Data center substation is among the special types of substations, which are specially designed for highly reliable, high power quality, and uninterrupted power supply to critical IT processes in the data center. These substations stress majorly on the importance of redundancy of power supply with reliability to various components in the IT industry. It steps down the high transmission voltage of power to the distribution voltage as required by various servers, cooling systems, and accessories of data centers.
Table of Contents
Need for data center substation
Very high reliability: Since the data centers host many critical applications, like cloud services, banking, telecom, defence, etc, any outage of power can cause huge financial implications and data loss. To ensure this, data center substations normally employ an N+1 or N+2, or even 2N system of redundancy so that no power failure can occur. Multiple sources of incoming feeders and automation in switching schemes ensure a continuous supply of power from the data center substations.
Uninterrupted power supply: The data center’s server and storage devices need 24*7*365 power availability, and because of it the data center substation requires a backup power system ( DG gen set, UPS, and a large number of battery banks). The data center substation has to make sure that the load transfer from the grid to the backup source is very quick and automatic, so that there is no power outage. Substation SCADA and digital infrastructure of the substation ensure quick fault detection and switching.

Power Quality: The Infrastructure of data centers and IT is very sensitive to voltage fluctuation, harmonics, frequency fluctuation, and surges. Therefore, the data center substations need a power Static VAR compensator, STATCOM devices to counter voltage fluctuation, harmonic filters, and precise frequency regulation to prevent any anomalies in data processes and the system.
Scalability: Data centers’ load growth is a very rapid process, as the demand for AI, IoT, and cloud-based services is growing at a very fast pace. In order to support this load growth, the data center substations must be designed in a GIS modular compartment, and the transformer must not be saturated to support the growth of the load with minimum redesign of the data center substation.
In short, the data center substation must support high reliability, with zero disconnections and high power quality for the digital economy.
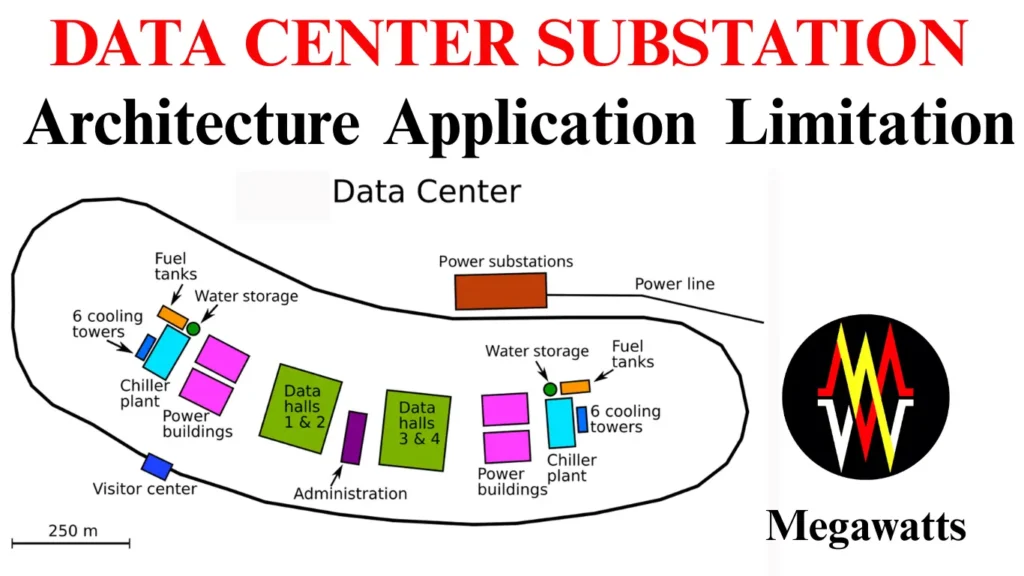
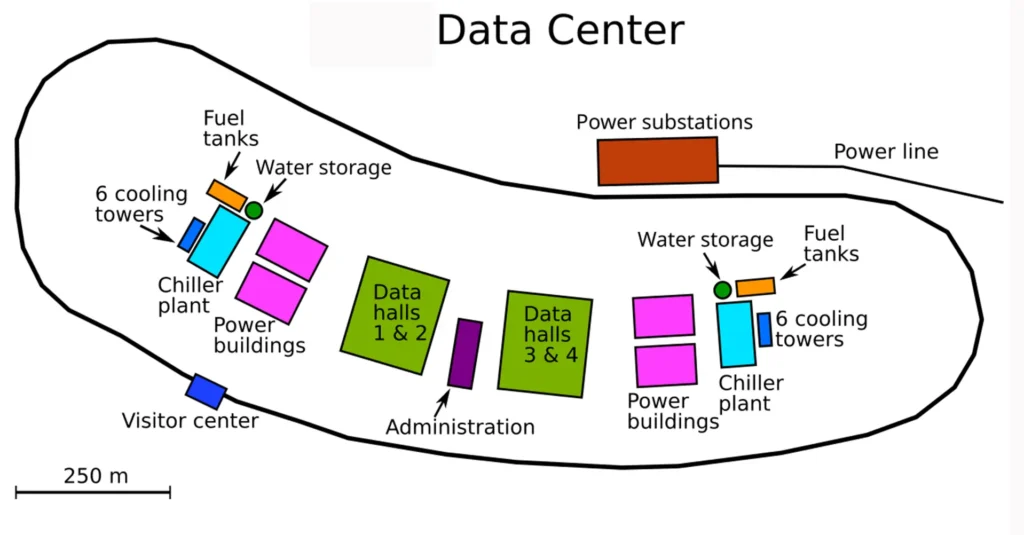
Architecture of the Data Center Substation
Redundant Grid feeds: Redundant grid feed is most important in the data center substations as it makes sure that the substation will receive power even when one transmission line fails. The transmission line feeders must be from two different substations so that the reliability is increased. By the diversification of the incoming feed, maintenance of one transmission line is possible without causing any power interruption.
Two Transformer Paths: The data center substations employ two paths for the transformer, each capable of carrying the full load independently. This ensures redundancy and an uninterrupted power supply. If one path or feeder fails, the other takes up the supply in no time. This method supports N+1 and 2N redundancy. N+1, which basically means if N no of feeders are present, the +1 feeder must be kept spare to support any feeder (from N) in case of emergency. 2N redundancy means complete duplication of the feeder; 4 feeders will be needed to supply 2 feeders with 2N redundancy.
Auxiliary power: In case of total grid failure, the data center and its processes must survive without any major loss. The UPS and battery bank system helps to manage the power outage for a little time before the DG generator set starts. The diesel generator provides emergency power during the outage, which enables the continuous operation. This layered power supply is critical for data centers, as a millisecond of power failure can cause huge losses of data.
Busbar Scheme: The data center substation uses a ring bus or one-and-a-half breaker scheme because this configuration ensures power supply to the load when one breaker or section fails. This design also allows maintenance without any interruption of the power supply, enabling zero downtime. Compared to the single bus scheme, the ring bus arrangement provides higher fault tolerance.
Substation SCADA: It enables smart monitoring and remote control of all operations of the substation. Use of the IEC 61850 communication protocol between the IEDs and the substation SCADA system allows the substation automation, protection, and control. The availability of the historical data in the HMI of the SCADA helps the operator to plan for predictive maintenance of substation components. The health of the equipment can also be remotely monitored, and prompt actions can be taken by the operator as the SCADA provides real-time data for making informed decisions. This ensures reliable operation of the substation and makes sure to reduce the downtime with increased safety and efficiency.
Application of data center substation
Hyperscale data center: These are data centers of tech giants like Google, Meta, and Amazon, which require a huge amount of reliable and uninterrupted power for various processes like cloud computing and AI. These substations are designed with ultra-high reliability and 2N redundancy with enhanced grid connectivity.
Enterprise data center: These are the data centers that are used by the banking sector, telecom providers, and government agencies for their data services. These require a reliable substation to maintain sensitive operation. Uninterrupted power benefits the financial transactions and various public services to run smoothly.
Co-location data center: These data centers host IT services for multiple clients; hence, a reliable power supply is essential for the uptime of the services.
Edge data center: These data centers are located closer to the users and support latency-sensitive technologies like 5G, IoT, etc. The substation for its power needs is designed to be compact, modular, reliable, and stable, with a stable power supply in a smaller area. As these data center supports autonomous driving, critical health care, and smart cities, any downtime in power supply can result in critical outcomes.
Limitations of the data center substation
High Cost: Construction of these substations requires a high financial investment, and they require high operational expenditure for reliable performance.
High land requirement: To support redundancy design, these substation requires a higher land area compared to conventional designs.
Complex design: The redundancy needs and dual transformer path, integration of backup power involves a complex design of the protection system to isolate faults.
Skilled operators: As these substations are specially designed, it require experienced and skilled operators, proficient in SCADA, relay, transformer, and emergency protocols to support the operation.
This article is a part of the page Substation Guide.
