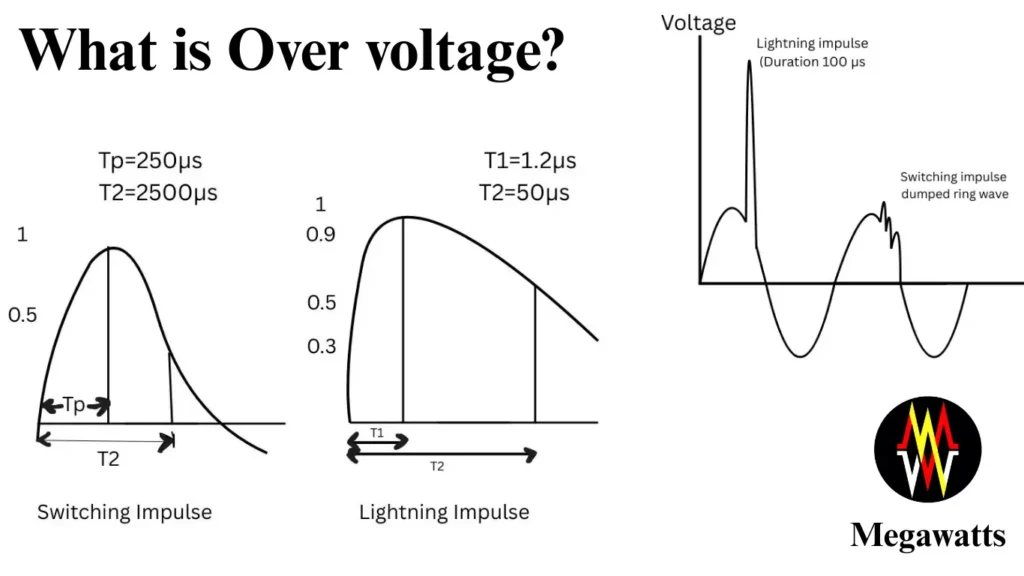
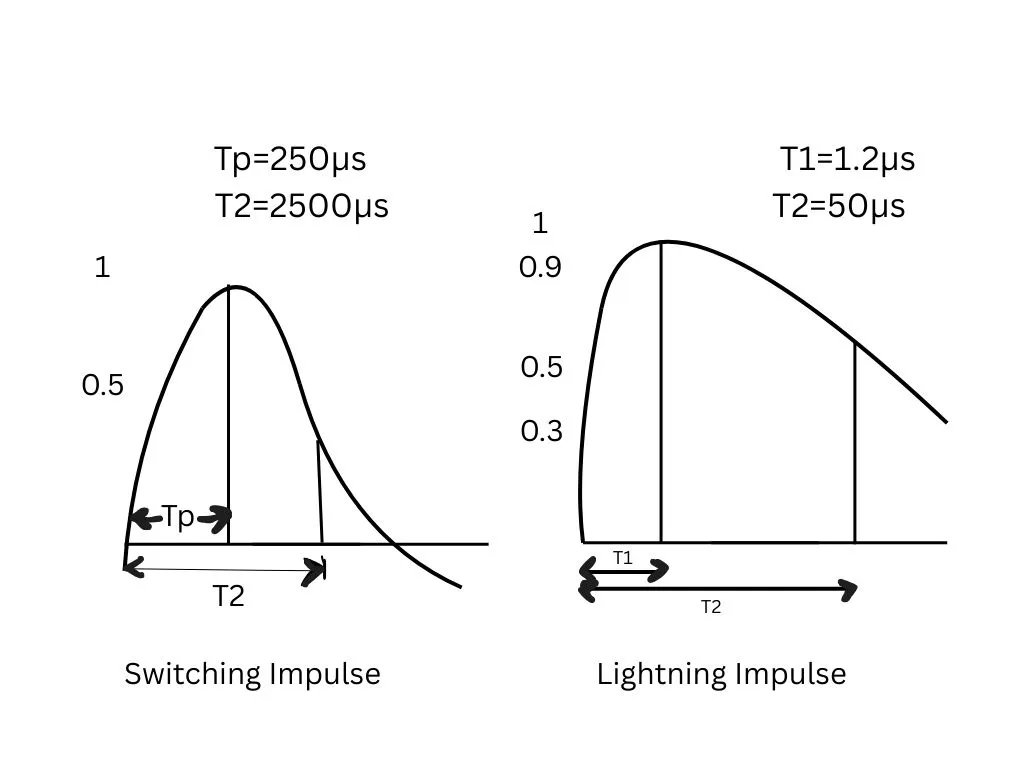
Over voltage is an occurrence in a power system when the voltage goes beyond the rated threshold of the system. Over voltage occurs in a system and persists for a very short time. Voltage is a stress and overstressing can result in subsequent damage to the electrical equipment connected to the system.
Table of Contents
Causes of Over voltage in Power System
In an electrical power system, causes of over voltage can be broadly classified as
- External causes
- Internal causes
External Causes:
This type of high voltage results from changes in the atmospheric conditions. These voltage surges have no direct relation with the operating system voltage and can occur due to the following:
- Direct lightning stroke on the electrical system.
- When lightning is discharged near an electrical system, over voltage surge can occur because of electromagnetic induction.
- In long transmission lines, changes in temperature over the line length can induce voltage.
- Clouds that are charged can electrostatically induce voltage to a nearby transmission line.
- Due to changes in altitude, small particles like dust and snow can cause over voltage in a transmission line due to their frictional effects.
Internal causes
Different operating conditions may give rise to voltage surges. However, the main reasons due to internal causes are discussed below:
1. Switching over voltages:
Whenever a fault occurs in the system, the circuit breaker operates for fault isolation. The switching of the circuit breaker to open and close causes a voltage surge. Therefore the voltage surge caused by to switching action of a circuit breaker either in normal condition or faulty condition is called switching over voltage.
When a transmission line is charged without load, absence of power factor, and with line impedance, the voltage will spike and can reach twice the system voltage. Also due to the Ferranti effect, the remote end voltage rises when an unloaded long transmission line is switched and charged. Similarly charging of a transformer or reactor also causes voltage surges which fades in a few cycles.
2. Temporary over voltages:
When a sudden drop of load occurs in a long transmission line, a temporary overvoltage surge occurs. When a charged line suddenly earthed due to insulation failure, it results in a temporary overvoltage surge.
At frequencies related to 5th harmonics or higher, a condition occurs when the inductive reactance becomes equal in magnitude to capacitive reactance XL = XC. These reactances oppose and nullify each other, such a condition is called resonance. During resonance, the impedance of the line is equal to the resistance of the line. At the resonance state, a small harmonic current can cause a voltage surge.
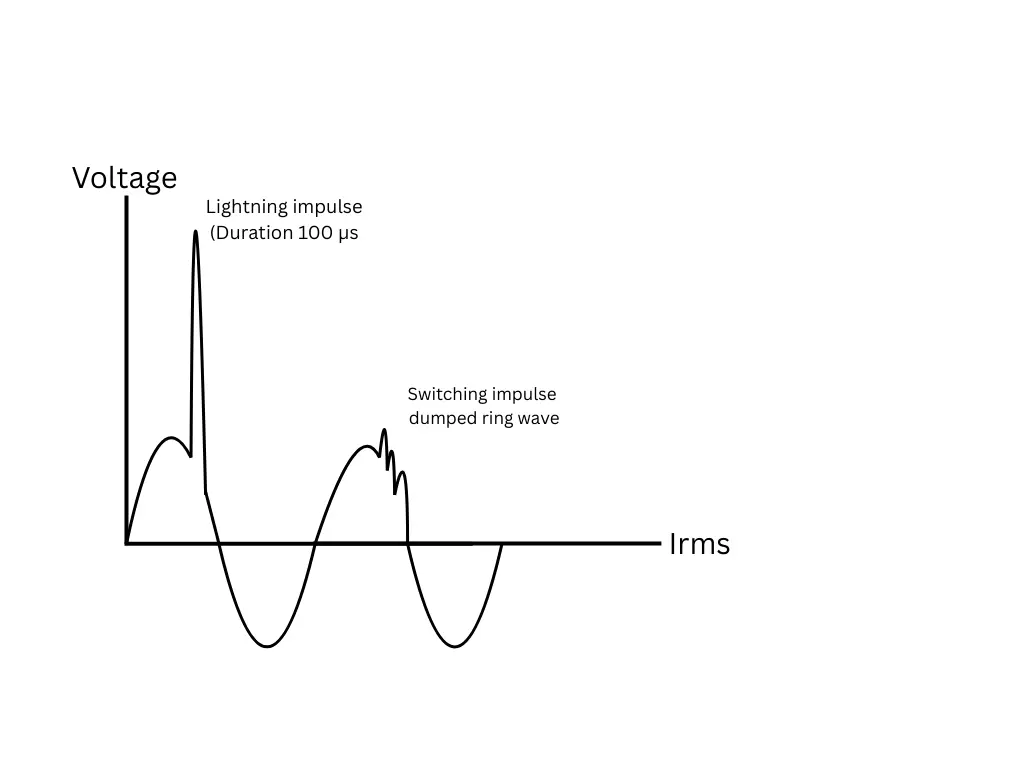
EFFECTS OF OVER VOLTAGES ON POWER SYSTEMS
Voltage itself is a stress, over voltage puts an additional amount of stress on the insulation of the electrical equipment, and on frequent occurrences, it can result in insulation failure. Overvoltage surge can also lead to flashover between the phase and the ground as the air insulation breaks down, where phase-to-earth clearance is minimal. Chances of breakdown of gas, liquid, and solid insulation are always there due to overvoltage and can result in damage to transformers, motors, reactors, etc.
Overvoltage surges due to internal causes like switching over voltage or temporary over voltage are generally not very critical as they seldom reach critical magnitude. Properly rated insulation of equipment can easily handle these voltage surges as they hardly reach twice the rated voltage.
However, the overvoltage surge due to external causes like lightning creates havoc on the insulation of the power system causing severe damage. Hence the overvoltage protection needs to be designed such that it counters the lightning surges and thus protects the system elements.
Over voltage Protection
Electrical power systems are always at risk of interruption because of beyond-normal voltage levels caused by the reasons discussed above such as switching surges, lightning surges, load drop,s etc. For normal and smooth functioning of the power system elements and long insulation life, these voltage surges need to be avoided. Overvoltage protection thus ensures that these surges are diverted to the ground or eliminated.
Methods of Over voltage protection
The main methods practiced for protection against overvoltage are:
Earthing Screen
In this arrangement, a net-like structure made up of galvanized iron wire is mounted over the substation, which is properly grounded at various gantry structures. This network thus provides a very low resistance path for lightning strokes to be directly grounded. This method of overvoltage protection is very simple and economical. However, it cannot protect the system from traveling waves of overvoltage, entering the substation from various transmission line feeders.
Overhead Ground Wire
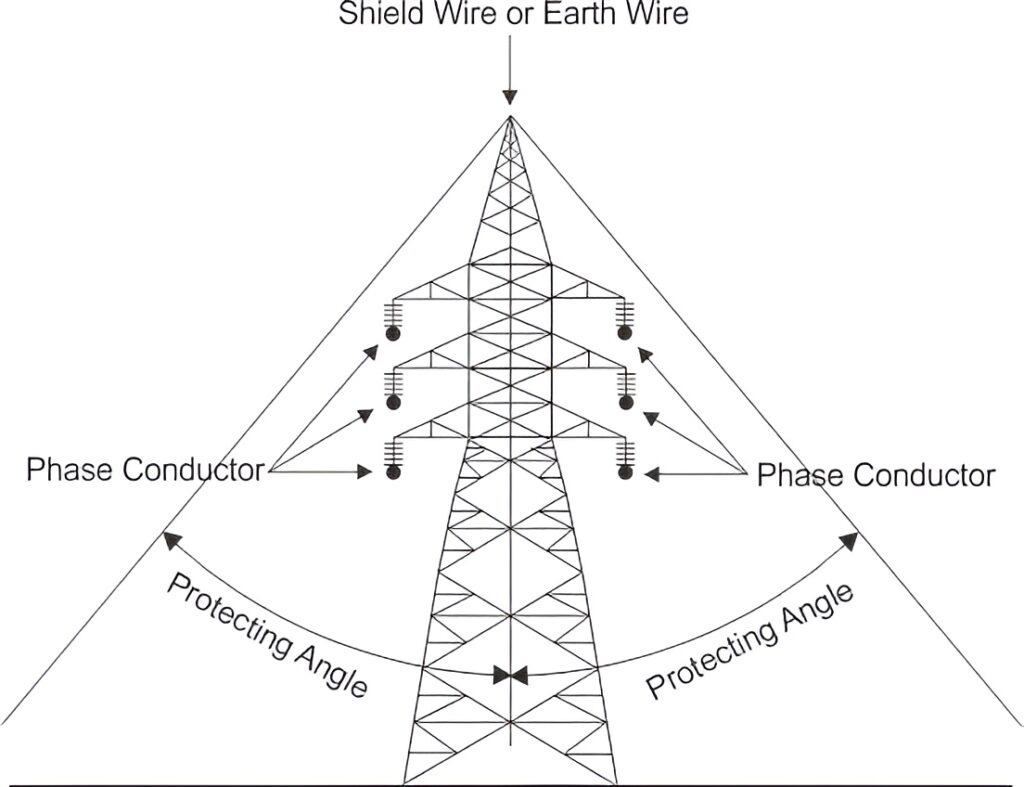
Overhead ground wire is used for the protection of transmission lines. Here, one or two stranded GI wires of suitable cross-sections are placed at the top of the transmission conductors supported by the tower peak with a protection angle of 3 degrees. The wires are properly grounded at each tower which diverts all the lightning strokes to the ground thus protecting the transmission conductors from direct lightning stroke.
Lightning Arrester
Lightning arresters are like nonlinear resistors. The resistance drops as the voltage shoots up and becomes high as the voltage normalizes. At rated system voltage, the lightning arrester acts as an insulator, restricting any flow of current to the ground.
whenever an overvoltage surge or wave tries to travel across, the lightning arrester provides a low impedance path to the excess charge of the surge, thus diverting it to the ground. After the voltage profile normalizes, the device again regains its insulation properties and restricts further flow of current to the ground.
Can over voltage blow a fuse?
No, Over current can blow a fuse but not over voltage.
What causes an over voltage fault?
Switching of inductive load, Lightning, resonance, load drop, etc
What are transient over voltages?
These are short duration (micro to mili Seconds) high amplitude (volts to kilovolts) voltage surges that fades within a few cycles.
How much over voltage is acceptable?
In transmission and distribution, 10% higher than nominal voltage is acceptable. For a 132KV system, over voltage up to 145 KV is acceptable. For a 33 KV system up to 36 KV is acceptable.
This article is a part of the Protection System, where other articles related to the protection of electrical equipments are discussed in details.

