Vacuum circuit breakers uses high vacuum inside the interrupter unit as a dielectric media for suspension of the arc that is generated on contact separation. Vacuum has a very high dielectric strength in the range 106 -108 Volts/meter with excellent arc quenching characteristics. At high vacuum inside the interrupter unit, little to no molecules are present for the ionisation, however the metal vapours of the contacts only supports the arc formation.
Table of Contents
Construction:
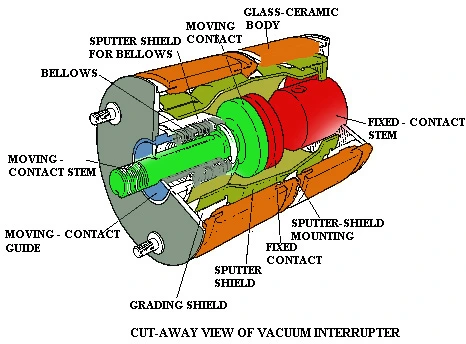
The Vacuum circuit breaker constitutes of three vacuum switches and a operating mechanism. The fixed and moving contacts made up of alloy, are housed inside the glass or ceramic made envelope. The top flange holds the fixed contact and the moving contact is supported by the bottom flange with the help of stainless steel bellows. These bellows help the movement of the contact and also provides the sealing to the vacuum switch.
The vacuum inside the switch is approximately about 10-7 mm of Hg. A sputter shield is used to restrict the movement of metal vapours and their condensation in the envelope, which otherwise will result in degrading of the insulation and can form a conductive path in the envelope. The sputter shield also collects the metal vapours which ensures controlled deposition of these products along with proper cooling.
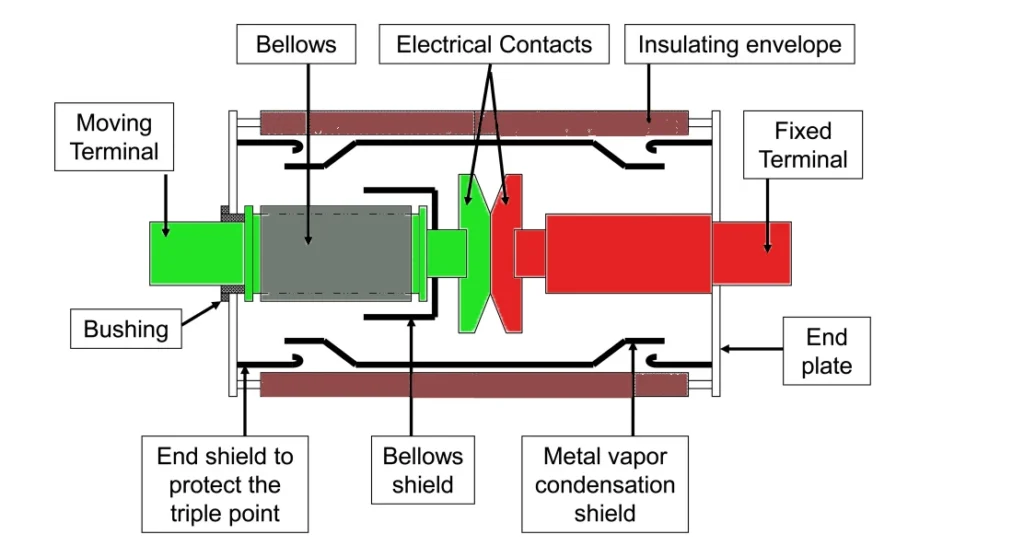
In order to remove the impurities from the interrupter unit and keep the vacuum performance high, gettering is a process which involves using a chemically reactive metal inside the interrupter, which will trap the residual gas atoms by chemically bonding and absorbing them. A special resin is used to insulate all live parts inside the switch. Vacuum circuit breaker can last more than 20 years, if properly maintained and processed.
Closing of contact is a natural tendency that can be obsered in vacuum circuit breakers, this is because of the differential pressure acting at the bellow, which continously forces the contacts to close. To counter this differential pressure, two springs are attached so that the spring force is in the opposite direction to the atmospheric pressure. As the closing coil is energized and the armature is closed, it compresses the reaction spring, which stores the mechanical energy, so that the contacts are closed and held with sufficient pressure. The compression of the springs are held by a mechanical latch, which gets detached by the action of the trip coil, opening the contacts.
Arc-interruption in Vacuum
The arc extinction in vacuum is completely different than the arc extinction in other media or dielectrics. In other cases the arc exists through a ionization of gaseous media between the contacts. However, in case of vacuum, it is the metal vapours at the contacts, through which the arc is formed. In other words, in vacuum the arc is a metallic vapour arc not a gaseous one.
The interruption of arc in vacuum is achieved via movement of the moving contact so that a contact gap of 10-20mm is created. The contact gap of vacuum circuit breaker is a function of system voltage and current zero of the cycle. The current is interrupted at the current zero of the cycle because at this instant the temperature drops sharply as metal vapour deinoizes.
Absense of contaminants required for ionization and high dielectric strength of vacuum results in no restrikes. It may thus be noted that after current interruption at current zero of the cycle, the arc exists only for next half cycle before total extinction.
Operating Mechanism:
Since the vacuum has a very high dielectric strength, the contact gap for these breakers are usually very less than other types of breaker. The electrical contact of vacuum circuit breaker is of butt type made of copper chromium alloy.
During a short circuit fault, high fault current flows through the contacts of the circuit breaker. This high current develops a repulsive electrodynamic force at the contact given by lorentz equation F= I * L* B. This forces the contact apart resulting in contact lift off causing arcing and substential contact wear. In order to counter balance this force, each pole of vacuum circuit breaker has contact pressure spring which forces the contact in closed position without damaging the contacts.
The closing spring also delivers a push accelerating all mechanical parts during the contact making to ensure low resistance in the contact, nullifing bounching of contacts so that current can flow reliably. The closing mechanism also charges the contact pressure spring and tripping springs. Along with the closing spring, the atmospheric pressure acting at the bellow also contributes force to the moving contact stem, thus speeding up the contact during closing operation of the breaker.
The tripping springs exerts a small but high accelerating force during the opening operation. The high speed openning inertia of the moving contact has to be contained by efficiently damping the tripping force so as to prevent any damage to the interrupter and overtravel of the moving contact.
Motor-operated spring closing and solenoid mechanism are popularly used for operating the vacuum circuit breakers.
Solenoid-operated mechanism:
In this mechanism, a solenoid, which is a coil turned a number of times, produces a magnetic field on the application of electric current, which pulls apart the moving contact of the circuit breaker into the open position. The problem with this system is that the proper utilization of the solenoid’s potential does not take place as the plunger starts its movement before the rated force in the solenoid is built up fully.
Because of this mechanical plunger holding arrangements have to be made with a collapsible lever and spring-loaded balls mounted on the plunger to nullify the initial movement of the plunger until the rated force is developed by the solenoid.
The closing coil consumes high power for operation and requires an expensive battery attached to the system. This along with the holding arrangement makes the structure bulky.
Spring operated mechanism:
The springs store all the energy required for the separation and closure of the vacuum circuit breaker. The operation of the charged spring latch releases the spring power which is unleashed into the moving action of the contact inside the interrupter through a cam and four bar linked mechanisms. The rate of opening and closing is not affected by varied electrical parameters like voltage and current fluctuations, which makes it robust and stable. However, the speed of operation can be adjusted by altering the spring pressure.
Advantages of Vacuum Circuit breakers
Following are the listed advantages of VCBs
- The operating speed of VCBs are very high.
- Contacts of VCBs undergo very low wear.
- Contact resistance is stable because controlled depositions.
- Operation needs low power.
- VCBs have a long life because of low contact errosion.
- VCBs are sealed and requires low maintenance.
- VCBs have compact size compared to other breakers in same rating.
- VCBs are economical in the long run because of low maintenance, longer life and reliablity.
- No fire risk are involved along with no toxic releases in vacuum circuit breakers which is not the case with other breakers.
This article is a part of the Switchgear, where other articles related to switchgear are discussed in details.

