The term BCU refers to the Bay Control Unit of a substation’s associated bay or feeder. The BCU or Bay control unit performs various bay operations based on pre-defined logic. It acts as an interface between the operator and the electrical switchgear present in the associated bay. It is a unit of the control and relay panel that also links to the substation’s SCADA. The key functions are detailed below:

Table of Contents
KEY FUNCTIONS OF BAY CONTROL UNIT
Monitoring:
It monitors the status of various electrical bay equipment such as circuit breakers, transformers, isolators, etc that are present in the associated bay. It collects data on various transducers’ CURRENT TRANSFORMERS, VOLTAGE TRANSFORMER, temperature, and status indications.
Control:
It offers remote controlling operations of circuit breaker, and isolator as opening operation or closing operation both can be done via BCU.
Protection:
It looks over the implemented protection scheme also the selected bay scheme and is involved in coordination with all the relays available for the bay for efficient and reliable protection against various electrical faults.
Communication:
It involves communication with all other monitoring and control systems in the substation like SCADA. It exchanges data and also processes the commands from SCADA via an ethernet switch to provide better operational reliability. Data exchange is managed through the IEC61850 protocol.
Each Bay control unit is independent of each other. The functioning shall not be affected by any faults in other BCUs.
Switchgear interlocking:
Using the CFC or continuous function chart available in all BCUs. The switchgear interlocking arrangement can be conveniently configured. Inter-bay interlocking is also possible and rarely in use.
Synchronization:
The BCU upon initiating close command of a circuit breaker can check whether the synchronization characteristics of both partial networks are met or not. Thus an additional device for external synchronization check is not required. The unit can differentiate between synchronous and asynchronous networks and reacts differently as configured upon connection.
In synchronous networks, there are minor differences in voltage and phase angle moduli, so the circuit breaker response time is not taken into consideration. For, asynchronous networks, however, there is a large difference in the parameters and therefore it is wise to take the circuit breaker response time into consideration. The command is automatically dated in advance of this time so that the contacts close precisely at the right time.
The BCU offers to store various parameter sets for synchronization functions and select one of them for operation. Thus different properties of several circuit breakers can be taken into consideration and these are to be used at appropriate times. This is relevant if the bay has more than one circuit breaker and uses a different response time for each one.
Interrelay communication:
It is a very useful function that allows the BCU to communicate with other BCUs and relays. The communication is realized via port C which has an RS 485 interface. For communication over longer distances, an external converter to fiber optics cable can be used.

An example of inter-relay communication is BCU used for control of one and half CB schemes. One BCU is assigned to each of the three circuit breakers in a bay. This means the redundancy of the primary element is available. Even if one CB fails both the feeders can be supplied power. Control over the bay is retained even if one BCU fails. The three-bay control units use interrelay communication for the interchange of switch gear interlocking conditions.
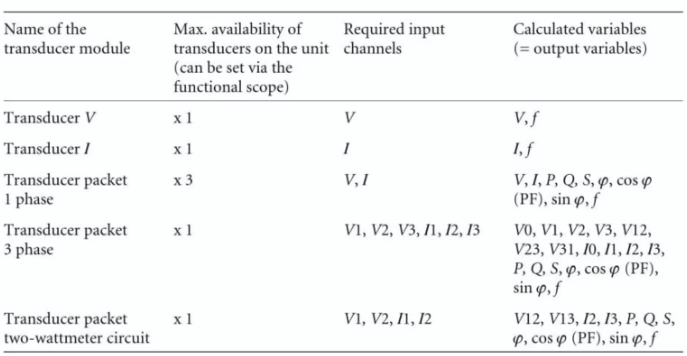
Measured Value processing:
Measured value processing is implemented by predefined function modules, which are likewise configured. The transducer module’s assignment matrix to current and voltage channels of BCU. From these input variables, it computes various other computation variables.
CONCLUSION
Other than the above-mentioned functions several other functions are available in modern BCUs. These have disturbance recorders, time synchronizers to keep up with the actual time, and High accuracy P, and Q values measurement is also done in the unit and are displayed in the small display unit of the instrument. The values are also communicated to SCADA via BCU. Bay control units are also equipped with several buttons that form a mini human-machine interface HMI and can take commands by pressing these buttons. The circuit breaker in the circuit can be operated via this interface. The logged data can also be seen on the display at the press of a button.
It therefore is the main unit of a bay that controls and indicates all bay functions in a substation.
FAQ’s
What is BCU in electrical?
In electrical systems, the full form of it is the Bay Control Unit, which is very essential part of a bay in a modern electric substation. It offers various control over different equipment used in an electrical bay.
What is the purpose of a bay control unit?
The main purpose of using a bay control unit is to have control over the switchgear used in a bay. It acts as an interface between the SCADA and other relays. All commands from SCADA are logged into the BCU via an ethernet switch and processed for further action. All protective relays are interconnected to the bay control unit. All the electrical parameters that are required to be displayed in the SCADA are routed via the bay control unit.
What are the auxiliary functions of a bay control unit?
Some bay control units are integrated with breaker failure protection, auto-reclosure functions for one or two breakers, pole discrepancy detection module, trip circuit supervision for multiple circuits, etc.
What is a bay in a power system?
In a substation, a bay is an electrical circuit that is normally composed of a Circuit breaker, Disconnector, and Current Transformer which essentially connects the electrical bus bar and a power line or power equipment like a transformer.
This article is a part of the Protection System, where other articles related to the protection of electrical equipments are discussed in details.
