PROTECTION CORE OF CT
It is known that current transformers are used for protection and metering purposes. A current transformer or CT can have more than one core in the case of a multi-core CT that is normally used in power stations. One is used for metering purposes, other for protection.
Table of Contents
The key difference between the metering core and the protection core of CT is that the metering core must be saturated in case of a fault in order to save the meters connected to the secondary of the core, from excessive fault current. However, the protection core of CT must faithfully reproduce the largest fault current on the secondary side.
This is done in the protection core of CT so that the relays connected to it’s secondary do not malfunction and there by always detect the fault current produced in the secondary.
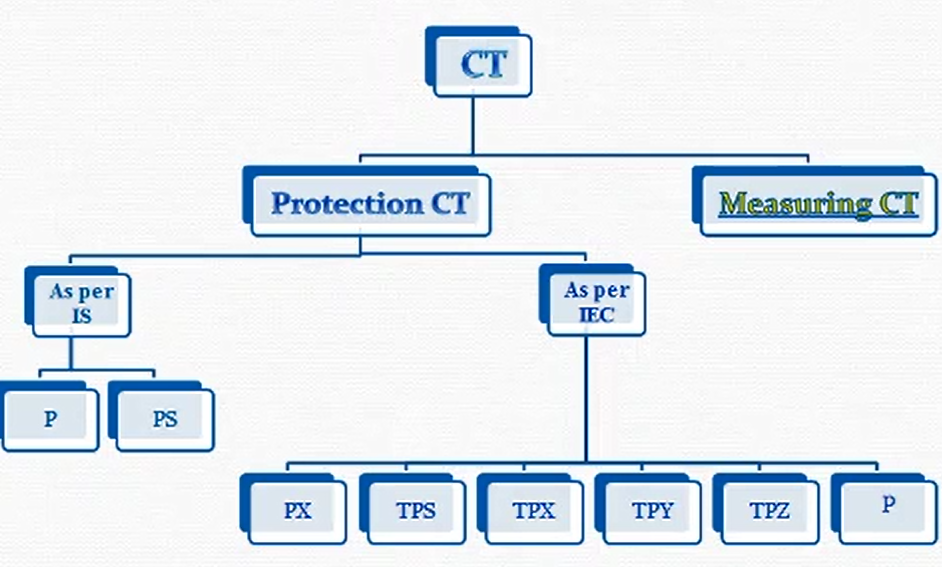
TYPES
As per IS-2705 standard two types of protection CTs are used in the industry they are P and PS class. As per the IEC-61869-2 PX, TPS, TPX, TPY, TPZ, and P class protection cores are available, However, P and PX class CTs are preferred in the industry. The TPS, TPX, TPY, and TPZ protection classes are basically for transient applications.
APPLICATION OF P & PS/PX PROTECTION CORE
For Low voltage, medium voltage, and high tension applications, where only the overcurrent (phase to phase fault) protection and earth fault (phase to earth) protection are used, P class protection is used.
Whereas in EHV and UHV systems, two sets of protection are used:
From 66 KV to 132 KV- Main protection (PX/PS core) and backup protection (P core) are used.
From 132KV and above- 2 sets of Main protection and backup protection are used.
The main protection is a close-looped protection or a particular zone protection called as unit protection. In other words, the boundary of protection for unit protection is always defined. In the main protection, the special class PX/PS is used as it has higher accuracy than the P class protection core of CT. The PX/PS protection core of CT has very few errors compared to the P class protection core of CT. Hence, the PX class is preferred for unit protections in EHV and UHV systems.
STANDARD ACCURACY OF P CLASS PROTECTION CORE
As per IEC-61869-2, the P class protection core has two standard accuracy classes with low remanence, they are 5 and 10. These classes have ratio errors of 1% and 3% at rated primary current. For example, a 400/1 CTR 5P class CT core will have a ratio error of 1% at 400A primary current and for the 10P class, the ratio error will be 3% at 400A primary current.

However, the error of 5P class core will increase to 5% at rated accuracy limit factor or ALF. And for 10P class the error will be 10% at rated ALF.
ACCURACY LIMIT FACTOR:
Accuracy limit factor or ALF is the limit of primary current up to which the protection core will have rated ratio error as per accuracy class. Beyond the ALF, the ratio error increases. It is the ratio of primary current up to which the error of the protection core is within range to the rated primary current.
For example, a CT core with a ratio of 400/1, and an accuracy class of 5P and ALF of 10 written as 5P10, will have a ratio error of 5% up to 10 times the rated primary current that is 400*10 = 4000A, beyond 4000A the ratio error of the protection core will increase massively.
The standard ALF values as per IEC-61869-2 are 5-10-15-20-30.
The accuracy class for the P-type protection core and with ALF is normally written as 5P5 or 5P15. Here, the first digit is for the accuracy class and the last digit is for ALF.
For PX class protection core has a ratio error not exceeding 1% as per the IEC-61869-2.
This article is a part of the Transformer page, where other articles related to the topic are discussed in details.

