SIGNIFICANCE OF CT POLARITY
Current transformer polarity is the direction of current in the secondary winding in relation to the primary current. It is often marked by square markings or P1 and P2. The polarity of the CT connection is of utmost importance in substation protection as the wrong connection causes the relays to malfunction, which is not desirable.
Table of Contents
NORMAL CONVENTION
In practice, the current transformer polarity P1 and P2 is marked, the P2 side of the current transformer is always connected in the direction of equipment to be protected. This is because the current will enter through the P1 side in the primary and in the secondary winding leave through the S1 terminal. We therefore make a star point in the S2, S3.. terminals of the CT. In other words, the star point of the CT should be made in the direction of protected equipment. We shall see why is this done with some examples.
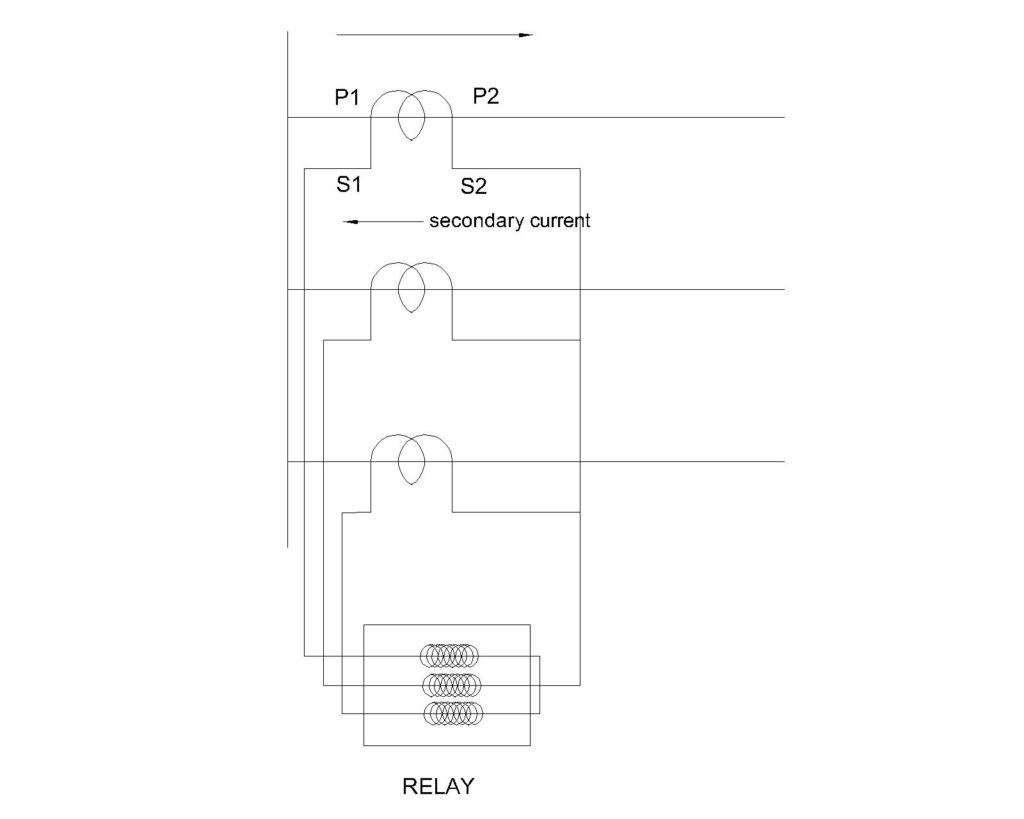
LINE CT
This CT is used for the protection of the transmission line. Here the P1 side of the CT is connected to the source and the P2 side is towards the load or the line. As current flows in the primary, through P1, in the secondary winding of the CT, current will leave through the S1 terminal. We shall make a star connection on the S2 terminal side.
If done the other way, the directional relay will see a reverse flow of current via the star point, which will result in no pickup and no isolation of fault. In the case of a distance protection relay, if the CT polarity is reversed then the relay will sense zone 4 protection pickup and trip for any forward faults. It is for this reason the P2 side is always placed in the direction of protected equipment.
TRANSFORMER PROTECTION.
In the case of the transformer/ reactor protection, CTs are used on both sides of the equipment, HV and LV. Any polarity mismatch will result in a malfunction of the differential relay 87. We shall see why.
HV side CT is connected with P2 in the transformer direction and LV side CT is also connected in the same way. In normal operation, as shown in the figure below, the current will flow on the HV side from P1 resulting in the flow of secondary current in S1 terminal. However, in the LV side of the transformer, the primary current will flow from P2. it will result in a secondary current in the S2 terminal which is star-connected. The current thus in the LV CT will flow reverse S2 to S1 in normal conditions.
In case of any internal fault or fault between two CTs will result in secondary current flowing in the S1 terminals, as the primary current will flow from P1 in the LV CT. Now, the 87 relay will easily sense the current difference as the direction in LV CT secondary is now flipped and issue a trip command to the associated circuit breakers. Also in case of external zone faults, the relays won’t pick up and issue false trip commands.

If the polarity, in this case, is changed in the HV side, the relay will not be able to detect the internal fault due to the reverse feed of fault current through CT secondary via the star point. A similar effect will be there for change in polarity in the LV side CT.
CONCLUSION
It is therefore utmost important that the current transformer polarity is maintained for the best performance of the protection used. The important point to be noted therefore, is star connection of CT is to be made in the direction of the equipment meant for protection be it transmission line or transformer or reactor.
This article is a part of the Transformer page, where other articles related to the topic are discussed in details.

