Air Circuit Breaker (ACB)
Air circuit breaker is the simplest form of circuit breaker. In this circuit breaker, the interruption of the arc is achieved by the natural deionization of gases by cooling. The arc is also lengthened for its resistance to get increased so that the source cannot sustain it, thereby extinguishing the arc.
Table of Contents
Working Principle
The working principle of the air circuit breaker is to prevent the restriking or the arc getting re-established after the interruption of current has been achieved. Upon opening operation of the circuit breaker, system recovery voltage gets established between the contacts of the breaker as the system wants to get back to the normal state. This is countered by creating necessary contact gap so that the breaker can withstand this recovery voltage.
In an air circuit breaker, the difference in the arc temperature creates a high voltage gradient. It is achieved by directing the arc to an arc chute made of insulating materials. The arc is driven in a serpentine like arc chute channel which effectively provides the cooling.
Because of the lengthening of arc, voltage drop increases along with arc resistance. The instantaneous supply voltage drops below the rated voltage levels as the current in the circuit is interrupted. It is because of high arc resistance and sufficient contact gap which restricts the transient recovery voltage and system recovery voltage from re-establishing the arc.
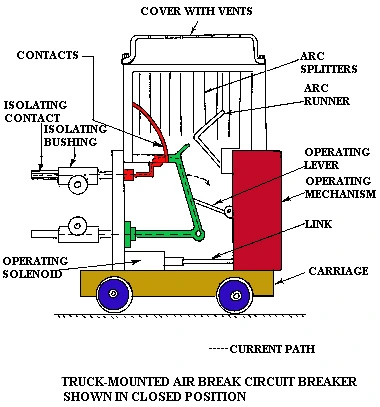
Construction
The following are the main parts of the air circuit breaker: –
Main Contacts: These contacts makes and breaks the circuit. Among them one is fixed and the other is moving. The contacts are designed to carry the continuous rated current of the circuit.
Moving Contact Assembly: The moving contact assembly is composed of solid copper spring-loaded rollers. These rollers freely roll upto some degrees, whenever the breaker is operated, thus giving motion to the moving contact. The assembly has linked insulators for electrical insulation of the entire mechanism. The operating rod in connection to the operating mechanism, utilizes spring action for very fast separation during the fault and closing.
The moving assembly is designed to guide the arc while separation to the arc chute for efficient arc extinguishment.
Fixed Contact Assembly: These are basically fixed contacts made of copper with silver padding on face. The fixed contacts are designed for maximum durability and minimum temperature rise.
Arcing Contacts: The arcing contacts are the one that faces extreme heat and voltage stress during operation of the breaker. These contacts opens last and closes first during operation thus protecting the main contacts from arc.
Arc Chute: Arc chutes are special desined insulated housing that contains several arc splitting plates at the top. The number of arcing contacts decides the size of the arc chute. The purpose of the arc splitting plate is to accelerate the upward rise of arc by magnetic action and thus split the arc.
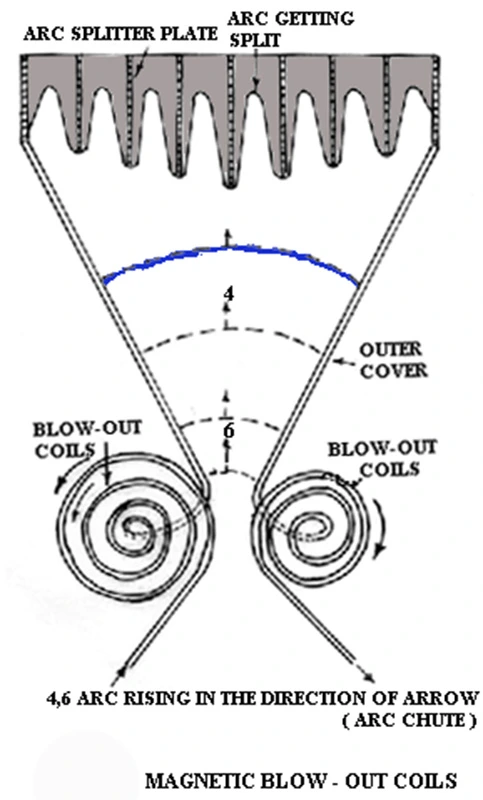
Functions of arc chute of air circuit breaker
- It splitting plates absorbs some heat thereby lowering the temperature.
- It helps in lengthening the arc thereby increasing the arc resistance.
- It splits the arc into smaller arcs for efficient extintion of the arc.
Operating Mechanism: For operating the air circuit breaker, the mechanim can be manual for low current application, electrical or spring charged. This mechanism includes latches, opening and closing springs, means of charging the springs. for closing operation closing spring is charged and by closing command the latch is released and breaker gets closed, similar is the process of tripping. The circuit breaker also has a lockout feature that restricts the closing operation.
Arc Runners or Arcing Horns: The arc runners or arcing horn are the part of an air circuit breaker via which the arc commutes just after formation or contact separation. During opening operation, the blowout coil is also energized in the breaker which provides the magnetic field. This field makes the arc to travel upwards and get increased in length. At certain length of the arc, the system voltage fails to sustain the arc any more and thus it gets extinguished.
Types of Air circuit breaker
There are various types of air circuit breakers.
Plain Break Type
In this type the contacts are horn shaped. The arc develops across the shortest distance between the horns, and steadily rises up. As the contacts fully separates, the contact gap increases form the initial position and the arc also follows the contact gap. This extension of contact gap results in cooling and extintion of arc. The extintion is relatively slower and risk of the arc extending to the grounded metal parts makes this nonsuitable for higher voltage application.
Magnetic Blow-out Type
Here, the magnetic blast is used to achieve arc extintion. When the circuit is interrupted, a magnetic field is generated by the coils connected in series. These coils are the blow out coils which functions to drive the arc into the arc chute. The arc shield limits the arc spread to nearby metallic surfaces. Breaking capacity of these breakers is high and finds it’s application upto 11KV voltage level.
Arc Splitter Type
These breakers have arc chutes which consists of steel inserts. The steel inserts induces magnetic field around them which causes the arc to rise upwards in high speed. The arc is splitted into several small arcs which causes rapid cooling and voltage drop due to temperature differences.
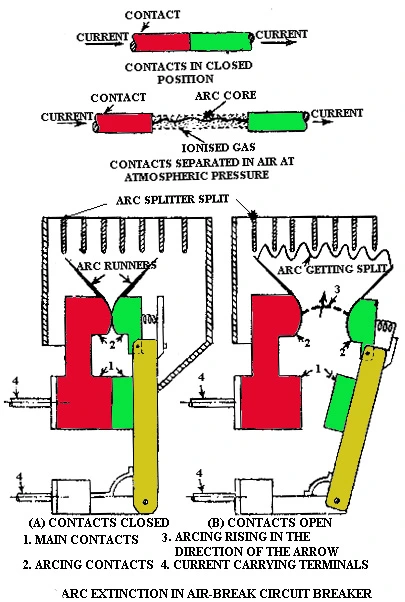
The voltage drop thus makes the arc hard to sustain by the source. The arc motion towards the splitter can be natural or aided by magnetic blow out coils. These breakers are usually having seperate poles and are gang operated.
FAQ’s
How does the Air circuit breaker work?
The air circuit breaker or ACB works by breaking the current flow in the electrical circuit, whenever there is a fault in the circuit, by quenching the arc thus generated from tripping utilizing atmospheric air.
Why do we use ACB breakers?
ACBs find it’s most application in the low voltage level application at 415v AC supply.
This article is a part of the Switchgear, where other articles related to switchgear are discussed in details.

