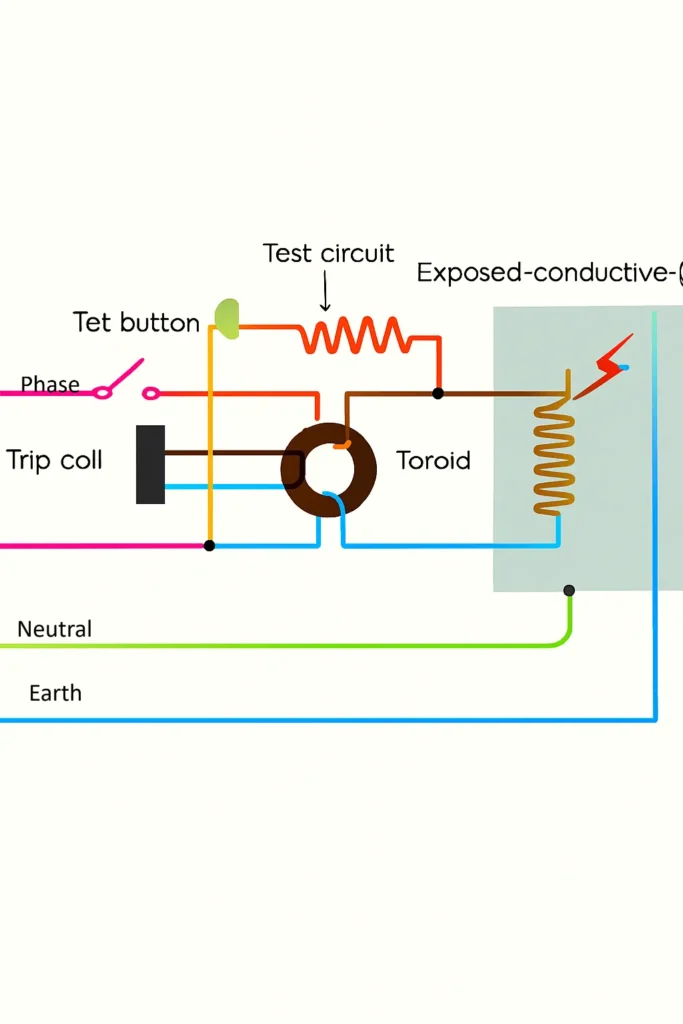
The other component of the RCD are a test button, which simulates a fault and checks the device’s functionalities, a reset button to reset the tripping mechanism before charging or restoring power. The assembly is enclosed in an insulated housing which ensures safety and enhances durability of the device.
Types of Residual current Devices
Fixed RCD: This devices are permanently mounted on the main distribution board or consumer unit. This device is capable of providing protection of both personnel and equipment to multiple circuit or entire installation. It continuously monitors all connected wiring for detecting any leakage current, therefore ensuring overall electrical safety and prevent electrical shocks and fire accidents.
Socket Outlet RCD: Socket outlet residual current devices are basically integrated into the power sockets. They are used to provide protection to the equipment or electrical appliance connected to the specific power outlet with the RCD integrated. The most commonly used socket outlet RCD are in the areas which are prone to high shock risks such as washroom or any wet location. Thse RCDs offers localized protection without interfering with other electrical circuits.
Portable RCD: These residual current devices are plug in devices connected between a socket and an equipment. These devices are ideally used for temporary protection of the connected equipment or for the portable equipment like power tools or outdoor devices. These RCDs provides personnel protection by disconnecting the power supply immediately when a leakage current is detected thus ensuring safety of the mobile application.
AC, A, S, F, and B type RCD: These residual current devices are classified by the detection of current they can handle. Type A RCD detects AC and pulsating DC while type F RCDs are capable of handling mixed frequencies usually from inverters. The Type B RCDs are capable of detecting AC, DC and smooth leakage of Direct Current from variable speed drives and chargers of electric vehicles. The type S RCDs have a time delay feature incorporated in it which makes it ideal for circuits with inrush currents like electric motors and transformers. The type S RCD is not suitable for personnel protection because of its time delay feature.
Ratings and Sensitivity
The residual current devices are designed with specific rating and sensitivity to protect against electrical shock and fire accidents indenting from leakage currents. The RCDs are usually rated in milliampere. The rated current of the RCD means the leakage current at which the trip mechanism will initiate to disconnect the circuit. Most common rating of RCD for personnel protection is 30mA, however lesser than 30 mA are also used for very specific protection. For industrial use, RCDs are available upto 500 mA.
The voltage rating of the Residual current devices are 120 Volts single phase and 208 Volts three phase for US while for UK its 230 Volts single phase and 415 Volts three phase.
The sensitivity of RCD determines how quickly it disengages the circuit interrupting the power supply. A high sensitive RCD is usually of the range of 30 milli seconds used in the wet areas while a medium sensitive range would be between 100-300 milli seconds ideal for equipment and appliance protection.
Applications
The residual current devices are widely used in domestic application like bathroom circuits, outdoor power sockets, building distribution boards for protection of human life from electrical accidents and fatal shocks. Also RCDs finds its application in industrial zones to safeguard the electrical equipment that are prone to current leakage. RCDs also finds its application in the temporary power setups like construction sites for safety or workers and prevent electrical hazard.
| Type AC | Type A | Type F | Type B |
| Electric shower | Inverter | Air conditioning | Inverters |
| Electric Oven | Class 1 and class 2 IT equipments | Class 1 power tools | Uninterruptible power supply |
| Immersion Heater | Induction hobs | Washing machine and Dishwashers | Photovoltaic system |
| Tungsten Light | Electric Vehicle charging | Dryers with synchronous motors | Lifts and escalators, welding machine etc |
Advantages
Effective protection against electric shock: As RCDs detects small leakage currents flowing through unintended paths, the power supply gets disconnected fast because of rapid tripping action of the device providing fast and effective protection against fatal electric shock.
Less Risk of fire due to earth fault: As an earth fault sends the current through un intended path that is the earth, the RCD detects it and trips the power supply, thereby preventing the over heating of the electrical circuit from high earth fault current and thus ensuring fire protection.
Easy Test and Reset: Test and Reset buttons are easily accessible in the body of the residual current devices, allowing users to test the proper functioning and quickly restoring power supply.
Limitations
No protection against overload: The residual current device donot provide protection against overload or short circuit.
Nuisance tripping: Residual current devices may sometimes cause nuisance tripping because of small harmless leakage current because of moisture presence. The humidity affects the insulation resistance and can cause frequent power cut in damp outdoor environments.
Proper earthing required: Without proper earthing the residual current devices will not function properly as accurate current leakage detection is not possible without proper earthing.
This article is a part of the Switchgear, where other articles related to switchgear are discussed in details.
